Abstract
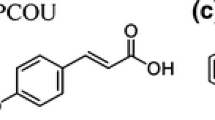
Dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of para-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA) was studied in the presence of Degussa P-25 titanium dioxide photocatalyst under concentrated solar radiation. This work includes the study of the effect of pH, and of the presence of different anions and cations on dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation (PCD) of PHBA on titanium dioxide. The results obtained clearly indicate that there is a link between the extent of adsorption of PHBA and its PCD. Conditions that favor greater adsorption of PHBA also favor a greater PCD. This points to the possibility that the mechanism of PCD involves a surface reaction between adsorbed PHBA and OH ° radical. Anions were generally found to have a detrimental effect on the photocatalytic degradation of PHBA. Cl– caused the greatest decrease in the PCD followed by NO3 –, HCO3 – and SO4 2–. Cations Cu2+ and Fe2+ were not found to assist the degradation of PHBA, possibly due to the anions associated with them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 May 2000 / Accepted: 15 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramanian, V., Pangarkar, V. & Beenackers, A. Photocatalytic degradation of para-hydroxybenzoic acid: Relationship between substrate adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Clean Products and Processes 2, 149–156 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100980000080
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100980000080