Abstract
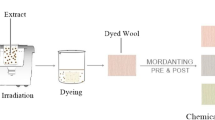
For a trial to improve the natural dyeing cultural heritage to meet the environmental future demands technology to reach high quality dyed patterns. This paper deals with extraction, dyeing of woollen fabric with “Sticta Coronata” under ultrasonic energy and glucose/hydrogen peroxide based redox system. The efficiency of ultrasonic-assisted extraction in presence of 9:1 water:acetone solvent and dyeing in presence of redox system, followed by alum mordanting have been studied in compared when the system was absent and the traditional thermal technique. The influence of redox system, ultrasonic energy and alum mordanting on the rate of dyeing and dye fixation has been demonstrated, and the mechanism of glucose/hydrogen peroxide redox system has been tentatively suggested. The extraction with 9:1 water:acetone solvent possesses higher absorbency in shorter extraction time compared with the aqueous one. Redox system reduced the rate of dyeing at lower temperature with significant enhancement on the dye exhaustion and fixation, involving covalent bonding in addition to the usual coulombic bond. Mordanting process exhibited negligible effect and might decline the percentages of dye exhaustion and fixation in presence of redox system. Ultrasonic energy provided easy efficient route for dye extraction, dyeing, and mordanting processes in compared with the traditional thermal technique.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendak A (1989) Low-temperature dyeing of protein and polyamide fibres using a redox system. Dyes Pigments 11(3):233–242
Czeczaga B, Taylor FJ (1991) Investigations on carotenoids in lichens XXVII carotenoids of some New Zealand lichens. NZ J Bot 29:1–5
David Lewis M, Loan TTVO (2007) Dyeing cotton with reactive dyes under neutral conditions. Colour Technol 123:306–311
Ernst-Russell MA, John Elix A, Christina Chai LL, Megan Rive J, Judith Wardlaw H (2005) The structure and stereochemistry of coronatoquinone, a new pyranonathazarin from the lichen Pseudocyphellaria coronata. Aust J Chem 53:303–306
Galloway J (1980) Pseudocyphellaria. Lichenologist 12:291–303
Haroun AA, Heba Mansour F (2008) New approaches for the reactive dyeing of the retanned carbohydrate crust leather. Dyes Pigments 76(1):213–219
Ibrahim NA, Haggag K (1987) Improved dyeing with redox systems: IV—dyeing of nylon-6 with disperse dyes. Dyes Pigments 8(5):327–334
John Leech Gallery, Fibre art, Historical and Contemporary New Zealand Art. http://www.johnleechgallery.co.nz/heritage/maori_pacific/fibreart.asp
Julia MR, Cot M, Erra P (1998) The use of citosan on hydrogen peroxide pretreated wool. Text Chem Colour 30(8):78–83
Jutao L (1991) Low temperature dyeing of real silk fabrics using a redox system. J Soc Dyers Colour 107(3):117–120
Kamel MM, Hanna HL, El Shishtawy R, Nahed Ahmed SE (2001) Improving nylon dyeability by using redox systems. Adv Polym Technol 20(1):237–247
Kamel M, El shishtawy R, Yousef BM, Mashaly HM (2005) Ultrasonic assisted dyeing III. “Dyeing of wool with lac as a natural dye”. Dyes Pigments 63:103–110
Kamel M, Mansour HF, Mashaly H, Haroun AA (2007) Clean dyeing technology on cotton fabrics with natural basic dyes using ultrasonic technique. Man-Made Textiles in India L:8
Keith Millington R (2006) Improving the photostability of whitened wool by applying an anti-oxidant and metal chelator rinse. Colour Technol 122:49–56
Kubelka P (1948) New contribution to the optics of intensity light-scattering materials, Part I. J Opt Soc Am 38(5):448–451
Lichens-Properties (1966) Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/L/Lichens/Properties/en
Martin W (1969) New Zealand lichens and their habitats. Tuatara 17(1):20–25
Peter Cohen A, Paul Robinson D (2001) 2,5-Diphenyl-3,6-dihydroxy-,4-benzoquinone (polyporic acid). Acta Crystallagr, Sect E 57:0596–0598
Saligram AN, Shukla SR (1993) The effects of proteolytic degumming on silk dyeing. Am Dyest Report 82(8):24
Saligram AN, Singh S, Shrivastava RP, Shukla SR (1993) Low temperature dyeing of silk with direct and basic dyes using redox system. Am Dyest Report 82(5):30–33
Shanker R, Padma Vanker S (2005) Ultrasonic energised dyeing of wool with Mirabilis jalpa flowers. Colourage 52(2):57–61
Trezl L, Horvath V, Lanczki M, Vida C, Rusznak I, Toke L, Bako P (1995) Increase in dye pick-up of wool caused by the Maillard reaction. J Soc Dyers Colour 111(9):293–297
Vajnhandl S, Le Marechal AM (2005) Ultrasound in textile dyeing and the decolouration and mineralisation of textile dyes. Dyes Pigments 65:89–101
Wassilieff M (2007) Lichens. Te Ara—the Encylopedia of New Zealand. URL:http://www.TeAra.govt.nz
Wright D (2003) California and New Zealand: some lichenological comparisons. Bull Calif Lichen Soc 10(1):1–27
Acknowledgments
Great appreciation and a gratefully acknowledge to the stuff of the department of chemical and physical science at Victoria University of Wellington, NZ. For their kindly support during my scientific mission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, H.F. Environment and energy efficient dyeing of woollen fabric with sticta coronata. Clean Techn Environ Policy 12, 571–578 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0267-7