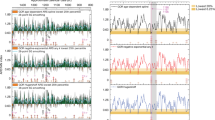
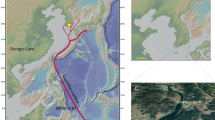
Abstract
In Eastern Mediterranean history, 1200 BCE is a symbolic date. Its significance is tied to the important upheavals that destabilised regional-scale economic systems, leading to the dislocation of mighty Empires and, finally, to the “demise” of a societal model (termed “the Crisis Years”). Recent studies have suggested that a centuries-long drought, of regional scale, termed the 3.2 ka BP event, could be one of the motors behind this spiral of decline. Here, we focus on this pivotal period, coupling new palaeoenvironmental data and radiocarbon dates from Syria (the site of Tell Tweini) and Cyprus (the site of Pyla-Kokkinokremnos), to probe whether climate change accelerated changes in the Eastern Mediterranean’s Old World, by inducing crop failures/low harvests, possibly engendering severe food shortages and even famine. We show that the Late Bronze Age crisis and the following Dark Ages were framed by an ~ 300-year drought episode that significantly impacted crop yields and may have led to famine. Our data underline the agro-productive sensitivity of ancient Mediterranean societies to environmental changes, as well as the potential link between adverse climate pressures and harvest/famine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Maqdissi M, Van Lerberghe K, Bretschneider J, Badawi M (2011) Tell Tweini: onze campagnes de fouilles syro-belges (1999–2010). Documents d’Archéologie Syrienne, Damas
Alpert P, Neuman J (1989) An ancient correlation between streamflow and distant rainfall in the Near East. J Near East Stud 48:313–314
Artzy M (1987) On boats and Sea Peoples. Bull Am Sch Orient Res 266:75–84
Bernhardt C, Horton BP, Stanley JD (2012) Nile Delta vegetation response to Holocene climate variability. Geology 40:615–618. https://doi.org/10.1130/G33012.1
Bretschneider J, Van Lerberghe K (2008) Tell Tweini, ancient Gibala, between 2600 BCE and 333 BCE. In: Bretschneider J, Van Lerberghe K (eds) In search of Gibala, an archaeological and historical study based on eight seasons of excavations at Tell Tweini (1999–2007) in the A and C fields. Aula Orientalis, Barcelona, pp 12–66 http://journals.openedition.org/abstractairanica/41442. Mar 2018
Bretschneider J, Van Lerberghe K, Vansteenhuyse K, Al-Maqdissi M (2008) The Late Bronze Age and Iron Age in the Jebleh region: a view from Tell Tweini. In: Kühne H, Czichon RM, Kreppner FJ (eds) Proceedings of the 4th International Congress of the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East. Harrassowitz Verlag, Wiesbaden, pp 33–46
Bretschneider J, Jans G, Van Vyve AS (2010) Les Fouilles du chantier A en 2009 et 2010. In: Al-Maqdissi M, Van Lerberghe K, Bretschneider J, Badawi M (eds) Tell Tweini: onze campagnes de fouilles syro-belges (1999–2010). Documents d’Archéologie Syrienne, Damas, pp 131–146
Bretschneider J, Kanta A, Driessen J (2015) Pyla-Kokkinokremos: preliminary report on the 2014 excavations. Ugarit-Forschungen 46:1–37
Bretschneider J, Kanta A, Driessen J (2017) Pyla-Kokkinokremos (Cyprus): preliminary report on the 2015-2016 campaigns. Ugarit-Forschungen 48:36–120
Bretschneider J, Jans G (2019) About Tell Tweini (Syria): artefacts, ecofacts and landscape. Research results of the Belgian mission. OLA Peeters, Leuven
Brinkman JA (1968) A political history of post-Kassite Babylonia, 1158–722 BC. Analecta Orientalia, Ville
Bryce T (2005) The kingdom of the Hittites. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199281329.001.0001
