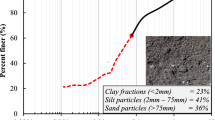
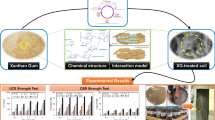
Abstract
This article presents a comprehensive study on the geotechnical behavior of problematic expansive subgrade stabilized by guar gum (GG) biopolymer. In this regard, many geotechnical tests were conducted (such as consistency limits, Proctor compaction, unconfined compressive strength (UCS), California bearing ratio (CBR), and resilient modulus tests) on expansive soil treated with varying GG contents (i.e., from 0 to 5%) and aging periods (0–60 days). The results show that GG treatment increases soil consistency and optimum moisture content, whereas the maximum dry density decreases. The stress–strain behavior, UCS values, and CBR tend to increase with the increase in GG content and aging period, highlighting that GG induced better load-carrying capacity against the imposed loading while retaining the ductile behavior. At 60 days of aging the UCS value at 1.5% GG was found to be increased by 342%, elastic modulus by 309%, energy absorption capacity by 250%, and soaked CBR by 176%, transforming the soil into a better-quality subgrade for pavement construction. The stabilization mechanism showed that the inclusion of GG results in the formation of hydrogels which induce a covering effect, that not only clogs the pore spaces but also binds the soil particles in the soil matrix upon hardening, thus reducing the swelling potential and greatly enhance the soil’s strength parameters. Besides, the GG biopolymer exhibits resistance to degradation and exhibits slight improvement considering the long-term aging effects of up to 365 days. Overall, the GG treatment provides a green sustainable approach to mitigate the adverse expansive subgrade problems.
Graphic Abstract

Graphical abstract of expansive clay strengthening using guar gum biopolymer treatment























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
ASTM D422–63e2 (2007), Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils, ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
ASTM D2487–17 (2017), Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system), ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
ASTM D4318–17e1 (2017), Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils, ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
ASTM D698–12 (2021), Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using standard effort (12,400 ft-lbf/ft3 (600 kN-m/m3)), ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
ASTM D1557–12e1 (2012), Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using modified effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft3 (2,700 kN-m/m3)), ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
ASTM D2166M-16 (2016), Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil, ASTM international, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
Ali M, Aziz M, Hamza M, Madni MF (2020) Engineering properties of expansive soil treated with polypropylene fibers. Geomech Eng 22:227–236. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2020.22.3.227
Anandha Kumar S, Sujatha ER (2021a) Assessing the potential of xanthan gum to modify in-situ soil as baseliners for landfills. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03721-4
Anandha Kumar S, Sujatha ER (2021b) Compaction and permeability characteristics of biopolymer-treated soil. In: Lecture notes in civil engineering. pp 107–117
Ayeldeen M, Negm A, El-Sawwaf M, Kitazume M (2017) Enhancing mechanical behaviors of collapsible soil using two biopolymers. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.007
Ayeldeen MK, Negm AM, El Sawwaf MA (2016) Evaluating the physical characteristics of biopolymer/soil mixtures. Arab J Geosci 9:371
Aziz M, Saleem M, Irfan M (2015) Engineering behavior of expansive soils treated with rice husk ash. Geomech Eng 8:173–186. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2015.8.2.173
Biju MS, Arnepalli DN (2020) Effect of biopolymers on permeability of sand-bentonite mixtures. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 12:1093–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.02.004
Bozyigit I, Javadi A, Altun S (2021) Strength properties of xanthan gum and guar gum treated kaolin at different water contents. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13:1160–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.06.007
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Chang I, Cho G-C (2019) Shear strength behavior and parameters of microbial gellan gum-treated soils: from sand to clay. Acta Geotech 14:361–375
Chang I, Cho GC (2014) Geotechnical behavior of a beta-1,3/1,6-glucan biopolymer-treated residual soil. Geomech Eng 7:633–647
Chang I, Im J, Cho G-C (2016) Geotechnical engineering behaviors of gellan gum biopolymer treated sand. Can Geotech J 53:1658–1670
Chang I, Im J, Prasidhi AK, Cho GC (2015) Effects of xanthan gum biopolymer on soil strengthening. Constr Build Mater 74:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.10.026
Chen R, Zhang L, Budhu M (2013) Biopolymer stabilization of mine tailings. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139:1802–1807. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000902
Chudzikowski RJ (1971) Guar gum and its applications. J Soc Cosmet Chem 22:43
Das (2013) Principles of geotechnical engineering. Cengage learning
Day RW (2006) Foundation engineering handbook: design and construction with the 2006 international building code. McGraw-Hill
El-Daw GEA (1994) A study of guar seed anf guar gum properties (Cyamopsis tetragonolabous). University of Khartoum, Faculty of Agriculture
Gupta SC, Hooda KS, Mathur NK, Gupta S (2009) Tailoring of guar gum for desert sand stabilization. Indian J Chem Technol 16:507–512
Hamza M, Aziz M, Xiang W et al (2022a) Strengthening of high plastic clays by geotextile reinforcement. Arab J Geosci 15:805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09972-w
Hamza M, Ijaz N, Fang C, Ijaz Z (2022b) Stabilization of problematic expansive clays using polypropylene fiber reinforcement. Jordan J Civ Eng 16:531–539
Hamza M, Nie Z, Aziz M et al (2022c) Strengthening potential of xanthan gum biopolymer in stabilizing weak subgrade soil. Clean Technol Environ Policy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-022-02347-5
Hamza M, Nie Z, Aziz M et al (2022d) Geotechnical properties of problematic expansive subgrade stabilized with xanthan gum biopolymer. Road Mater Pavement Des. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2022.2092027
Ijaz N, Dai F, Meng L et al (2020a) Integrating lignosulphonate and hydrated lime for the amelioration of expansive soil: a sustainable waste solution. J Clean Prod 254:119985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.119985
