Abstract
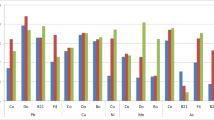
Kans grass (Saccharum spontaneum) is a weed species that is frequently found in many heavy metal-enriched waste dumps including fly ash pond sites. In this study, among a collection of phosphate-solubilizing bacterial strains isolated from the rhizosphere of Saccharum spontaneum present in the abandoned ash pond site of Mejia Thermal Power Station (MTPS-DVC), three strains were characterized for their plant growth-promoting abilities. The isolates identified as Bacillus anthracis strain MHR2, Staphylococcus sp. strain MHR3 and Bacillus sp. strain MHR4 had phosphate solubilization indices of 2.86, 2.31 and 2.40 and they produced soluble phosphates of 700, 600 and 640 mg l−1, respectively, in 4 days. In all the PSBs, pH significantly decreased, indicating the production of various organic acids. They showed other plant growth-promoting features like production of ammonia, siderophore, hydrocyanide and IAA. All of them were resistant to multiple heavy metals and antibiotics. Dry and fresh weight and shoot and root lengths of Brassica juncea L. increased in the presence of these isolates in pot cultures. The strains also increased phytoextraction ability of plants by enhancing the metal accumulation in plant tissues. Thus, the isolated indigenous and stress-adapted rhizobacteria may serve as potential biotechnological tool for the successful ecorestoration of various metal-contaminated sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahemad M (2015) Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria-assisted phytoremediation of metalliferous soils: a review. 3. Biotech 5:111–121
Aleem A, Isar J, Malik A (2003) Impact of long-term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizosphere soil. Bioresour Technol 8:7–13
Bai Y, D’Aoust F, Smith DL, Driscoll BT (2002) Isolation of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus strains from soybean root nodules. Can J Microbiol 48(3):230–238
Bakker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas SPP-mediated plant growth-stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Beneduzi A, Ambrosini A, Passaglia Luciane MP (2012) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): their potential as antagonists and biocontrol agents. Genet Mol Biol. 35(4):1044–1051
Bhandari MM (1990) Flora of the Indian desert. Pbl. MPS Repros, Jodhpur, pp 390–391
Borm PJA (1997) Toxicity and occupational health hazards of Coal Fly Ash (CFA): a review of data and comparison to coal mine dust. Ann Occup Hyg 6:6590–6676
Buchanan RE, Holt JG, Lessel EF (1966) Index Bergeyana. E&S Livingstone Ltd, Edinburgh
Cappuccino JC, Sherman N (1992) In: Microbiology: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. Benjamin/cummings Pub. Co., New York, pp 125–179
Chandel AK, Narasu ML, Chandrasekhar G, Manikyam A, Rao LV (2009) Use of Saccharum spontaneum (wild sugarcane) as biomaterial for cell immobilization and modulated ethanol production by thermotolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae VS3. Bioresour Techno 100:2404–2410
Chen YP, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Shen FT, Lai WA, Young CC (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34:33–41
Clark VL, Bavoil PM (1994) Methods in Enzymology 235(A). Academic Press, London, pp 315–372
Das M, Agarwal P, Singh R, Adholeya A (2013) A study of abandoned ash ponds reclaimed through green cover development. Int JPhytoremediation 15:320–329
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Ganz HH, Turner WC, Brodie EL, Kusters M, Shi Y, Sibanda H, Torok T, Getz WM (2014) Interactions between Bacillus anthracis and Plants May Promote Anthrax Transmission. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(6):e2903. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002903
Gravel V, Antoun H, Tweddell RJ (2007) Growth stimulation and fruit yield improvement of greenhouse tomato plants by inoculation with Pseudomonas putida or Trichoderma atroviride: possible role of indole acetic acid (IAA). Soil Biol Biochem 39:1968–1977
Haynes RJ (2009) Reclamation and revegetation of fly ash disposal sites-challenges and research needs. J Environ Manage 90:43–53
He H, Ye Z, Yang D, Yan J, Xiao L, Zhong T, Yuan M, Cai X, Fang Z, Jing Y (2013) Characterization of endophytic Rahnella sp. JN6 from Polygonum pubescens and its potential in promoting growth and Cd, Pb. Zn uptake by Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 90:1960–1965
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular Calif Agricul Exper Stat Circ 347:1–32
Howell CR, Beier RC, Stipanovic RD (1988) Production of ammonia by Enterobacter cloacae and its possible role in the biological control of Pythium pre-emergence damping-off by the bacterium. Phytopathology 78:1075–1078
Hugh-Jones M, Blackburn J (2009) The ecology of Bacillus anthracis. Mol Aspects Med 30(6):356–367
Ipek M, Pirlak L, Esitken A, FigenDönmez M, Turan M, Sahin F (2014) Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) increase yield, growth and nutrition of strawberry under high-calcareous soil conditions. J Plant Nutr 37(7):990–1001
Jiang C, Sheng X, Qian M, Wang Q (2008) Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant Burkholderia sp. from heavy metal-contaminated paddy field soil and its potential in promoting plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in metal-polluted soil. Chemosphere 72(2):157–164
Keim P, Kalif A, Schupp J, Hill K, Travis SE, Richmond K, Adair DM, Hugh-Jones M, Kuske C, Jackson P (1997) Molecular evolution and diversity in Bacillus anthracis as detected by amplified fragment length polymorphism markers. J Bacteriol 179(3):818–824