Butzer KW (1976) Early hydraulic civilization in Egypt. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Camenisch C, Keller KM, Salvisberg M, Amann B, Bauch M, Blumer S, Brázdil R, Brönnimann S, Büntgen U, Campbell BMS, Fernández-Donado L, Fleitmann D, Glaser R, González-Rouco F, Grosjean M, Hoffmann RC, Huhtamaa H, Joos F, Kiss A, Kotyza O, Lehner F, Luterbacher J, Maughan N, Neukom R, Novy T, Pribyl K, Raible CC, Riemann D, Schuh M, Slavin P, Werner JP, Wetter O (2016) The 1430s: a cold period of extraordinary internal climate variability during the early Spörer minimum with social and economic impacts in north-western and Central Europe. Clim Past 12:2107–2126. https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-12-2107-2016
Cheng H, Sinha A, Verheyden S, Nader FH, Li XL, Zhang PZ, Yin JJ, Yi L, Peng YB, Rao ZG, Ning YF, Edwards RL (2015) The climate variability in northern Levant over the past 20,000 years. Geophys Res Lett 42:8641–8650. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065397
Cline EH (2014) 1177 BC: the year civilization collapsed. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Cohen Y, Singer I (2006) Late synchronism between Ugarit and Emar. In: Amit Y, Zvi EB, Finkelstein I, Lipschits O (eds) Essays on Ancient Israel in its Near Eastern context. A tribute to Nadav Na’ama. Eisenbrauns, Winona Lake, pp 123–139
Coltelli M, Del Carlo P, Vezzoli L (2000) Stratigraphic constraints for explosive activity in the past 100 ka at Etna volcano, Italy. Int J Earth Sci 89:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005310000117
Cullen HM, deMenocal PB (2000) North Atlantic influence on Tigris-Euphrates streamflow. Int J Climatol 20:853–863. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0088(20000630)20:8%3C853::AID-JOC497%3E3.0.CO;2-M
Drews R (1993) The end of the Bronze Age: changes in warfare and the catastrophe ca. 1200 BC. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Driessen J (2018) The archaeology of forced migration. Crisis-induced mobility and the collapse of the 13th c. BCE Eastern Mediterranean (Aegis 15). Presses Universitaires de Louvain, Louvain
Eastwood WJ, Leng MJ, Roberts N, Davis B (2007) Holocene climate change in the eastern Mediterranean region: a comparison of stable isotope and pollen data from Lake Gölhisar, Southwest Turkey. J Quat Sci 22:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/jqs.1062
Faegri K, Iversen I (1989) Textbook of pollen analysis, fourth edn. Wiley, London
Finné M, Holmgren K, Shen CC, Hu HM, Boyd M, Stocker S (2017) Late bronze age climate change and the destruction of the Mycenaean palace of Nestor at Pylos. PLoS One 12:e0189447. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189447
Gilboa A (2006-2007) Fragmenting the Sea Peoples, with an emphasis on Cyprus, Syria and Egypt: a Tel Dor perspective. Scripta Mediterranea 27-28: 209–244
Glaser R, Himmelsbach I, Bösmeier A (2017) Climate of migration? How climate triggered migration from Southwest Germany to North America during the 19th century. Clim Past 13:1573–1592. https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-13-1573-2017
Göktürk OM, Fleitmann D, Badertscher S, Cheng H, Edwards RL, Leuenberger M, Fankhauser A, Tüysüz O, Kramers J (2011) Climate on the southern Black Sea coast during the Holocene: implications from the Sofular cave record. Quat Sci Rev 30:2433–2445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.05.007
Hassan FA (1997) The dynamics of a riverine civilization: a geoarchaeological perspective on the Nile Valley, Egypt. World Archaeol 29:51–74 .https://doi.org/10.1080/00438243.1997.9980363
Jung R (2018a) Push and pull factors of the Sea Peoples between Italy and the Levant. In: Driessen J (ed) The Archaeology of forced migration. Crisis-induced mobility and the collapse of the 13th c. BCE Eastern Mediterranean (Aegis 15). Presses Universitaires de Louvain, Louvain, pp 279–312
Jung R (2018b) Mycenaen pottery in coastal Syria. In: Badre L, Capet E, Vitale B (eds) Tell Kazel au Bronze Récent. Études Céramiques, Beyrouth, pp 47–51
