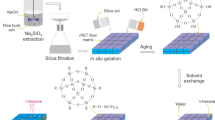
Abstract
Using rice husk ash as silicon source to prepare silica aerogels is one of the most possible ways to realize high value utilization of husk ash. However, the applications of rice husk ash-based silica aerogels (HSAs) using the conventional procedure (without incorporating special materials or processes) are limited due to their relatively inferior properties compared to silica aerogel prepared from conventional silicon sources. Therefore, it is necessary to explore new application areas where HSA can be competent. In this study, HSAs were prepared using a simple conventional protocol and utilized as fillers to enhance the corrosion resistance of epoxy coating. The results showed that the optimal HSA had a specific surface area of 470.3 m2/g and a water contact angle of 158.5°. The HSA/epoxy composite can be prepared simply using a magnetic stiran. When the addition amount is 6%, the coating has the best corrosion resistance. The protection efficiency remaining at 91.4%, after 20 days of immersion in a 3.5% NaCl solution, which was 48.7% for pure epoxy coating. The polarization resistance value was 7591.7% higher compared to pure epoxy coating. This performance was better than that reported for some conventional fillers in the literature. Besides the similar effect as other fillers, it is possible that the HSA may have trapped O2 and Cl−, preventing them from contacting directly with the metal.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Abbas N, Khalid RH, Ban G, Kim H, Lee H (2019) Silica aerogel derived from rice husk: an aggregate replacer for lightweight and thermally insulating cement-based composites. Constr Build Mater 195:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.227
Akbarzade K, Shishesaz MR, Danaee I, Zarei D (2017) The effect of nanoporous silica aerogel on corrosion protection properties of epoxy coatings on carbon steel. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 53:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117020022
Akhter F, Soomro SA, Inglezakis VJ (2023) Green, organic, and facile synthesis of mesoporous silica aerogels for highly efficient Pb (II) removal from synthetic wastewater: isotherm and kinetic studies. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04060-9
Anjum A, Sun K, Ali M, Riaz R, Jeong S (2020) Fabrication of coral-reef structured nano silica for self-cleaning and super-hydrophobic textile applications. Chem Eng J 401:125859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125859
Ban G, Song S, Lee HW, Kim HT (2019) Effect of acidity levels and feed rate on the porosity of aerogel extracted from rice husk under ambient pressure. Nanomaterials 9:300. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020300
Bao W, Deng Z, Zhang S, Ji Z, Zhang H (2019) Next-generation composite coatingsystem nanocoating. Front Mater 6:116876920. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2019.00072
Barletta M, Lusvarghi L, Pighetti Mantini F, Rubino G (2007) Epoxy-based thermosetting powder coatings: surface appearance, scratch adhesion and wear resistance. Surf Coat Technol 201:7479–7504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.02.017
Bouibed A, Doufnoune R (2019) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid materials based on graphene oxide and silica nanoparticles and their effect on the corrosion protection properties of epoxy resin coatings. J Adhes Sci Technol 33:834–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2019.1571660
Chang B, Park S (2010) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem 3:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.anchem.012809.102211
Chang K, Lin H, Lin C, Kuo T, Huang H, Hsu S, Yeh J, Yang J, Yu Y (2008) Effect of amino-modified silica nanoparticles on the corrosion protection properties of epoxy resin-silica hybrid materials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:3040–3049. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2008.086
Chen S, Li X, Chen S, Wang Y, Gong Z, Zhang Y (2021) A new application of atomic force microscopy in the characterization of pore structure and pore contribution in shale gas reservoirs. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 88:103802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2021.103802
Conradi M, Kocijan A, Kek-Merl D, Zorko M, Verpoest I (2014) Mechanical andanticorrosion properties of nanosilica-filled epoxy-resin composite coatings. Appl Surf Sci 292:432–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.155
Cui S, Yu S, Lin B, Shen X, Gu D (2015) Preparation of SiO2 aerogel from rice husk ash. RSC Adv 5:65818–65826. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08886K
Do NH, Can NN, Le PK (2023) Thermal insulation of flame retardant silica aerogel composites from rice husk ash and plastic waste fibers. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02805-7
Dong J, Ke W (2009) The accelerated test of simulated atmospheric corrosion and the rust evolution of low carbon steel. J Electrochem 15:170–178. https://doi.org/10.13208/j.electrochem.2009.02.009
