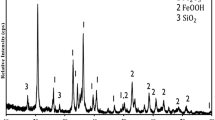
Abstract
In this article, an innovative backfill material is introduced as a green material largely utilizing two major coal mining waste: coal refuse and coal sludge. Coal refuse is rock-like solid waste, comparatively, raw coal sludge is slurry. A smart recipe design of backfill material was introduced, which contains only 1 % of cement and the rest 99 % of raw material is from industry waste. The backfill material at 75 % pulp density shows excellent performance such as high unconfined compressive strength, great flowability, and low bleeding rate. Also, the article discusses the morphology change of the backfill harden body during different curing ages, the observation through SEM–EDS illustrates the distinguished morphological characterization of the needle-like ettringite and amorphous gel. Furthermore, TCLP results indicate that this designed backfill material is environmentally acceptable and none of the heavy metal leaching has over the limitation by US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACI 229R-99 Report (1999) Controlled low strength materials. American Concrete Institute, Farmington Hills, 1999
Aqil U, Tatsuoka F, Uchimura T, Lohani T, Tomita Y, Matsushima K (2005) Strength and deformation characteristics of recycled concrete aggregate as a backfill material. Japanese Geotechnical Society 45(5):53–72
Archibald JF, Chew JL, Lausch P (1999) Use of ground waste glass and Portland cement mixtures for improving slurry and paste backfill support performance. CIM Bull 92:74–80
ASTM D6103-97 (1997) Standard test method for flow consistency of controlled low strength material (CLSM). American Society for Testing and Materials, Conshohocken
ASTM C232-07 (2008) Standard test methods for bleeding of concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, Conshohocken
Aubertin M, Bussiére B, Bernier L (2002) Environnementetgestion des résidusminiers. Presses Internationales Polytechnique, Montréal CD-ROM
Baigorri R, Fuentes M, Gaitano G, García-Mina J, Almendros G, González-Vila F (2009) Complementary multianalytical approach to study the distinctive structural features of the main humic fractions in solution: gray humic acid, brown humic acid, and fulvic Acid. J Agric Food Chem 57(8):3266–3372
Benzaaoua M, Ouellet J, Servant S, Newman P, Verburg R (1999) Cementitious backfill with high sulfur content physical, chemical, and mineralogical characterization. CemConcr Res 29(5):719–725
Benzaazoua M, Belem T, Jolette D (2000) Investigation de la stabilitéchimique etde son impact sur la qualité des remblaisminierscimentés. IRSST Report No. R260, Montreal, pp 1–172
Benzaazoua M, Belem T, Bussiere B (2002) Chemical factors that influence the performance of mine sulphidic paste backfill. CemConcr Res 32(7):1133–1144
Benzaazoua M, Marion P, Picquet I, Bussière B (2004) The use of pastefill as a solidification and stabilization process for the control of acid mine drainage. Miner Eng 17:233–243
Benzaazoua M, Fiset J, Bussiere B, Villeneuve M, Plante B (2006) Sludge recycling within cemented paste backfill: study of the mechanical and leachability properties. Miner Eng 19:420–432
Brackebusch FW (1994) Basics of paste backfill systems. Min Eng 46(10):1175–1178
Brown S, Henry C, Chaney R, Compton H, DeVolder P (2003) Using municipal biosolids in combination with other residuals to restore metal-contaminated mining areas. Plant Soil 249(1):203–215
Chin Y, Aiken G, Loughlin E (1994) Molecular weight, polydispersity, and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Environ SciTechnol 28(11):1853–1858
Coal River Mountain Watch (2011) Coal River Mountain Watch. http://www.sludgesafety.org/what-coal-slurry
CTAB (2010) International energy agency coal industry advisory board—32nd plenary meeting discussion report. OECD Headquarters in Paris
Davidovits J (2005) Geopolymer chemistry and sustainable development, the poly (sialate) terminology: a very useful and simple model for the promotion and understanding of green-chemistry. In: Proceedings of 2005 geopolymer conference, pp 9–15
Dobbs R, Wise R, Dean R (1972) The use of ultra-violet absorbance for monitoring the total organic carbon content of water and wastewater. Water Res 6(10):1173–1180
Fiorentino G, Spaccini R, Piccolo A (2006) Separation of molecular constituents from a humic acid by solid-phase extraction following a transesterification reaction. Talanta 68(4):1135–1142