Kaniewski D, Paulissen E, Van Campo E, Al-Maqdissi M, Bretschneider J, Van Lerberghe K (2008) Middle East coastal ecosystem response to middle-to-late Holocene abrupt climate changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13941–13946. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803533105
Kaniewski D, Paulissen E, Van Campo E, Bakker J, Van Lerberghe K, Waelkens M (2009) Wild or cultivated Olea europaea L. in the eastern Mediterranean during the middle-late Holocene? A pollen-numerical approach. The Holocene 19:1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683609341000
Kaniewski D, Paulissen E, Van Campo E, Weiss H, Otto T, Bretschneider J, Van Lerberghe K (2010) Late second-Early first millennium BC abrupt climate changes in coastal Syria and their possible significance for the history of the eastern Mediterranean. Quat Res 74:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2010.07.010
Kaniewski D, Van Campo E, Van Lerberghe K, Boiy T, Vaansteenhuyse K, Jans G, Nys K, Weiss H, Morhange C, Otto T, Bretschneider J (2011) The Sea Peoples, from cuneiform tablets to carbon dating. PLoS One 6:e20232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020232
Kaniewski D, Van Campo E, Guiot J, LeBurel S, Otto T, Baeteman C (2013a) Environmental roots of the Late Bronze Age crisis. PLoS One e71004:8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071004
Kaniewski D, Van Campo E, Morhange C, Guiot J, Zviely D, Shaked I, Otto T, Artzy M (2013b) Early urban impact on Mediterranean coastal environments. Sci Rep 3:354. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03540,2013b
Kaniewski D, Guiot J, Van Campo E (2015) Drought and societal collapse 3200 years ago in the eastern Mediterranean: a review. WIREs Clim Change 6:369–382. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.345
Kaniewski D, Van Campo E (2017) The 3.2 kyr BP event and the Late Bronze Age crisis, a climate-induced spiral of decline. In: Weiss H (ed) Megadrought and collapse. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 161–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780199329199.001.0001
Kaniewski D, Marriner N, Ilan D, Morhange C, Thareani Y, Van Campo E (2017) Climate change and water management in the biblical city of Dan. Sci Adv 3:e1700954. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700954
Karageorghis V, Demas M (1984) Pyla-Kokkinokremnos, a late 13th-century B.C. fortified settlement in Cyprus. Chr. Nicolaou & Sons LTD, Nicosia
Karageorghis V, Kanta A (2014) Pyla-Kokkinokremnos, a late 13th-century B.C. fortified settlement in Cyprus, excavatioons 2010–2011. Studies in Mediterranean Archaeology vol. CXLI - Aströms Förlag, Uppsala
Kay PA, Johnson DL (1981) Estimation of the Tigris-Euphrates streamflow from regional palaeoenvironmental proxy data. Clim Chang 3:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00136671
Killebrew AE (2005) Biblical peoples and ethnicity: an archaeological study of Egyptians, Canaanites, Philistines, and early Israel, 1300-1100 BC. SBLABS, Atlanta. 33:59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-0922.2007.001498.x
Killebrew AE, Lehmann G (2013) The Philistines and other Sea Peoples in text and archaeology. SBLABS, Atlanta. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctt46n483
Krom MD, Stanley JD, Cliff RA, Woodward JC (2002) Nile River sediment fluctuations over the past 7000 yr and their key role in sapropel development. Geology 30:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0071:NRSFOT>2.0.CO;2
Langgut D, Finkelstein I, Litt T (2013) Climate and the Late Bronze Collapse: new evidence from the southern Levant. Tel Aviv 40:149–175. https://doi.org/10.1179/033443513X13753505864205
