Abstract
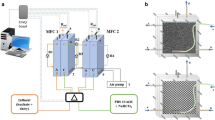
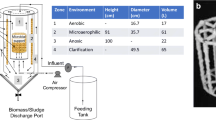
A large dairy farm located on the island of Oahu, Hawaii was the site for an investigation for the potential integration of the existing facultative lagoon system with a cost effective pretreatment unit process. Based on the results from a laboratory study, a pilot plant was installed with two anaerobic bioreactors (10 m³ each) and one aerobic reactor (3.8 m³). Two layers of media “Bio-nest,” providing a void volume of 98%, were placed into each anaerobic bioreactor with 19% space-based on the bioreactor water volume. For better performance and reduction of shock-load, the equalization/settling tank was employed prior to the first anaerobic Bio-nest reactor. The intermediate holding tank settled effluent suspended solids from the Bio-nest reactor and adjusted the loading rate in order to improve the performance of the aerobic EMMC (entrapped mixed microbial cell) bioreactors. Based on the start-up operation of the Bio-nest system at an organic loading rate of about 1.5 g TCOD/l/day, the production rate of biogas from the first and second Bio-nest reactors was 0.64 and 0.15 l/l/day, respectively. This indicates that the anaerobic degradation of organics occurs mainly in the first Bio-nest reactor due to the low loading rate. The removal efficiency from the Bio-nest system shows TCOD removal of about 70%. The EMMC process provided further treatment to achieve a removal efficiency of TCOD at about 50% and a TN of about 35%. The cost for these pretreatments in order to be integrated with the existing lagoon system is US $1.1 per 1,000 gallons (3.8 m³) for dairy wastewater and $91 for each ton of TCOD removal. This integration system provides a sustainable improvement of environment and agricultural production.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
\({\text{OLR}} = {\raise0.7ex\hbox{${[{\text{COD}}]_{{{\text{in}}}} }$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{[{\text{COD}}]_{{{\text{in}}}} } {{\text{HRT}}}}}\right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \!\lower0.7ex\hbox{${{\text{HRT}}}$}}\)
References
APHA (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Cho ES, Zhu J, Yang PY (2007) Intermittently aerated EMMC–biobarrel (entrapped mixed microbial cell with bio-barrel) process for concurrent organic and nitrogen removal. J Environ Manage 84:257–265
Crook J, Surampalli RY (1996) Water reclamation and reuse criteria in the US. Water Sci Technol 33(10–11):451–562
Dong L, (2003) An integrated treatment and reuse system of dairy wastewater-a case study in the state of Hawai'i. MS Thesis, Department of Molecular Biosciences and Bioengineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI
Dong L, and Yang PY (2003) Design and analysis of an anaerobic bioreactor for milk parlor wastewater treatment, presented at the Asian Waterqual, 19–23 October 2003, Bangkok, Thailand
EPA (1983) Design manual: municipal waste stabilization ponds, EPA 625/1-83-015
Hach (1992) Hach DR/3000 spectrophotometer manual. Loveland, Colorado, USA
Kongsil P (2006) Engineering and economic evaluation of innovative bioreactor for milk parlor waste water treatment/reuse, MS Thesis, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI
Koppar A (2005) A psuedo-steady model for anaerobic bio-nest reactor for treatment of milk parlor wastewater, MS Thesis, Department of Molecular Biosciences and Bioengineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI
Mara DD, Alabaster GP, Pearson HW, Mills SW (1992) Waste stabilization ponds: a design manual for Eastern Africa. Lagoon Technology International, Leeds
Maynard HE, Ouki SK, Williams SC (1999) Tertiary lagoons: a review of removal mechanisms and performance. Water Res 33(1):1–13
Pearson HW, Mara DD, Mills SW, Smallman DJ (1987) Factors determining algal populations in waste stabilization ponds and the influence of algae on pond performance. Water Sci Technol 19(12):131–140
Yang PY, Chang CJ, Whalon SA (1991) An anaerobic/aerobic pretreatment of sugarcane mill wastewater for application of drip irrigation. Water Sci Technol 24:243–250
Yang PY, Zhang ZQ, Jeong BG (1997) Simultaneous removal of carbon and nitrogen using and entrapped-mixed-microbial-cell process. Water Res 31(10):2617–2625
Yang PY, Cao K, Kim SJ (2002a) Entrapped mixed microbial cell process for combined secondary and tertiary wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 74:226–234
Yang PY, Shimabukuro M, Kim SJ (2002b) A pilot scale bioreactor using EMMC for carbon and nitrogen removal. Clean Technol Environ Policy 3:407–412
Yang PY, Chen HJ, Kim SJ (2003a) Integrating EMMC process for biological removal of carbon and nitrogen from dilute swine wastewater for agricultural reuse. Bioresour Technol 86:245–252
Yang PY, Su R, Kim SJ (2003b) EMMC process for combined removal of organics, nitrogen and odor producing substance. J Environ Manage 69:381–389
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of Hawaii at Manoa, and the funding provided by a grant from the Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture Research (T-STAR) program, USDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kongsil, P., Irvine, J.L. & Yang, P.Y. Integrating an anaerobic Bio-nest and an aerobic EMMC process as pretreatment of dairy wastewater for reuse: a pilot plant study. Clean Techn Environ Policy 12, 301–311 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0211-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0211-x