Abstract
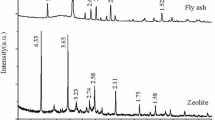
The aim of present study was to verify the applicability of fly ash from the combustion of brown-coal in power plant ENO Nováky (Slovak Republic) for synthesis of zeolitic materials ZM1 and ZM3 by hydrothermal alternation with 1 M NaOH and 3 M NaOH, respectively. For characterization of fly ash and zeolitic material, instrumental methods such as XRF analysis and SEM-EDX analysis were used. Obtained zeolitic materials were applied as sorbents to remove Cd2+ ions as a model of toxic heavy metals from water solutions. It was shown that cadmium removal is a time dependent process significantly influenced by solution pH. Using the Akaike's information criteria, we found that the sorption of cadmium by both types of zeolites obeys Langmuir adsorption isotherm model. The maximum sorption capacities Q max at pH 6.0 calculated from Langmuir isotherm were 696 ± 22 μmol Cd2+ g−1 of ZM1 and 1,160 ± 44 μmol Cd2+ g−1 of ZM3. Box–Behnken design under the response surface methodology was used for investigation of interaction and competitive effects in binary metal system Cd2+–Cs+. Three independent variables (initial concentration of cadmium ions, initial concentration of cesium ions and solution pH) were correlate to response (cadmium removal) using a second-order polynomial model. The adequacy of model was confirmed by analysis of variance, coefficient of determination (R 2), and adjusted R 2. Maximum sorption capacities of ZM3 in binary system Cd2+–Cs+ were 1,025 μmol Cd2+ g−1 and 1,231 μmol Cs+ g−1, indicating higher affinity for Cs+ comparing with Cd2+ ions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczyk Z, Białecka B (2005) Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from polish coal fly ash. Pol J Environ Stud 14:713–719
Ahmaruzzaman M (2010) Review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog Energy Combust Sci 36:327–363
Ahmed NM, Emira HS, Selim MM (2011) Anticorrosive performance of ion-exchange zeolites in alkyd-based paints. Pigment Resin Technol 40:91–99
ASTM C 618-92a (1994) Standard specification for coal fly ash and raw or calcined natural pozzolan for use as a mineral admixture in Portland cement concrete. Annual book of ASTM standards, vol 04.02. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Bačíková M, Števulová N (2009) Examination of fly ash utilization suitability for the production of cement–concrete cover of pavement. Chem Technol 50:24–29
Chojnacki A, Chojnacka K, Hoffman J, Górecki H (2004) The application of natural zeolites for mercury removal: from laboratory tests to industrial scale. Miner Eng 17:933–937
Covarrubias C, Arriagada R, Yanez J, Garcia R, Angelica M, Barros SD, Arroyo P, Sousa-Aguiar EF (2005) Removal of chromium(III) from tannery effluents, using a system of packed columns of zeolite and activated carbon. J Chem Tech Biot 80:899–908
Cundy CS, Cox PA (2005) The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: precursors, intermediates and reaction mechanism. Micropor Mesopor Mater 82:1–78
Ćurković L, Cerjan-Stefanović Š, Filipan T (1997) Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites. Water Res 31:1379–1382
El-Kamash AM, Zaki AA, El Geleel MA (2005) Modeling batch kinetics and thermodynamics of zinc and cadmium ions removal from waste solutions using synthetic zeolite A. J Hazard Mater B127:211–220
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:309–314
Franus W (2012) Characterization of X-type zeolite prepared from coal fly ash. Pol J Environ Stud 21:337–343
Hernández-Montoya V, Pérez-Cruz MA, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Moreno-Virgen MR, Bonilla-Petriciolet A (2013) Competitive adsorption of dyes and heavy metals on zeolitic structures. J Environ Manag 116:213–221
Hui KS, Chao CYH, Kot SC (2005) Removal of mixed heavy metal ions in wastewater by zeolite A4 and residual products from recycled coal fly ash. J Hazard Mater B127:89–101
Izidoro JC, Abbott JE, Fungaro DA, Wang S (2013) Synthesis of zeolites X and A from fly ashes for cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solutions in single and binary ion systems. Fuel 103:827–834
Janoš P, Buchtová H, Rýznarová M (2003) Sorption of dyes from aqueous solutions onto fly ash. Water Res 37:4938–4944
Junak J, Števulová N, Sičáková A (2009) Cement replacement by modified coal fly ash in concrete. Proceedings of the 11th international conference on environmental science and technology. Chania, Greece, September 3–5, B394–B399
Karagozoglu B, Tasdemir M, Demirbas E, Kobya M (2007) The adsorption of basic dye (Astrazon Blue FGRL) from aqueous solutions onto sepiolite, fly ash and apricot shell activated carbon: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 147:297–306
Koukouzas N, Vasilatos C, Itskos G, Mitsis I, Moutsatsou A (2010) Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using CFB-coal fly ash zeolitic materials. J Hazard Mater 173:581–588
Leinonen H, Lehto J (2001) Purification of metal finishing waste waters with zeolites and activated carbons. Waste Manag Res 19:45–47