Dong J, Han E, Liu C, Ke W (2006) Corrosion behavior of rusted mild steel under means of wet/dry alternate conditions. Corros Sci Prot Technol 18:414–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(06)60046-7
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi MH (2008) Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Technol 199:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.060
Feng Q, Chen K, Ma D, Lin H, Liu Z, Qin S, Luo Y (2018) Synthesis of high specific surface area silica aerogel from rice husk ash via ambient pressure drying. Colloids Surf 539:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.12.025
Flis J, Kanoza M (2006) Electrochemical and surface analytical study of vinyl-triethoxy silane films on iron after exposure to air. Electrochim Acta 51:2338–2345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.01.065
Fooladgar S, Teimouri A, Nasab GS (2019) Highly efficient removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions using chitosan/rice husk ash/nano alumina with a focus on optimization by response surface methodology: isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J Polym Environ 27:1025–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01385-3
Ganesan K, Rajagopal K, Thangavel K (2008) Rice husk ash blended cement: assessment of optimal level ofreplacement for strength and permeability properties ofconcrete. Constr Build Mater 22:1675–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.06.011
Ge D, Yang L, Li Y, Zhao J (2009) Hydroph, obic and thermal insulation properties of silica aerogel/epoxy composite. J Non Cryst Solids 355:2610–2615. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNONCRYSOL.2009.09.017
Gergely A, Pfeifer É, Bertóti I, Török T, Kálmán E (2011) Corrosion protection of cold-rolled steel by zinc-rich epoxy paint coatings loaded with nano-size alumina supported polypyrrole. Corros Sci 53:3486–3499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.06.014
Ghanbari A, Attar MM (2015) A study on the anticorrosion performance of epoxy nanocomposite coatings containing epoxy-silane treated nano-silica on mild steel substrate. J Ind Eng Chem 23:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JIEC.2014.08.008
Gu W, Lv J, Quan B, Liang X, Zhang B, Ji G (2019) Achieving MOF-derived one-dimensional porous ZnO/C nanofiber with lightweight and enhanced microwave response by an electrospinning method. J Alloys Compd 806:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.334
Gupta N, Ricci W (2008) Processing and compressive properties of aerogel/epoxy composites. J Mater Process Technol 198:178–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMATPROTEC.2007.06.084
Hossain SS, Mathur L, Roy PK (2018) Rice husk/rice husk ash as an alternative source of silica in ceramics: A review. J Asian Ceram Soc 6:299–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2018.1539210
Hrubesh LW (1991) Aerogels: the world’s lightest solids. ChemInform 22:96845900. https://doi.org/10.1002/CHIN.199113360
Hu L, He Z, Zhang S (2020) Sustainable use of rice husk ash in cement-based materials: environmental evaluation and performance improvement. J Clean Prod 264:121744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121744
Huang X, Shahzad S, Li Y, Zhang Y, Sang L, Zhou H, Jiang H, Lo K, Yu C (2017) Silver nanoclusters capped silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric photoluminescence nanosensor for the selective detection of I− and S2−. Anal Chim Acta 988:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.07.056
Hüsing N, Schubert U (1998) Aerogels—airy materials: chemistry, structure, and Properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:22–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980202)37:1/2%3C22::AID-ANIE22%3E3.0.CO;2-I
Kanthasamy R, Algarni M, Peng LC, Zakaria NA, Zwawi M (2023) The effects of solvent on superhydrophobic polyurethane coating incorporated with hydrophilic SiO2 nanoparticles as antifouling paint. Polymers 15:1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061328
Karmouch R, Ross G (2010) Superhydrophobic wind turbine blade surfaces obtained by a simple deposition of silica nanoparticles embedded in epoxy. Appl Surf Sci 257:665–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.07.041
Khan AA, Khan A, Zafar Z, Ahmad I, Islam B (2023) Corrosion protection of aluminum alloy 7075 using functionalized micro-silica based epoxy coatings. Mater Res Express 10:045301. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/acc6b5
Kim M, Bhanja P, Amiralian N, Urata C, Hozumi A, Hossain MSA, Alshehri SM, Bando Y, Ahamad T, Yamauchi Y (2023) Mesostructured silica nanoparticles with organic corrosion inhibitors to enhance the longevity of anticorrosion effect. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 96:394–397. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20230004
Kim NH, Hwang HS, Lee JL, Choi KH, Park I (2011) Proc.18th Int. Conference on Composite Materials, Jeju Island.
