Abstract
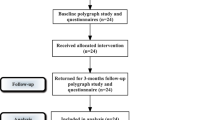
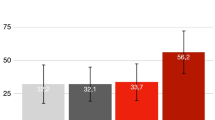
Snoring is a sleep phenomenon due to the partial upper airway obstruction during sleep which causes vibration of the tissues of the rhino-oro-hypopharynx and less frequently the larynx. This study evaluated the use and effectiveness of the erbium:YAG 2940-nm laser as an adjunctive in providing treatment for patients suffering from chronic snoring-related sleep disorders. A prospective study of 40 consecutive patients with snoring and sleep disorders was performed, assessing data before and after three Er:YAG laser treatment sessions. During laser treatment, the pain was almost absent. There were no side effects, except a very mild sore throat in 1 out of 40 patients. The patient’s evaluation of satisfaction of the results obtained after the treatments showed that 85% of cases were very satisfied, 5 patients (12.5%) reported being fairly satisfied with the treatment and only 1 subject (2.5%) was not satisfied. Mallampati, Friedman Tongue Position, and degree of O (oropharynx) at nose oropharynx hypopharynx and larynx classification were significantly decreased after the laser sessions. The decrease of Epworth Sleepiness Scale and Visual Analogue Scale for loudness of snoring, waking up during sleep because of snoring, dry mouth on waking, and choking was all statistically significant. The incidence of dreaming during the night also raised significantly; 30/40 (75%) of cases perceived less tightness in their throat and better breathing after treatment. These results were stable at 20 months follow-up (14–24 q) in 72% of cases. Nonsurgical and non-invasive Er:YAG laser treatment demonstrated to be a valid procedure in reducing the loudness of snoring.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 October 2018
In the originally published article, the name of the first author was incorrectly labeled. Given name is Isabelle and family name is Fini Storchi.
22 October 2018
In the originally published article, the name of the first author was incorrectly labeled. Given name is Isabelle and family name is Fini Storchi.
References
Mannarino MR, Di Filippo F, Pirro M (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur J Intern Med 23(7):586–593
Gałecki P, Florkowski A, Zboralski K, Pietras T, Szemraj J, Talarowska M (2011) Psychiatric and psychological complications in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pneumonol Alergol Pol 79(1):26–31
Petruson B (1990) Snoring can be reduced when the nasal airflow is increased by the nasal dilator. Nozovent Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116(4):462–464
Sanches I, Martins V, dos Santos JM (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea refractory to treatment due to floppy epiglottis. Arch Bronconeumol 51(2):94
Xu H, Yu H, Jia R, Gao Z, Huang W, Peng H (2015) The preliminary study of the origin characters of snore in simple snorers. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 29(11):977–979 983
Server EA, Alkan Z, Yiğit Ö, Yasak AG (2016) Long-term results of pillar implant procedure. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 26(5):258–264
Olszewska E, Panek J, O’Day J, Rogowski M (2014) Usefulness of snoreplasty in the treatment of simple snoring and mild obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome—preliminary report. Otolaryngol Pol 68(4):184–188
Chiesa Estomba CM, Rivera Schmitz T, Ossa Echeverri CC, Betances Reinoso FA, Fariña Conde J, Alonso Parraga D (2015) The treatment of snoring by radiofrequency-assisted uvulopalatoplasty and results after one-session protocol: a prospective, longitudinal, non-randomized study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(10):3059–3063
Pazos G, Mair EA (2001) Complications of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of sleep-disordered breathing. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125(5):462–466
Rombaux P, Hamoir M, Bertrand B, Aubert G, Liistro G, Rodenstein D (2003) Postoperative pain and side effects after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty, and radiofrequency tissue volume reduction in primary snoring. Laryngoscope 113:2169–2173
Nishigawa K, Hayama R, Matsuka Y (2017) Complications causing patients to discontinue using oral appliances for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. J Prosthodont Res 61(2):133–138
Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ Jr, Friedman N, Malhotra A, Patil SP, Ramar K, Rogers R, Schwab R, Weaver EM, Weinstein MD (2009) Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J Clin Sleep Med 5:263–276
