Abstract
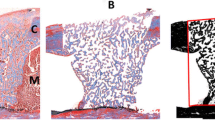
This study was aimed to evaluate the effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) in the treatment of trabecular bone loss induced by skeletal unloading. Twelve mice have taken denervation operation. At 2 weeks after denervation, LLLT (wavelength, 660 nm; energy density, 3 J/cm2) was applied to the right tibiae of six mice (LASER) for 5 days/week over 2 weeks by using a minimally invasive laser needle system (MILNS) which consists of a 100 μm optical fiber in a fine needle (diameter, 130 μm). Structural parameters and histograms of bone mineralization density distribution (BMDD) were obtained before LLLT and at 2 weeks after LLLT. In addition, osteocyte, osteoblast, and osteoclast populations were counted. Two weeks after LLLT, bone volume fraction, trabeculae number, and trabeculae thickness were significantly increased and trabecular separations, trabecular bone pattern factor, and structure model index were significantly decreased in LASER than SHAM (p < 0.05). BMDD in LASER was maintained while that in SHAM was shifted to lower mineralization. Osteocyte and osteoblast populations were significantly increased but osteoclast population was significantly decreased in LASER when compared with those in SHAM (p < 0.05). The results indicate that LLLT with the MILNS may enhance bone quality and bone homeostasis associated with enhancement of bone formation and suppression of bone resorption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ko CY, Seo DH, Kim HS (2011) Deterioration of bone quality in the tibia and fibula in growing mice during skeletal unloading: gender-related differences. J Biomech Eng 133(11):111003
Suzue N, Nikawa T, Onishi Y, Yamada C, Hirasaka K, Ogawa T, Furochi H, Kosaka H, Ishidoh K, Gu H, Takeda S, Ishimaru N, Hayashi Y, Yamamoto H, Kishi K, Yasui N (2006) Ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b downregulates bone formation through suppression of IGF-I signaling in osteoblasts during denervation. J Bone Miner Res 21(5):722–734
Ito M, Nishida A, Nakamura T, Uetani M, Hayashi K (2002) Differences of three-dimensional trabecular microstructure in osteopenic rat models caused by ovariectomy and neurectomy. Bone 30(4):594–598
Warden SJ, Bennell KL, Forwood MR, McMeeken JM, Wark JD (2001) Skeletal effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on the ovariectomized rodent. Ultrasound Med Biol 27(7):989–998
Lim D, Ko CY, Seo DH, Woo DG, Kim JM, Chun KJ, Kim HS (2011) Low-intensity ultrasound stimulation prevents osteoporotic bone loss in young adult ovariectomized mice. J Orthop Res 29(1):116–125
Renno AC, de Moura FM, dos Santos NS, Tirico RP, Bossini PS, Parizotto NA (2006) Effects of 830-nm laser light on preventing bone loss after ovariectomy. Photomed Laser Surg 24(5):642–645
Renno AC, de Moura FM, dos Santos NS, Tirico RP, Bossini PS, Parizotto NA (2006) Effects of 830-nm laser, used in two doses, on biomechanical properties of osteopenic rat femora. Photomed Laser Surg 24(2):202–206
Woo DG, Ko CY, Kim HS, Seo JB, Lim D (2010) Evaluation of the potential clinical application of low-intensity ultrasound stimulation for preventing osteoporotic bone fracture. Ann Biomed Eng 38(7):2438–2446
Rubin C, Sommerfeldt D, Judex S, Qin YX (2001) Inhibition of osteopenia by low magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimuli. Drug Discov Today 6(16):848–858
Fujihara NA, Hiraki KR, Marques MM (2006) Irradiation at 780 nm increases proliferation rate of osteoblasts independently of dexamethasone presence. Lasers Surg Med 38(4):332–336
Ozawa Y, Shimizu N, Kariya G, Abiko Y (1998) Low-energy laser irradiation stimulates bone nodule formation at early stages of cell culture in rat calvarial cells. Bone 22(4):347–354
Pinheiro AL, Gerbi ME (2006) Photoengineering of bone repair processes. Photomed Laser Surg 24(2):169–178
Stein A, Benayahu D, Maltz L, Oron U (2005) Low-level laser irradiation promotes proliferation and differentiation of human osteoblasts in vitro. Photomed Laser Surg 23(2):161–166
Xu M, Deng T, Mo F, Deng B, Lam W, Deng P, Zhang X, Liu S (2009) Low-intensity pulsed laser irradiation affects RANKL and OPG mRNA expression in rat calvarial cells. Photomed Laser Surg 27(2):309–315
Pires Oliveira DA, de Oliveira RF, Zangaro RA, Soares CP (2008) Evaluation of low-level laser therapy of osteoblastic cells. Photomed Laser Surg 26(4):401–404
Diniz JS, Nicolau RA, de Melo Ocarino N, do Carmo Magalhaes F, de Oliveira Pereira RD, Serakides R (2009) Effect of low-power gallium-aluminum-arsenium laser therapy (830 nm) in combination with bisphosphonate treatment on osteopenic bone structure: an experimental animal study. Lasers Med Sci 24(3):347–352
Muniz Renno AC, de Moura FM, dos Santos NS, Tirico RP, Bossini PS, Parizotto NA (2006) The effects of infrared-830 nm laser on exercised osteopenic rats. Lasers Med Sci 21(4):202–207
Luger EJ, Rochkind S, Wollman Y, Kogan G, Dekel S (1998) Effect of low-power laser irradiation on the mechanical properties of bone fracture healing in rats. Lasers Surg Med 22(2):97–102
Ninomiya T, Hosoya A, Nakamura H, Sano K, Nishisaka T, Ozawa H (2007) Increase of bone volume by a nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation is caused by a decreased osteoclast number and an activated osteoblasts. Bone 40(1):140–148