Li W, Song Z, Cui S (2022) Preparation of hydrophobic SiO2 aerogel via ambient pressure drying with water alas. J Nanjing Tech Univ (natural Science Edition) 44:387–394
Linhares T, Pessoa De Amorim M, Durães L (2019) Silica aerogel composites with embedded fibres: a review on their preparation, properties and applications. J Mater Chem A 7:22768–22802. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA04811A
Ömer G, Veyis S, Öyküm B, Hasan S, Ibrahim SY (2021) Adsorption properties and synthesis of silica aerogel-hollow silica microsphere hybrid (sandwich) structure. J Solgel Sci Technol 100:74–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-021-05622-X
Palraj S, Selvaraj M, Maruthan K, Rajagopal G (2015) Corrosion and wear resistance behavior of nano-silica epoxy composite coatings. Prog Org Coat 81:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2015.01.005
Peng Z, Li Y, Chen Y, Liang G, Huang Y, Zi C (2020) Progress in High Value-added Utilization of Silicon Resource from Biomass Ash. Biomass Chem Eng 54:61–66. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2020.02.009
Pode R (2016) Potential applications of rice husk ash waste from rice husk biomass power plant. Renew Sust Energ Rev 53:1468–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.051
Pourhashem S, Vaezi MR, Rashidi A, Bagherzadeh MR (2017) Distinctive roles of silane coupling agentson the corrosion inhibition performance of graphene oxide in epoxy coatings. Prog Org Coat 111:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PORGCOAT.2017.05.008
Prabunathan P, Thennarasu P, Song JK, Alagar M (2017) Achieving low dielectric, surface free energy and UV shielding green nanocomposites via reinforcing bio-silica aerogel with polybenzoxazine. New J Chem 41:5313–5321. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj00138j
Rajanna S, Kumar D, Vinjamur M, Mukhopadhyay M (2015) Silica Aerogel Microparticles from Rice Husk Ash for Drug Delivery. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:949–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/IE503867P
Ramezanzadeh B, Attar M, Farzam M (2011) A study on the anticorrosion performance of the epoxy-polyamide nanocomposites containing ZnO nanoparticles. Prog Org Coat 72:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2011.05.014
Rout T, Jha G, Singh A, Bandyopadhyay N, Mohanty O (2003) Development of conducting polyaniline coating: a novelapproach to superior corrosion resistance. Surf Coat Technol 167:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(02)00862-9
Sarawade P, Kim J, Hilonga A, Quang D, Jeon S, Kim H (2011) Synthesis of sodium silicate-based hydrophilic silica aerogel beads with superior properties: Effect of heat-treatment. J Non Cryst Solids 357:2156–2162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.02.022
Sharma P, Kaur R, Baskar C, Chung W (2010) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous waste usingrice husk and rice husk ash. Desalination 259:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.044
Shlyakhtina AV, Oh YJ (2008) Transparent SiO2 aerogels prepared by ambient pressure drying with ternaryazeotropes as components of pore fluid. J Non Cryst Solids 354:1633–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.10.033
Sing K (2013) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Soleimani M, Bagheri E, Mosaddegh P, Rabiee T, Fakhar A, Sadeghi M (2021) Stable waterborne epoxy emulsions and the effect of silica nanoparticles on their coatings properties. Prog Org Coat 156:106250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106250
Tadjarodi A, Haghverdi M, Mohammadi V (2012) Preparation and characterization of nano-porous silica aerogel from rice husk ash by drying at atmospheric pressure. Mater Res Bull 47:2584–2589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.04.143
