Abstract
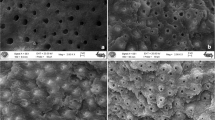
The aim of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of all-in-one self-etch adhesives and their respective nanocomposites in class V cavities prepared by erbium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet (Er:YAG) laser and bur. Class V cavities were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of 72 premolars by Er:YAG laser or bur and divided into six groups (n = 24). The occlusal margins were enamel and the cervical margins were cementum. The groups were as follows: group 1 Er:YAG laser preparation (E) + Xeno V (X) + CeramX (C); group 2 bur preparation (B) + X + C; group 3 E + AdheSE One (A) + Tetric EvoCeram (T); group 4 B + A + T; group 5 E + Clearfil S3 Bond (CSB) + Clearfil Majesty Esthetic (CME); group 6 B + CSB + CME. All teeth were stored in distilled water at 37°C for 24 h, then thermocycled 500 times (5–55°C). Ten teeth from each group were chosen for the microleakage investigation and two teeth for the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) evaluation. The teeth that were prepared for the microleakage test were immersed in 0.5% basic fuchsin dye for 24 h. After immersion, the teeth were sectioned and observed under a stereomicroscope for dye penetration. Data were analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney U tests (P < 0.05). Bur-prepared cavities presented less microleakage in all groups for enamel (P < 0.05); however, in cervical margins, there were no differences between laser-prepared and bur-prepared cavities in the Xeno V + CeramX and AdheSE One + Tetric EvoCeram groups (P > 0.05). SEM observations of restorative material–dentin interfaces seemed to correspond with those of the microleakage test. Microleakage at the cervical interfaces was greater than that at the occlusal interfaces. Er:YAG laser-prepared class V cavities yielded more microleakage in occlusal margins with all-in-one self-etch adhesives and the respective manufacturer’s nanocomposites.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitra SB, Wu D, Holmes BN (2003) An application of nanotechnology in advanced dental materials. J Am Dent Assoc 134:1382–1390
Van Meerbeek B, De Munck J, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Vargas M, Vijay P, Van Landuyt K, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G (2003) Buonocore memorial lecture. Adhesion to enamel and dentin: current status and future challenges. Oper Dent 28:215–235
Perdigão J, Geraldeli S, Hodges JS (2003) Total-etch versus self-etch adhesive. Effect on postoperative sensitivity. J Am Dent Assoc 134:1621–1629
Attar N, Korkmaz Y (2007) Effect of two light-emitting diode (LED) and one halogen curing light on the microleakage of class V flowable composite restorations. J Contemp Dent Pract 8:80–88
Hobson RS, McCabe JF (2002) Relationship between enamel etch characteristics and resin-enamel bond strength. Br Dent J 192:463–468. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.4801401a
Miyazaki S, Iwasaki K, Onose H, Moore BK (2001) Enamel and dentin bond strengths of single application bonding systems. Am J Dent 14:361–366
Leinfelder KF, Kurdziolek SM (2003) Self-etching bonding agents. Compend Contin Educ Dent 24:447–454
Perdigão J, Anauate-Netto C, Carmo AR, Lewgoy HR, Cordeiro HJ, Dutra-Corrêa M, Castilhos N, Amore R (2004) Influence of acid etching and enamel beveling on the 6-month clinical performance of a self-etch dentin adhesive. Compend Contin Educ Dent 25:33–34, 36–38, 40
Christensen GJ (2002) Preventing postoperative tooth sensitivity in class I, II and V restorations. J Am Dent Assoc 133:229–231
Eick JD, Gwinnett AJ, Pashley DH, Robinson SJ (1997) Current concepts on adhesion to dentin. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 8:306–335
Marshall GW Jr, Marshall SJ, Kinney JH, Balooch M (1997) The dentin substrate: structure and properties related to bonding. J Dent 25:441–458. doi:10.1016/S0300-5712(96)00065-6