Langgut D, Neumann FH, Stein M, Wagner A, Kagan EJ, Boaretto E, Finkelstein I (2014) Dead Sea pollen record and history of human activity in the Judean highlands (Israel) from the Intermediate Bronze into the Iron Ages (∼ 2500–500 BCE). Palynology 38:280–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2014.906001
Langgut D, Finkelstein I, Litt T, Neumann FH, Stein M (2015) Vegetation and climate changes during the bronze and iron ages (~3600–600 BCE) in the southern Levant based on palynological records. Radiocarbon 57:217–235. https://doi.org/10.2458/azurc.57.18555
Litt T, Ohlwein C, Neumann FH, Hense A, Stein M (2012) Holocene climate variability in the Levant from the Dead Sea pollen record. Quat Sci Rev 49:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.06.012
Manning J (2018) The open sea: the economic life of the ancient Mediterranean world from the Iron Age to the rise of Rome. Princeton University Press, Princeton. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444338386.wbeah06321/full
Neumann J, Parpola S (1987) Climatic change and the eleventh-tenth-century eclipse of Assyria and Babylonia. J Near East Stud 46:161–182. https://doi.org/10.1086/373244
Nougayrol J, Laroche E, Virolleaud C, Schaeffer C (1968) Ugaritica V, Nouveaux textes accadiens, hourrites et ugaritiques des archives et bibliothèques privées d'Ugarit. Mission de Ras Shamra, 16. Librairie Orientaliste Paul Geuthner, Paris
Pribyl K (2017) Farming, famine and plague, the impact of climate in Late Medieval England. Springer, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55953-7
Regattieri E, Zanchetta G, Drysdale RN, Isola I, Hellstrom JC, Dallai L (2014) Lateglacial to Holocene trace element record (Ba, mg, Sr) from Corchia Cave (Apuan Alps, Central Italy): paleoenvironmental implications. J Quat Sci 29:381–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/jqs.2712
Reuveny R (2007) Climate change-induced migration and violent conflict. Polit Geogr 26:656–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polgeo.2007.05.001
Roberts N, Reed JM, Leng MJ, Kuzucuoglu C, Fontugne M, Bertaux J, woldring H, Bottema S, Black S, Hunt E, Karabiyikoglu M (2001) The tempo of Holocene climate change in the eastern Mediterranean region: new high-resolution crater-lake sediments data from Central Turkey. The Holocene 11:721–736. https://doi.org/10.1191/09596830195744
Roberts N, Eastwood WJ, Kuzucuoglu C, Fiorentino G, Caracuta V (2011) Climatic, vegetation and cultural change in the eastern Mediterranean during the mid-Holocene environmental transition. The Holocene 21:147–162. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683610386819
Sadori L, Narcisi B (2001) The postglacial record of environmental history from Lago di Pergusa, Sicily. The Holocene 11:655–670. https://doi.org/10.1191/09596830195681
Schiebel V, Litt T (2018) Holocene vegetation history of the southern Levant based on a pollen record from Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee), Israel Vegetation. Hist Archaeobotany 27:577–590. https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.884740
Sharifi A, Pourmand A, Canuel EA, Ferer-Tyler E, Peterson LC, Aichner B, Feakins SJ, Daryaee T, Djamali M, Naderi A, Lahijani HAK, Swart PK (2015) Abrupt climate variability since the last deglaciation based on a high-resolution, multi-proxy peat record from NW Iran: the hand that rocked the cradle of civilization? Quat Sci Rev 123:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.07.006
Singer I (1999) A political history of Ugarit. In: Watson WGE, Wyatt N (eds) Handbook of Ugaritic Studies, vol 120. Handbuch der Orientalistik, Erste Abteilung, Leiden, pp 603–733. https://doi.org/10.2307/606647
Singer I (2000) New evidence on the end of the Hittite empire. In: Oren ED (ed) The Sea Peoples and their world: a reassessment. University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pp 21–33