Ninomiya T, Miyamoto Y, Ito T, Yamashita A, Wakita M, Nishisaka T (2003) High-intensity pulsed laser irradiation accelerates bone formation in metaphyseal trabecular bone in rat femur. J Bone Miner Metab 21(2):67–73
Nissan M, Rochkind S, Razon N, Bartal A (1986) HeNe laser irradiation delivered transcutaneously: its effect on the sciatic nerve of rats. Lasers Surg Med 6(5):435–438
Roschger P, Paschalis EP, Fratzl P, Klaushofer K (2008) Bone mineralization density distribution in health and disease. Bone 42(3):456–466
Boivin G, Farlay D, Bala Y, Doublier A, Meunier PJ, Delmas PD (2009) Influence of remodeling on the mineralization of bone tissue. Osteoporos Int 20(6):1023–1026
Kang H, Ko CY, Ryu Y, Seo DH, Kim HS, Jung B (2012) Development of a minimally invasive laser needle system: effects on cortical bone of osteoporotic mice. Lasers Med Sci 27(5):965–969
David V, Laroche N, Boudignon B, Lafage-Proust MH, Alexandre C, Ruegsegger P, Vico L (2003) Noninvasive in vivo monitoring of bone architecture alterations in hindlimb-unloaded female rats using novel three-dimensional microcomputed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 18(9):1622–1631
Ko CY, Jung YJ, Seo DH, Schreiber J, Lim D, Kim HS (2012) Trabecular Bone Loss in Lumbar Vertebrae and Tibiae following Sciatic Nerve Injury: Correlation between Baseline Bone Quantity (BV/TV) and the Magnitude and Rate of Bone Loss. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(9):1705–1708
Ko CY, Jung YJ, Park JH, Seo DH, Han P, Bae K, Schreiber J, Kim HS (2012) Trabecular bone response to mechanical loading in ovariectomized Sprague–Dawley rats depends on baseline bone quantity. J Biomech 45(11):2046–2049
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Muller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 25(7):1468–1486
Mulder L, Koolstra JH, Van Eijden TM (2004) Accuracy of microCT in the quantitative determination of the degree and distribution of mineralization in developing bone. Acta Radiol 45(7):769–777
Meganck JA, Kozloff KM, Thornton MM, Broski SM, Goldstein SA (2009) Beam hardening artifacts in micro-computed tomography scanning can be reduced by X-ray beam filtration and the resulting images can be used to accurately measure BMD. Bone 45(6):1104–1116
Hazenberg JG, Taylor D, Lee TC (2007) The role of osteocytes and bone microstructure in preventing osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 18(1):1–8
Ciarelli TE, Fyhrie DP, Parfitt AM (2003) Effects of vertebral bone fragility and bone formation rate on the mineralization levels of cancellous bone from white females. Bone 32(3):311–315
Basso N, Jia Y, Bellows CG, Heersche JN (2005) The effect of reloading on bone volume, osteoblast number, and osteoprogenitor characteristics: studies in hind limb unloaded rats. Bone 37(3):370–378
Dufour C, Holy X, Marie PJ (2007) Skeletal unloading induces osteoblast apoptosis and targets alpha5beta1-PI3K-Bcl-2 signaling in rat bone. Exp Cell Res 313(2):394–403
Ahdjoudj S, Lasmoles F, Holy X, Zerath E, Marie PJ (2002) Transforming growth factor beta2 inhibits adipocyte differentiation induced by skeletal unloading in rat bone marrow stroma. J Bone Miner Res 17(4):668–677
Aguirre JI, Plotkin LI, Stewart SA, Weinstein RS, Parfitt AM, Manolagas SC, Bellido T (2006) Osteocyte apoptosis is induced by weightlessness in mice and precedes osteoclast recruitment and bone loss. J Bone Miner Res 21(4):605–615
Skerry TM (2008) The response of bone to mechanical loading and disuse: fundamental principles and influences on osteoblast/osteocyte homeostasis. Arch Biochem Biophys 473(2):117–123
Aarden EM, Burger EH, Nijweide PJ (1994) Function of osteocytes in bone. J Cell Biochem 55(3):287–299
Tomkinson A, Reeve J, Shaw RW, Noble BS (1997) The death of osteocytes via apoptosis accompanies estrogen withdrawal in human bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(9):3128–3135
Metz LN, Martin RB, Turner AS (2003) Histomorphometric analysis of the effects of osteocyte density on osteonal morphology and remodeling. Bone 33(5):753–759
David R, Nissan M, Cohen I, Soudry M (1996) Effect of low-power He–Ne laser on fracture healing in rats. Lasers Surg Med 19(4):458–464
Reddy GK (2004) Photobiological basis and clinical role of low-intensity lasers in biology and medicine. J Clin Laser Med Surg 22(2):141–150
Kreisler M, Daublander M, Willershausen-Zonnchen B, d’Hoedt B (2001) Effect of diode laser irradiation on the survival rate of gingival fibroblast cell cultures. Lasers Surg Med 28(5):445–450
Yamaguchi H, Kobayashi K, Osada R, Sakuraba E, Nomura T, Arai T, Nakamura J (1997) Effects of irradiation of an erbium:YAG laser on root surfaces. J Periodontol 68(12):1151–1155
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Leading Foreign Research Institute Recruitment Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST; 2010-00757).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chang-Yong Ko and Heesung Kang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, CY., Kang, H., Ryu, Y. et al. The effects of minimally invasive laser needle system on suppression of trabecular bone loss induced by skeletal unloading. Lasers Med Sci 28, 1495–1502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1265-x