Marešová J, Pipíška M, Rozložník M, Horník M, Remenárová L, Augustín J (2011) Cobalt and strontium sorption by moss biosorbent: modeling of single and binary metal systems. Desalination 266:134–141
Medina A, Gamero P, Querol X, Moreno N, De León B, Almanza M, Vargas G, Izquiedo M, Font O (2010) Fly ash from a Mexican mineral coal I: mineralogical and chemical characterization. J Hazard Mater 181:82–90
Merrikhpour H, Jalali M (2013) Comparative and competitive adsorption of cadmium, copper, nickel, and lead ions by Iranian natural zeolite. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:303–316
Mezencevová A, Števulová A (2002) Characterization of fluidized fly ashes and possibilities of modifications of their properties by mechanical activation. Chem Listy 96:515–516
Michalíková F (1999) Energetické odpady—zdroj surovín. Acta Montan Slov 4:281–288 (in Slovak)
Miyaji F, Masuda S, Suyama Y (2010) Adsorption removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution with coal fly ash-derived zeolite/sepiolite composite. J Ceram Soc Jpn 118:1062–1066
Musyoka NM, Petrik LF, Gitari WM, Balfour G, Hums E (2012) Optimization of hydrothermal synthesis of pure phase zeolite Na-P1 from South African coal fly ashes. J Environ Sci Health A 47:337–350
Panuccio MR, Sorgonà A, Rizzo M, Cacco G (2009) Cadmium adsorption on vermiculite, zeolite and pumice: batch experimental studies. J Environ Manag 90:364–374
Pehlivan E, Cetin S, Yanik BH (2006) Equilibrium studies for the sorption of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions using sugar beet pulp and fly ash. J Hazard Mater B135:193–199
Pipíška M, Horník M, Remenárová L, Augustín J, Lesný J (2010) Biosorption of cadmium, cobalt and zinc by moss Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus in the single and binary component systems. Acta Chim Slov 57:163–172
Querol X, Umaña JC, Plana F, Alastuey A, López-Soler A, Medinaceli A, Valero A, Domingo MJ, Garcia-Rojo E (2001) Synthesis of Na zeolites from fly ash in a pilot plant scale: examples of potential environmental applications. Fuel 80:857–865
Querol X, Moreno N, Umaña JC, Alastuey A, Hermández E (2002) Synthesis of zeolites from fly ash: an overview. Int J Coal Geol 50:413–423
Rao GPC, Satyaveni S, Ramesh A, Seshaiah K, Murthy KSN, Choudary NV (2006) Sorption of cadmium and zinc from aqueous solutions by zeolite 4A, zeolite 13X and bentonite. J Environ Manag 81:265–272
Remenárová L, Pipíška M, Horník M, Rozložník M, Augustín J, Lesný J (2012) Biosorption of cadmium and zinc by activated sludge from single and binary solutions: mechanism, equilibrium and experimental design study. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43:433–443
Ríos CAR, Williams CD, Roberts CL (2009) A comparative study of two methods for the synthesis of fly ash-based sodium and potassium type zeolites. Fuel 88:1403–1416
Şahan T, Öztürk D (2013) Investigation of Pb(II) adsorption onto pumice samples: application of optimization method based on fractional factorial design and response surface methodology. Clean Technol Environ Policy. doi:10.1007/s10098-013-0673-8
Shah B, Mistry C, Shah A (2013) Seizure modeling of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by chemically modified sugarcane bagasse fly ash: isotherms, kinetics, and column study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2109–2209
Shawabked R, Al-Harahsheh A, Hami M, Khlaifat A (2004) Conversion of oil shale ash into zeolite for cadmium and lead removal from wastewater. Fuel 83:981–985
Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk AP, Namieśnik J (2006) Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:21–28
Srivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Equilibrium modelling of single and binary adsorption of cadmium and nickel onto bagasse fly ash. Chem Eng J 117:79–91
Srivastava VCH, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2009) Competitive adsorption of cadmium(II) and nickel(II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto rice husk ash. Chem Eng Process 48:370–379
Sun D, Zhang X, Wu Y, Liu X (2010) Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution on fly ash. J Hazard Mater 181:335–342
Turabik M (2008) Adsorption of basic dyes from single and binary component systems onto bentonite: simultaneous analysis of Basic Red 46 and Basic Yellow 28 by first order derivative spectrophotometric analysis method. J Hazard Mater 158:52–64
Vedaraman N, Shamshath Begum SS, Srinivasan SV (2013) Response surface methodology for decolourisation of leather dye using ozonation in a packed bed reactor. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:607–616
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to give special thanks to Juraj Miština, M. A. for English language proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Remenárová, L., Pipíška, M., Florková, E. et al. Zeolites from coal fly ash as efficient sorbents for cadmium ions. Clean Techn Environ Policy 16, 1551–1564 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0728-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0728-5