Ijaz N, Dai F, Rehman Z, ur, (2020b) Paper and wood industry waste as a sustainable solution for environmental vulnerabilities of expansive soil: a novel approach. J Environ Manage 262:110285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110285
Ijaz N, Ye W, Rehman Z, ur et al (2022) New binary paper/wood industry waste blend for solidification/stabilisation of problematic soil subgrade: macro-micro study. Road Mater Pavement Des. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2022.2064905
Khan MI, Irfan M, Aziz M, Khan AH (2017) Geotechnical characteristics of effluent contaminated cohesive soils. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 25:75–82. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2016.1210155
Kumar SA, Sujatha ER (2021) Experimental investigation on the shear strength and deformation behaviour of xanthan gum and guar gum treated clayey sand. Geomech Eng 26:101–115
Latifi N, Horpibulsuk S, Meehan CL et al (2017) Improvement of problematic soils with biopolymer—an environmentally friendly soil stabilizer. J Mater Civ Eng 29:04016204. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0001706
Latifi N, Horpibulsuk S, Meehan CL et al (2016) Xanthan gum biopolymer: an eco-friendly additive for stabilization of tropical organic peat. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5643-0
Latifi N, Marto A, Eisazadeh A (2015) Analysis of strength development in non-traditional liquid additive-stabilized laterite soil from macro-and micro-structural considerations. Environ Earth Sci 73:1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3468-2
Mahmoud NM (2000) Physico-chemical study on guar gum
Mudgil D, Barak S, Khatkar BS (2014) Guar gum: processing, properties and food applications—a review. J Food Sci Technol 51:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0522-x
Muguda S, Booth SJ, Hughes PN et al (2017) Mechanical properties of biopolymer-stabilised soil-based construction materials. Géotech Lett 7:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.17.00081
Nugent RA, Zhang G, Gambrell RP (2009) Effect of exopolymers on the liquid limit of clays and its engineering implications. Transp Res Rec 2101:34–43
Obrzud RF, Truty A (2018) The hardening soil model—a practical guidebook. Zace Serv Ltd Softw Eng 05:205
Onah HN, Nwonu DC, Ikeagwuani CC (2022) Feasibility of lime and biopolymer treatment for soft clay improvement: a comparative and complementary approach. Arab J Geosci 15:337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09552-y
Petersen D, Link R, Pandian N, Krishna K (2003) The pozzolanic effect of fly ash on the california bearing ratio behavior of black cotton soil. J Test Eval 31:11586
Puppala AJ, Pedarla A (2017) Innovative ground improvement techniques for expansive soils. Innov Infrastruct Solut 2:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-017-0079-2
Reddy NG, Rao BH, Reddy KR (2018) Biopolymer amendment for mitigating dispersive characteristics of red mud waste. Geotech Lett 8:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1680/JGELE.18.00033
Schaefer VR, White DJ, Ceylan H, Stevens LJ (2008) Design guide for improved quality of roadway subgrades and subbases. Iowa Highw Res Board 7:8–72
Shimizu Y, Tanabe T, Yoshida H et al (2018) Viscosity measurement of xanthan–poly(vinyl alcohol) mixture and its effect on the mechanical properties of the hydrogel for 3D modeling. Sci Rep 8:16538. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34986-4
Smitha S, Rangaswamy K, Keerthi DS (2021) Triaxial test behaviour of silty sands treated with agar biopolymer. Int J Geotech Eng 15:484–495. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2019.1679441
Soldo A, Miletić M, Auad ML (2020) Biopolymers as a sustainable solution for the enhancement of soil mechanical properties. Sci Rep 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57135-x
Specifications G (1998) National highway authority (NHA), NHA Headquarters, 27-Mauve Area. G-9/1, Islamabad, Pakistan
Subramani AK, Ramani SE, Selvasembian R (2021) Understanding the microstructure, mineralogical and adsorption characteristics of guar gum blended soil as a liner material. Environ Monit Assess 193:855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09644-4
Sujatha ER, Saisree S (2019) Geotechnical behaviour of guar gum-treated soil. Soils Found 59:2155–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2019.11.012
T307–99 A (2000) Standard method of test for resilient modulus of subgrade soils and untreated base/subbase materials
Vydehi KV, Moghal AAB (2022) Effect of biopolymeric stabilization on the strength and compressibility characteristics of cohesive soil. J Mater Civ Eng 34:4021428. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004068
Wang H, Wang Z, Blight RJ, Sheehy EC (2015) Derivation of pay adjustment for in-place air void of asphalt pavement from life-cycle cost analysis. Road Mater Pavement Des 16:505–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2015.1020848
Wang L, Weng Z, Liu Q et al (2021) Improving the mechanical properties of red clay using xanthan gum biopolymer. Int J Polym Sci 2021:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1535772
Wang S-L, Baaj H (2021) Treatment of weak subgrade materials with cement and hydraulic road binder (HRB). Road Mater Pavement Des 22:1756–1779. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2020.1712224
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the laboratory and technical support provided by the Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory at the School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, China, College of Civil Engineering, Tongji University, and the University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH: Conceptualization, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Review, and editing. ZN: Supervision, Project, Administration, Review, and editing. MA: Visualization, Formal analysis, Review, and editing. NI: Conceptualization, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Review, and editing. CF: Visualization, Formal analysis, Review, and editing. MUG: Methodology, Software, Validation, Review, and editing. ZI: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Review, and editing. SN: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Review, and editing. MS: Visualization, Formal analysis, Review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamza, M., Nie, Z., Aziz, M. et al. Geotechnical properties of problematic expansive subgrade stabilized with guar gum biopolymer. Clean Techn Environ Policy 25, 1699–1719 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02466-7