Cetinkaya EA, Turker M, Kiraz K, Gulkesen HK (2016) Er:Yag laser treatment of simple snorers in an outpatient setting. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 78(2):70–76
Sher AE, Thorpy MJ, Shprintzen RJ, Spielman AJ, Burack B, McGregor PA (1985) Predictive value of Muller maneuver in selection of patients for uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Laryngoscope 95:1483–1487
Vicini C, De Vito A, Benazzo M, Frassineti S, Campanini A, Frasconi P, Mira E (2012) The nose oropharynx hypopharynx and larynx (NOHL) classification: a new system of diagnostic standardized examination for OSAHS patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(4):1297–1300
Westcott CJ, Hopkins MB, Bach K, Postma GN, Belafsky PC, Koufman JA (2004) Fundoplication for laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 199(1):23–30
Friedman M, Hamilton C, Samuelson CG, Lundgren ME, Pott T (2013) Diagnostic value of the Friedman tongue position and Mallampati classification for obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148(4):540–547
Smith SS, Oei TP, Douglas JA, Brown I, Jorgensen G, Andrews J (2008) Confirmatory factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med 9(7):739–744
Majaron B, Srinivas SM, Huang HL, Nelson JS (2000) Deep coagulation of dermal collagen with repetitive Er:YAG laser irradiation. Lasers Surg Med 2:215–222
Beltram M, Drnovsek-Olup B (2004) Histological and biomolecular analysis of new collagen synthesis after “smooth” mode Er:YAG laser skin resurfacing. Lasers Surg Med Suppl 16:56
Beltram M, Zivin M, Drnovsek B (2010) Collagen synthesis after laser skin resurfacing of the periocular skin. ZdravVestn 79:I-111–I-116
Dams SD, de Liefde-van Beest M, Nuijs AM, Oomens CW, Baaijens FP (2010) Pulsed heat shocks enhance procollagen type I and procollagen type III expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Skin Res Technol 16(3):354–364
Mantovani M, Rinaldi V, Salamanca F, Torretta S, Carioli D, Gaffuri M, Pignataro L (2015) Should we stop performing uvulopalatopharyngoplasty? Ind J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67(Suppl 1):161–162
Li S, Wu D, Shi H (2015) Reoperation on patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome after failed uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(2):407–412
Tang JA, Salapatas AM, Bonzelaar LB, Friedman M (2017) Long-term incidence of velopharyngeal insufficiency and other sequelae following uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 156(4):606–610
Sippus J (2015) Case report: NightLase procedure—laser snoring and sleep apnea reduction treatment. J Laser Health Acad. ISSN 1855–1913
Svahnström K (2013) Er:YAG laser treatment of sleep-disordered breathing. J. Laser Health Acad. ISSN No.2:1855–9913
Miracki K, Vizintin Z (2013) Nonsurgical minimally invasive Er:YAG laser snoring treatment. J. Laser Health Acad. ISSN No.1:1855–9913
Lovato A, Kotecha B, Vianello A, Giacomelli L, Staffieri A, Marchese-Ragona R (2015) Nasal and oral snoring endoscopy: novel and promising diagnostic tools in OSAS patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(7):1793–1799
Lee CYS (2015) Evaluation of a non-ablative Er: YAG laser procedure to increase the oropharyngeal airway volume: a pilot study. Dent Oral Craniofac 1(3):56–59
Unver T, Aytugar E, Ozturan O, Kıran T, Ademci E, Usumez A (2016) Histological effects of Er:YAG laser irradiation with snoring handpiece in the rat soft palate. Photomed Laser Surg 34(8):321–325
Soares D, Folbe AJ, Yoo G, Badr MS, Rowley JA, Lin HS (2013) Drug-induced sleep endoscopy vs awake Müller’s maneuver in the diagnosis of severe upper airway obstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148(1):151–156
De Vito A, Carrasco Llatas M, Vanni A et al (2014) European position paper on drug-induced sedation endoscopy (DISE). Sleep Breath 18:453–465
Campanini A, Canzi P, De Vito A, Dallan I, Montevecchi F, Vicini C (2010) Awake versus sleep endoscopy: personal experience in 250 OSAHS patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 30:73–77
Jmarchn 2017 Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0), https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mallampati.svg
Winter 2017 Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0), https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/mouth#/media/File:Mouth_illustration-Otis_Archives.jpg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storchi, I.F., Parker, S., Bovis, F. et al. Outpatient erbium:YAG (2940 nm) laser treatment for snoring: a prospective study on 40 patients. Lasers Med Sci 33, 399–406 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2436-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2436-6