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2007) Role of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27:29–43
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16(2):111–120
Krieg NR, Holt JG (1984) Bergy’s manual of determinative bacteriology, vol 1. Baltimore, The Williams and Wilkins Co
Kumar KV, Singh N, Behl HM, Srivastava S (2008) Influence of plant growth promoting bacteria and its mutant on heavy metal toxicity in Brassica juncea grown in fly ash amended soil. Chemosphere 72:678–683
Kumar KV, Srivastava S, Singh N, Behl HM (2009) Role of metal resistant plant growth promoting bacteria in ameliorating fly ash to the growth of Brassica juncea. J Hazard Mater 170:51–57
Kumar P, Dubey RC, Maheshwari DK (2012) Bacillus strains isolated from rhizosphere showed plant growth promoting and antagonistic activity against phytopathogens. Microbiol Res 167(8):493–499
Kumar A, Ahirwal J, Maiti SK, Das R (2015) An Assessment of Metal in flyAsh and Their Translocation and Bioaccumulation in Perennial Grasses Growing at the Reclaimed Opencast Mines. Int J Environ Res 9:1089–1096
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kumari B, Singh S (2011) Phytoremediation of metals from fly ash through bacterial augmentation. Ecotoxicology 20:166–176
Loper JE, Scroth MN (1986) Influence of bacterial sources on indole-3 acetic acid on root elongation of sugarbeet. Phytopathology 76:386–389
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kenelly ED (2001) A fern that hyper accumulates arsenic. Nature 409:579–582
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Improvement of plant growth and nickel uptake by nickel resistant-plant-growth promoting bacteria. HAZMAT-9242
Mishra UC (2004) Environmental impact of coal industry and thermal power plants in India. J Environ Radioact 72:35–40
Misra N, Gupta G, Jha PN (2012) Assessment of mineral phosphate solubilizing properties and molecular characterization of zinc tolerant bacteria. J Basic Microbiol 52:549–558
Murphy J, Riley JR (1962) A modified solution method for determination of phosphate in natural water. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Pal C, Bengtsson-Palme J, Kristiansson E, Larsson DGJ (2015) Co-occurrence of resistance genes to antibiotics, biocides and metals reveals novel insights into their co-selection potential. BMC Genom 16:964
Pandey VC, Singh N (2014) Fast green capping on coal fly ash basins through ecological engineering. Ecol Eng 73:671–675
Pandey VC, Prakash P, Bajpai O, Kumar A, Singh N (2015a) Phytodiversity on fly ash deposits: evaluation of naturally colonized species for sustainable phytorestoration. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:2776
Pandey VC, Bajpai O, Pandey DN, Singh N (2015b) Saccharum spontaneum: an underutilized tall grass for revegetation and restoration programs. Genet Resour Crop Ev. 62:443–450
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorous in soil in the connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikorobiologiya 17:362–370
Rajkumar M, Nagendran R, Lee KJ, Lee WH (2005) Characterization of a novel Cr6 + reducing Pseudomonas sp. with plant growth-promoting potential. Curr Microbiol 50:266–271
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28:142–149
Saile E, Koehler TM (2006) Bacillus anthracis multiplication, persistence, and genetic exchange in the rhizosphere of grass plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(5):3168–3174
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sarwart M, Arshad M, Matens DA, Frankenberger WT (1992) Tryptophan-dependent biosynthesis of auxins in soil. Plant Soil 147:207–215
Silver S, Misra TK (1988) Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol 42:717–743
Sterne M (1939) The use of anthrax vaccines prepared from avirulent (uncapsulated) variants of Bacillus anthracis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Industry 13:307–312
Sterne M (1959) “Anthrax,” in Infectious Diseases of Animals Vol. 1 eds Stableforth A W, Galloway IA, editors. (London: Butterworths;): 16–52
Temminghoff EJM, Houba VJG (2004) Digestion with HNO3-H2O2-HF. In: Temminghoff EJM, Houba VJG (eds) Plant Analysis Procedures, 2nd edn. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 16–19
Turnbull PC (1991) Anthrax vaccines: past, present and future. Vaccine 9(8):533–539
Turnbull PCB (1999) Definitive identification of Bacillus anthracis—a review. J Appl Microbiol 87:237–240
Turnbull PCB, Hutson RA, Ward MJ, Jones MN, Quinn CP et al (1992) Bacillus anthracis but not always anthrax. J Appl Bacteriol 72(1):21–28
Wani PA, Khan MS (2010) Bacillus species enhance growth parameters of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in chromium stressed soils. Food Chem Toxicol 48(11):3262–3267
Wu SC, Cheung KC, Luo YM, Wong MH (2006) Effects of inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on metal uptake by Brassica juncea. Environ Pollut 140(1):124–135
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64:991–997
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge our host institute Techno India University for funding this research work. We are also grateful to DVC-MTPS authority and particularly to Mrs Kalyani Pyne for providing us the fly ash sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, P., Roychowdhury, R. & Roy, M. Phytoremediation potential of rhizobacterial isolates from Kans grass (Saccharum spontaneum) of fly ash ponds. Clean Techn Environ Policy 19, 1373–1385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1336-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1336-y