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark A, Olivier J, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore sizedistribution(IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Tikhomirov B (2018) Sorption of Atmospheric Gases (N2, O2, Ar, CO2, and H2O) by Silica Aerogel. Atmospheric Ocean Opt 31:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856018030156
Uvida M, Almeida A, Pulcinelli S, Santilli C, Hammer P (2022) Structural Properties of Epoxy-Silica Barrier Coatings for Corrosion Protection of Reinforcing Steel. Polymers 14:3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173474
Wang N, Cheng K, Wu H, Wang C, Wang Q, Wang F (2012) Effect of nano-sized mesoporous silica MCM-41 and MMT on corrosion properties of epoxy coating. Prog Org Coat 75:386–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2012.07.009
Wei W, Liu Z, Wei R, Diao N, Lv Y (2021) Research on Preparation of Superhydrophobicl Composite Coating Based on MOFs Materia and Its Anti-corrosion on Carbon Steel. Mater Rep 35:20068–20075. https://doi.org/10.11896/cldb.20080173
Wilson S, Gabriel V, Tezel F (2020) Adsorption of components from air on silica aerogels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 305:110297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110297
Wu X, Fan M, Shen X, Cui S, Tan G (2018) Silica aerogels formed from soluble silicates and methyl-trimethoxysilane (MTMS) using CO2 gas as a gelation agent. Ceram Int 44:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.005
Xia C, Hao M, Liu W, Zhang X, Miao Y, Ma C, Gao F (2023) Synthesis of Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel from water glass with high thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. J Solgel Sci Technol 106:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-023-06085-Y
Yu F, Wang X, Zhang Z (2023) Research Progress of Nanofillers for Epoxy Anti-corrosion Coatings. J Chin Soc Corros Prot 43:220–230
Zeng D, Liu Z, Zou L, Wu H (2021) Corrosion resistance of epoxy coatings modified by bis-silane prepolymer on aluminum alloy. Coatings 11:842. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070842
Zeng Q, Kang L, Fan J, Song L, Wan S, Liao B, Guo X (2022) Durable superhydrophobic silica/epoxy resin coating for the enhanced corrosion protection of steel substrates in high salt and H2S environments. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 654:130137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130137
Zhang S, Zheng X, Yang Y, Yan Z, Zhang Y, Feng L (2023) Preparation of self-healing coating using pH-sensitive corrosion inhibitor loaded microcapsules and study on its anticorrosion property on carbon steel. Electroplat Finish. https://doi.org/10.19289/j.1004-227x.2023.02.007
Zhou C, Li R, Luo W, Chen Y, Zou H, Liang M, Li Y (2016) The preparation and properties study of polydimethylsiloxane-based coatings modified by epoxy resin. J Polym Res 14:100985274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0903-3
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate BOSSARD for providing the salt spray test facilities.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2021YFC2102205) and the Carbon Peak Carbon Neutralization Science and Technology Innovation Special Fund of Jiangsu Province (No. BE2022303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW wrote the main manuscript text, prepared the data, and analyzed the data. KD, IB, and CZ optimized and adjusted the structure of the article. YJ, WZ, KD, and XW were responsible for the software used and for the drawing of the graphs. JH, Professor, and Professor YD reviewed and revised important parts of the work. Prof. JH, and Prof. YD reviewed and revised the important contents of the work. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Du, K., Jia, Y. et al. A simplified preparation of silica aerogel/epoxy composite coating based on rice husk ash for enhancing corrosion resistance. Clean Techn Environ Policy (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02821-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02821-2