Abstract
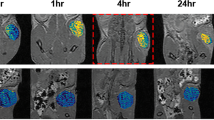
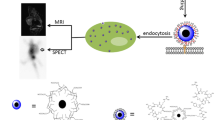
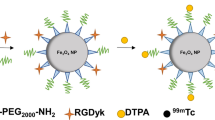
Antibody targeted delivery is an effective strategy to improve the diagnostic imaging outcome of nanoscale imaging agents in the focal areas. Dual targeting micelles encapsulating superparamagnetic iron oxide were prepared from the amphiphilic block copolymer poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PEG-b-PCL) with different targeting ligands cRGD and scFv-ErbB single chain antibody conjugated to the distal ends of PEG block. The breast cancer animal model was established by subcutaneous injecting the BT474 cells into the BALB/c-nu female nude mice and then employed to assess the potential of the dual ligand targeted magnetic micelles as a novel MRI contrast agent on a 1.5 T clinical MRI scanner. The T 2 signal intensity of the tumor in animals receiving the dual ligand targeted magnetic micelles via tail vein decreased more significantly than the single ligand targeted and nontargeted magnetic micelles. These results indicate that the dual ligand targeted magnetic micelles, cRGD/scFv-ErbB-PEG-PCL-SPION, have great potential to act as a new type of effective nanoscale MRI contrast agent for early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay, J., Shin, H.R., Bray, F., Forman, D., Mathers, C. and Parkin, D.M., Int. J. Cancer, 2010, 127(12): 2893
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M.M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E. and Forman, D., CA Cancer J. Clin., 2011, 61(2): 69
Jemal, A., Center, M.M., DeSantis, C. and Ward, E.M., Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 2010, 19(8): 1893
Shen, J., Zhou, C.P., Zhong, X.M., Guo, R.M., Griffith, J.F., Cheng, L.N. and Liang, B.L., Radiology, 2010, 254(3): 729
Greish, K., Cancer Nanotechnology Methods in Molecular Biology, 2010, 624: 25
Guo, Y., Chen, W., Wang, W., Shen, J., Guo, R., Gong, F. and Shuai, X., ACS nano, 2012, 6(12): 10646
Shen, M., Gong, F., Pang, P., Zhu, K., Meng, X., Wu, C. and Shuai, X., Int. J. Nanomed., 2012, 7: 3319
Yang, X., Chen, Y., Yuan, R., Chen, G., Blanco, E., Gao, J. and Shuai, X., Polymer, 2008, 49(16): 3477
Hong, G., Yuan, R., Liang, B., Shen, J., Yang, X. and Shuai, X., Biomed. Microdevices, 2008, 10(5): 693
Chen, G., Chen, W., Wu, Z., Yuan, R., Li, H., Gao, J. and Shuai, X., Biomaterials, 2009, 30(10): 1962
Zutter, M.M., Mazoujian, G. and Santoro, S.A., Am. J. Pathol., 1990, 137(4): 863
Nahta, R., Yuan, L.X., Zhang, B., Kobayashi, R. and Esteva, F.J., Cancer Res., 2005, 65(23): 11118
Nasongkla, N., Shuai, X., Ai, H., Weinberg, B.D., Pink, J., Boothman, D.A., and Gao, J., Angew. Chem., 2004, 116(46): 6483
Yang, X., Deng, W., Fu, L., Blanco, E., Gao, J., Quan, D. and Shuai, X., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 2008, 86(1): 48
Sun, S., Zeng, H., Robinson, D.B., Raoux, S., Rice, P.M., Wang, S.X. and Li, G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(1): 273
Wang, W., Cheng, D., Gong, F., Miao, X. and Shuai, X., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(1): 115
Zhou, J., Huang, L., Wang, W., Pang, J., Zou, Y., Shuai, X. and Gao, X., Chinese Sci. Bull., 2009, 54(18): 3137
Liao, C., Sun, Q., Liang, B., Shen, J. and Shuai, X., Eur. J. Radiol., 2011, 3(80): 699
Lu, J., Ma, S., Sun, J., Xia, C., Liu, C., Wang, Z. and Gu, Z., Biomaterials, 2009, 30(15): 2919
Shuai, X., Ai, H., Nasongkla, N., Kim, S. and Gao, J., J. Control. Release, 2004, 98(3): 415
Shuai, X., Merdan, T., Schaper, A.K., Xi, F. and Kissel, T., Bioconjugate Chem., 2004, 15(3): 441
Ai, H., Flask, C., Weinberg, B., Shuai, X.T., Pagel, M.D., Farrell, D. and Gao, J., Adv. Mater, 2005, 17(16): 1949
Sun, Q., Cheng, D., Yu, X., Zhang, Z., Dai, J., Li, H. and Shuai, X., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(39): 15316
Nasongkla, N., Bey, E., Ren, J., Ai, H., Khemtong, C., Guthi, J. S. and Gao, J., Nano Lett., 2006, 6(11): 2427
Tromsdorf, U.I., Bigall, N.C., Kaul, M.G., Bruns, O.T., Nikolic, M.S., Mollwitz, B. and Weller, H., Nano Lett., 2007, 7(8): 2422
Cheng, D., Hong, G., Wang, W., Yuan, R., Ai, H., Shen, J. and Shuai, X., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(13): 4796
Imai, Y., Kaneko, E., Asano, T., Kumagai, M., Ai, M., Kawakami, A. and Shimokado, K., J. Atheroscler. Thromb., 2007, 14(2): 65
Langley, J., Liu, W., Jordan, E.K., Frank, J.A. and Zhao, Q., Magn. Reson. Med., 2011. 65(5): 1461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the 863 Programs of China (No. 2009AA03Z310), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21174166, 30973419), the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20100171110011), the Postdoctoral Foundation (No. 201003370), Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 9351027501000003, S2011020003140) and S&T Programs of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2010B031500011, 2009B030803003, 2009B030801107, 2012B031800135), and SYSU Projects for Promotion of Key and Emerging Interdisciplinary Researches (10ykjc18) and Young Teachers (11lgpy44).
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Fm., Zhang, Zq., Chen, Xd. et al. A dual ligand targeted nanoprobe with high MRI sensitivity for diagnosis of breast cancer. Chin J Polym Sci 32, 321–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-014-1399-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-014-1399-8