Swift EJ Jr (2002) Dentin/enamel adhesives: review of the literature. Pediatr Dent 24:456–461
Walshaw PR, McComb D (1996) Clinical considerations for optimal dentinal bonding. Quintessence Int 27:619–625
Peumans M, Kanumilli P, De Munck J, Van Landuyt K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B (2005) Clinical effectiveness of contemporary adhesives: a systematic review of current clinical trials. Dent Mater 21:864–881. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2005.02.003
Gokcelik A, Ozel Y, Ozel E, Arhun N, Attar N, Firatli S, Firatli E (2007) The influence of Er:YAG laser conditioning versus self-etching adhesives with acid etching on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets. Photomed Laser Surg 25:508–512. doi:10.1089/pho.2007.2096
Cozean C, Arcoria CJ, Pelagalli J, Powell GL (1997) Dentistry for the 21st century? Erbium:YAG laser for teeth. J Am Dent Assoc 128:1080–1087
Keller U, Hibst R, Geurtsen W, Schilke R, Heidemann D, Klaiber B, Raab WH (1998) Erbium:YAG laser application in caries therapy. Evaluation of patient perception and acceptance. J Dent 26:649–656. doi:10.1016/S0300-5712(97)00036-5
Corona SA, Borsatto MC, Pecora JD, Rocha De SA, RA RTS, Palma-Dibb RG (2003) Assessing microleakage of different class V restorations after Er:YAG laser and bur preparation. J Oral Rehabil 30:1008–1014. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01173.x
Aranha AC, Turbino ML, Powell GL, Eduardo Cde P (2005) Assessing microleakage of class V resin composite restorations after Er:YAG laser and bur preparation. Lasers Surg Med 37:172–177. doi:10.1002/lsm.20208
Delme KI, Deman PJ, De Moor RJ (2005) Microleakage of class V resin composite restorations after conventional and Er:YAG laser preparation. J Oral Rehabil 32:676–685. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2842.2005.01550.x
Korkmaz Y, Ozel E, Attar N (2007) Effect of flowable composite lining on microleakage and internal voids in class II composite restorations. J Adhes Dent 9:189–194
Cenci M, Demarco F, de Carvalho R (2005) Class II composite resin restorations with two polymerization techniques: relationship between microtensile bond strength and marginal leakage. J Dent 33:603–610. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2005.01.001
Sidhu SK, Henderson LJ (1992) In vitro marginal leakage of cervical composite restorations lined with a light-cured glass ionomer. Oper Dent 17:7–12
Quo BC, Drummond JL, Koerber A, Fadavi S, Punwani I (2002) Glass ionomer microleakage from preparations by an Er/YAG laser or a high-speed handpiece. J Dent 30:141–146. doi:10.1016/S0300-5712(02)00011-8
Ozel E, Korkmaz Y, Attar N (2008) Influence of location of the gingival margin on the microleakage and internal voids of nanocomposites. J Contemp Dent Pract 9:65–72
Asmussen E, Jorgensen KD (1978) Restorative resins: coefficient of thermal expansion—a factor of clinical significance? Quintessence Int Dent Dig 9:79–82
Chinelatti MA, Ramos RP, Chimello DT, Borsatto MC, Pécora JD, Palma-Dibb RG (2004) Influence of the use of Er:YAG laser for cavity preparation and surface treatment in microleakage of resin-modified glass ionomer restorations. Oper Dent 29:430–436
De Munck J, Van Meerbeek B, Satoshi I, Vargas M, Yoshida Y, Armstrong S, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G (2003) Microtensile bond strengths of one- and two-step self-etch adhesives to bur-cut enamel and dentin. Am J Dent 16:414–420
Frankenberger R, Perdigao J, Rosa BT, Lopes M (2001) “No-bottle” vs “multi-bottle” dentin adhesives—a microtensile bond strength and morphological study. Dent Mater 17:373–380. doi:10.1016/S0109-5641(00)00084-1
Perdigao J, Gomes G, Duarte S Jr, Lopes MM (2005) Enamel bond strengths of pairs of adhesives from the same manufacture. Oper Dent 30:492–499