Freese B, Clemmer S, Nogee A (2008) Coal power in a warming world—a sensible transition to cleaner energy options. Union of Concerned Scientists, UCS Publications, Cambridge
Gauthier P (2004) Valorisation des liants et des rejetsindustrielsdans les remblaisminiers. DESS Thesis, Université du Québec en Abitbi-Témiscamingue Rouyn-Noranda, Canada, 2004
Grice T (1998) Underground mining with backfill, Australian Mining Consultants. In: The 2nd annual summit-mine tailing disposal systems, Brisbane, pp 24–25
Katz A, Kovler K (2004) Utilization of industrial by-products for the production of controlled low strength materials (CLSM). Waste Manage 24(5):501–512
Li C, Sun H, Li L (2010a) Glass phase structure of blast furnace slag. Adv Mater Res 168–170:3–7
Li C, Sun H, Li L (2010b) A review: the comparison between alkali-activated slag (Si + Ca) and metakaolin (Si + Al) cements. CemConcr Res 40(9):1341–1349
Ludwig R, McGregar R, Blowes D, Benner S, Mountjoy K (2002) A permeable reactive barrier for treatment of heavy metals. Ground Water 40(1):59–66
Nassar R, Soroushian R (2012) Strength and durability of recycled aggregate concrete containing milled glass as partial replacement for cement. Constr Build Mater 29:368–377
Nobili D, Bragato M, Alcaniz J, Puigbo A, Comellas L (1990) Characterization of electrophoretic fractions of humic substances with different electrofocusing behavior. Soil Sci 150(5):763–770
Petrolito J, Anderson RM, Pigdon SP (2005) A review of binder materials used in stabilized backfills. CIM Bull 98:1–7
Peyronnard O, Benzaazoua M (2011) Estimation of the cementitious properties of various industrial by-products for applications requiring low mechanical strength. Res Con Rec 56:22–23
Peyronnard O, Benzaazoua M (2012) Alternative by-product based binders for cemented mine backfill: recipes optimization using Taguchi method. Miner Eng. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2011.12.010
Rahier H, Simons W, van Mele B, Biesemans M (1997) Recent literature in geopolymer science and technology. J Mater Sci 32(9):2237–2247
Schwab P, Zhu D, Banks M (2007) Heavy metal leaching from mine tailings as affected by organic amendments. BioresourceTechnol 98(15):2935–2941
Southam DC, Brent GF, Felipe F, Carr C, Hart RD, Wright K (2007) Towards more sustainable minefills—replacement of ordinary Portland cement with geopolymer cements. Publications of the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 9:157–164
Spence RD, Shi CJ (2005) Stabilization and solidification of hazardous radioactive and mixed wastes. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Sun H, Huang Y, Yang B (2002) The contemporary cemented filling technology. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Swift RS (1996) Organic matter characterization (Chap. 35). In: DL Sparks et al. (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America Book Series, vol 5. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 1018–1020
Tatzber M, Stemmer M, Spiegel H, Katzlberger C, Haberhauer G, Mentler A, Gerzabek M (2007) FTIR-spectroscopic characterization of humic acids and humin fractions obtained by advanced NaOH, Na4P2O7, and Na2CO3 extraction procedures. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170(4):522–529
Thurman E, Malcolm R (1981) Preparative isolation of aquatic humic substances. Environ SciTechnol 15(4):463–466
Turkel S (2006) Long-term compressive strength and some other properties of controlled low strength materials made with pozzolanic cement and class C fly ash. J Hazard Mater 137(1):261–266
US EPA (2011) Materials characterization paper in support of the final rulemaking: identification of nonhazardous materials that are solid waste-coal refuse
Van Jaarsveld JGS, Van Deventer JSJ, Lorenzen L (1997) The potential use of geopolymeric materials to immobilise toxic metals: part I. Theory Appl Miner Eng 10:659–669
Yao Y, Sun H (2012a) Characterization of a new silica alumina-based backfill material utilizing large quantities of coal combustion byproducts. Fuel 97:329–336
Yao Y, Sun H (2012b) A novel silica alumina-based backfill material composed of coal refuse and fly ash. J Hazard Mater 213–214:71–82
Acknowledgments
The author gratefully acknowledges the support from Prof. Randal J. Southard at UC-Davis for his XRD technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Sun, H., Jiang, S. et al. Performance and leaching analysis of a novel coal sludge-based backfill material. Clean Techn Environ Policy 15, 657–666 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0550-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0550-x