Soto-Berelov M, Fall PL, Falconer SE, Ridder E (2015) Modeling vegetation dynamics in the southern Levant through the Bronze Age. J Archaeol Sci 53:94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2014.09.015
Stevens LR, Ito E, Schwalb A, Wright HE Jr (2006) Timing of atmospheric precipitation in the Zagros Mountains inferred from a multi-proxy record from Lake Mirabad, Iran. Quat Res 66:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2006.06.008
Sun Q, Liu Y, Salem A, Marks L, Welc F, Ma F, Zhang W, Chen J, Jiang J, Chen Z (2019) Climate-induced discharge variations of the Nile during the Holocene: evidence from the sediment provenance of Faiyum Basin, North Egypt. Glob Planet Chang 172:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.10.005
Tarasov PE, Cheddadi R, Guiot J, Bottema S, Peyron O, Belmonte J, Ruiz-Sanchez V, Saadi F, Brewer S (1998) A method to determine warm and cool steppe biomes from pollen data; application to the Mediterranean and Kazakhstan regions. J Quat Sci 13:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1417(199807/08)13:4<335::AID-JQS375>3.0.CO;2-A
Warburton D (2003) Love and war in the Later Bronze Age: Egypt and Hatti. In: Matthews R, Roemer C (eds) Ancient perspectives on Egypt. University College of London Press, London, pp 75–100
Weiss B (1982) The decline of Late Bronze Age civilization as a possible response to climatic change. Clim Chang 4:173–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02423389
Wetter O, Pfister C, Werner JP, Zorita E, Wagner S, Seneviratne SI, Herget J, Grünewald U, Luterbacher J, Alcoforado MJ, Barriendos M, Bieber U, Brázdil R, Burmeister KH, Camenisch C, Contino A, Dobrovolný P, Glaser R, Himmelsbach I, Kiss A, Kotyza O, Labbé T, Limanówka D, Litzenburger L, Nordl Ø, Pribyl K, Retsö D, Riemann D, Rohr C, Siegfried W, Söderberg J, Spring JL (2014) The year-long unprecedented European heat and drought of 1540 - a worst case. Clim Chang 125:349–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1184-2
Wick L, Lemcke G, Sturm M (2003) Evidence of Lateglacial and Holocene climatic change and human impact in eastern Anatolia: high-resolution pollen, charcoal, isotopic and geochemical records from the laminated sediments of Lake Van, Turkey. The Holocene 13:665–675. https://doi.org/10.1191/0959683603hl653rp
Zanchetta G, Van Welden A, Baneschi I, Drysdale RN, Sadori L, Roberts N, Giardini M, Beck C, Pascucci V, Sulpizio R (2012) Multiproxy record for the last 4500 years from Lake Shkodra (Albania/Montenegro). J Quat Sci 27:780–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/jqs.2563
Zanchetta G, Bini M, Di Vito MA, Sulpizio R, Sadori L (2018) Tephrostratigraphy of paleoclimatic archives in Central Mediterranean during the Bronze Age. Quat Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2018.06.012
Funding
Support was provided by the Institut Universitaire de France, CLIMSORIENT program, the University of Ghent—Department of Archaeology and the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO, G010218 N). This work is a contribution to Labex OT-Med (n° ANR-11-LABX-0061) and has received funding from the Excellence Initiative of Aix-Marseille University—A*MIDEX, a French “Investissements d’Avenir” project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Societal Impacts of Historical Droughts
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaniewski, D., Marriner, N., Bretschneider, J. et al. 300-year drought frames Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age transition in the Near East: new palaeoecological data from Cyprus and Syria. Reg Environ Change 19, 2287–2297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-018-01460-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-018-01460-w