Van Landuyt KL, De Munck J, Snauwaert J, Coutinho E, Poitevin A, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Peumans M, Suzuki K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B (2005) Monomer-solvent phase separation in one-step self-etch adhesives. J Dent Res 84:183–188
Pashley DH, Tay FR (2001) Aggressiveness of contemporary self-etching adhesives. Part II: etching effects on unground enamel. Dent Mater 17:430–444. doi:10.1016/S0109-5641(00)00104-4
Lizarelli RF, Silva PC, Neto ST, Bagnato VS (2004) Study of microleakage at class V cavities prepared by Er:YAG laser using rewetting surface treatment. J Clin Laser Med Surg 22:51–55. doi:10.1089/104454704773660976
Korkmaz Y, Attar N (2007) Dentin bond strength of composites with self-etching adhesives using LED curing lights. J Contemp Dent Pract 8:34–42
Wright GZ, Hatibovic-Kofman S, Millenaar DW, Braverman I (1999) The safety and efficacy of treatment with air abrasion technology. Int J Paediatr Dent 9:133–140. doi:10.1046/j.1365-263x.1999.00103.x
Niu W, Eto JN, Kimura Y, Takeda FH, Matsumoto K (1998) A study on microleakage after resin filling of class V cavities prepared by Er:YAG laser. J Clin Laser Med Surg 16:227–231
Hatibovic-Kofman S, Wright GZ, Braverman I (1998) Microleakage of sealants after conventional, bur, and air-abrasion preparation of pits and fissures. Pediatr Dent 20:173–176
Armengol V, Jean A, Rohanizadeh R, Hamel H (1999) Scanning electron microscopic analysis of diseased and healthy dental hard tissues after Er:YAG laser irradiation: in vitro study. J Endod 25:543–546. doi:10.1016/S0099-2399(99)80376-8
Corona SA, Borsatto M, Dibb RG, Ramos RP, Brugnera A, Pécora JD (2001) Microleakage of class V resin composite restorations after bur, air-abrasion or Er:YAG laser preparation. Oper Dent 26:491–497
Setien VJ, Cobb DS, Denehy GE, Vargas MA (2001) Cavity preparation devices: effect on microleakage of class V resin-based composite restorations. Am J Dent 14:157–162
Wright GZ, McConnell RJ, Keller U (1993) Microleakage of class V composite restorations prepared conventionally with those prepared with an Er:YAG laser: a pilot study. Pediatr Dent 15:425–426
Palma Dibb RG, Milori Corona SA, Borsatto MC, Ferreira KC, Pereira Ramos R, Djalma Pécora J (2002) Assessing microleakage on class V composite resin restorations after Er:YAG laser preparation varying the adhesive systems. J Clin Laser Med Surg 20:129–133. doi:10.1089/104454702760090209
Ceballo L, Toledano M, Osorio R, Tay FR, Marshall GW (2002) Bonding to Er-YAG-laser-treated dentin. J Dent Res 81:119–122
De Munck J, Van Meerbeek B, Yudhira R, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G (2002) Micro-tensile bond strength of two adhesives to erbium:YAG-lased vs. bur-cut enamel and dentin. Eur J Oral Sci 110:322–329. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0722.2002.21281.x
Sano H, Takatsu T, Ciucchi B, Horner JA, Matthews WG, Pashley DH (1995) Nanoleakage: leakage within the hybrid layer. Oper Dent 20:18–25
Roebuck EM, Sauders WP, Whitters CJ (2000) Influence of erbium:YAG laser energies on the microleakage of class V resin-based composite restorations. Am J Dent 13:280–284
Yap AU, Mok BY, Pearson G (1997) An in vitro microleakage study of the ‘bonded-base’ restorative technique. J Oral Rehabil 24:230–264. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2842.1997.tb00318.x
Prati C, Chersoni S, Mongiorgi R, Pashley DH (1998) Resin-infiltrated dentin layer formation of new bonding systems. Oper Dent 23:185–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korkmaz, Y., Ozel, E., Attar, N. et al. Microleakage and scanning electron microscopy evaluation of all-in-one self-etch adhesives and their respective nanocomposites prepared by erbium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet laser and bur. Lasers Med Sci 25, 493–502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0672-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0672-5