Abstract
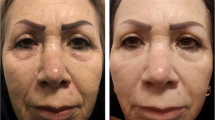
Ablative fractional lasers were introduced for treating facial rhytides. Few studies have compared fractional CO2 and Er:YAG lasers on cutaneous photodamages by a split trial. The aim of the present study was to compare these modalities in a randomized controlled double-blind split-face design with multiple sessions and larger sample size compared to previous studies done before. Forty patients with facial wrinkles were enrolled. Patients were randomly assigned to receive three monthly treatments on each side of the face, one with a fractional CO2 and one with a fractional Er:YAG laser. The evaluations included investigating clinical outcome determined by two independent dermatologists not enrolled in the treatment along with measuring skin biomechanical property of cheeks using a sensitive biometrologic device with the assessment of cutaneous resonance running time (CRRT). Moreover, possible side effects and patients’ satisfaction have been recorded at baseline, 1 month after each treatment, and 3 months after the last treatment session. Clinical assessment showed both modalities significantly reduce facial wrinkles (p value < 0.05), with no appreciable difference between two lasers. Mean CRRT values also decreased significantly after the laser treatment compared to the baseline in both laser groups. There was no serious long-standing adverse effect after both laser treatments, but the discomfort was more pronounced by the participants after CO2 laser treatment. According to the present study, both fractional CO2 and fractional Er:YAG lasers show considerable clinical improvement of facial skin wrinkles with no serious adverse effects, but post-treatment discomfort seems to be lower with Er:YAG laser.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Yaar M, Gilchrest BA (2007) Photoageing: mechanism, prevention and therapy. Br J Dermatol 157:874–87
El-Domyati M, Attia S, Saleh F, Brown D, Birk DE, Gasparro F, Ahmad H, Uitto J (2002) Intrinsic aging vs. photoaging: a comparative histopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp Dermatol 11:398–405
Kim BJ, Choi JH, Lee Y (2015) Development of facial rejuvenation procedures: thirty years of clinical experience with face lifts. Arch Plast Surg 42:521–31
Riggs K, Keller M, Humphreys TR (2007) Ablative laser resurfacing: high-energy pulsed carbon dioxide and erbium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet. Clin Dermatol 25:462–73
Hunzeker CM, Weiss ET, Geronemus RG (2009) Fractionated CO2 laser resurfacing: our experience with more than 2000 treatments. Aesthet Surg J 29:317–22
Karsai S, Czarnecka A, Jünger M, Raulin C (2010) Ablative fractional lasers (CO(2) and Er:YAG): a randomized controlled double-blind split-face trial of the treatment of peri-orbital rhytides. Lasers Surg Med 42:160–7
Jung KE, Jung KH, Park YM, Lee JY, Kim TY, Kim HO, Kim HS (2013) A split-face comparison of ablative fractional lasers (CO(2) and Er:YAG) in Asian patients; postprocedure erythema, pain and patient’s satisfaction. J Cosmet Laser Ther 15:70–3
Trelles MA, Mordon S, Velez M, Urdiales F, Levy JL (2009) Results of fractional ablative facial skin resurfacing with the erbium:yttrium-aluminium-garnet laser 1 week and 2 months after one single treatment in 30 patients. Lasers Med Sci 24:186–94
Fleming D (1999) Controversies in skin resurfacing: the role of erbium. J Cutan Laser Ther 1:15–21
Robati RM, Einollahi B, Einollahi H, Younespour S, Fadaifard S (2016) Skin biophysical characteristics in patients with keratoconus: a controlled study. Scientifica (Cairo) 2016:6789081
Robati RM, Abdollahimajd F, Robati AM (2015) Evaluation of subcision for the correction of the prominent nasolabial folds. Dermatol Res Pract 2015:976153
Dierickx CC, Khatri KA, Tannous ZS, Childs JJ, Cohen RH, Erofeev A, Tabatadze D, Yaroslavsky IV, Altshuler GB (2008) Micro-fractional ablative skin resurfacing with two novel erbium laser systems. Lasers Surg Med 40:113–23
Hantash BM, Bedi VP, Kapadia B, Rahman Z, Jiang K, Tanner H, Chan KF, Zachary CB (2007) In vivo histological evaluation of a novel ablative fractional resurfacing device. Lasers Surg Med 39:96–107
Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Dover JS, Arndt KA (2008) The spectrum of laser skin resurfacing: nonablative, fractional, and ablative laser resurfacing. J Am Acad Dermatol 58:719–37
Waibel J, Beer K, Narurkar V, Alster T (2009) Preliminary observations on fractional ablative resurfacing devices: clinical impressions. J Drugs Dermatol 8:481–5
Khatri KA, Ross V, Grevelink JM, Magro CM, Anderson RR (1999) Comparison of erbium:YAG and carbon dioxide lasers in resurfacing of facial rhytides. Arch Dermatol 135:391–7
Xin S, Man W, Fluhr JW, Song S, Elias PM, Man MQ (2010) Cutaneous resonance running time varies with age, body site and gender in a normal Chinese population. Skin Res Technol 16:413–21
Seirafi H, Farsinejad K, Firooz A, Davoudi SM, Robati RM, Hoseini MS, Ehsani AH, Sadr B (2009) Biophysical characteristics of skin in diabetes: a controlled study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23:146–9
Lee HM, Haw S, Kim JE, Won CH, Lee MW, Choi JH, Chang SE, Kim YJ, Goo BL (2012) A fractional 2940 nm short-pulsed, erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser is effective and minimally invasive for the treatment of photodamaged skin in Asians. J Cosmet Laser Ther 14:253–9
El-Domyati M, Abd-El-Raheem T, Medhat W, Abdel-Wahab H, Al Anwer M (2014) Multiple fractional erbium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser sessions for upper facial rejuvenation: clinical and histological implications and expectations. J Cosmet Dermatol 13:30–7
Manuskiatti W, Iamphonrat T, Wanitphakdeedecha R, Eimpunth S (2013) Comparison of fractional erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet and carbon dioxide lasers in resurfacing of atrophic acne scars in Asians. Dermatol Surg 39(1 Pt 1):111–20
Acknowledgements
This paper has been extracted from the dermatology residency thesis written by Dr. Elmira Asadi in School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (registration no. 528).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Clinical trial registration number: IRCT ID: 2014122820468N1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robati, R.M., Asadi, E. Efficacy and safety of fractional CO2 laser versus fractional Er:YAG laser in the treatment of facial skin wrinkles. Lasers Med Sci 32, 283–289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2111-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2111-8