Abstract
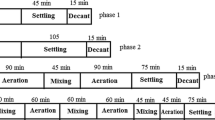
Nutrient removal from synthetic wastewater was carried out by using a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor. Three different operations consisting of different numbers of steps were tested and their performances were compared. These operations were the three-step operation consisting of anaerobic(An)/anoxic(Ax)/oxic(Ox) steps; the four-step (An/Ox/Ax/Ox), and the five-step (An/Ax/Ox/Ax/Ox) operations. Effects of number of operating stages and the total cycle time on COD, nitrogen (NH4-N, NO3-N) and phosphate (PO4-P) removal from synthetic wastewater were investigated. Experiments were carried out with a constant sludge age of 10 days. The highest nutrient removals were realized by using the five-step operation with percent COD, NH4-N, NO3-N and PO4-P removals of 94%, 90%, 64% and 57%, respectively. Removal efficiencies of COD and NH4-N in three- and four-step operations were slightly higher than those of the five-step operation However,NO3-N and PO4-P removal efficiencies obtained by the five-step operation were clearly higher than those for the other operations. Therefore, the five-step operation with 10.5 h overall cycle time was selected as the most appropriate one for effective nutrient removal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA, 1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th edn. APHA, Washington, D.C.
Andreottola G, Bortone G, Tilche A (1997) Experimental validation of a simulation and design model for nitrogen removal in sequencing batch reactors. Water Sci Technol 35:113–120
Baozhen W, Jun L, Lin W, Meisheng N, Ji L (1998) Mechanism of phosphorus removal by SBR submerged biofilm system. Water Res 32:2633–2638
Belia E, Smith PG (1997) The bioaugmentation of sequencing batch reactor sludges for biological phosphorus removal. Water Sci Technol 35:19–26
Carucci A, Majone M, Ramadori R, Rosetti S (1997). Biological phosphorus removal with different organic substrates in an anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactor Water Sci Technol 35:161–187
Chang CH, Hao OJ (1996) Sequencing batch reactor system for nutrient removal: ORP and pH profiles. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 67:27–38
Colunga AM, Martinez SG (1996) Effects of population displacements on biological phosphorus removal in a biofilm SBR. Water Sci Technol 34:303–313
Danesh S, Oleszkiewicz JA (1997) Use of a new anaerobic–aerobic sequencing batch reactor system to enhance biological phosphorus removal. Water Sci Technol 35:137–144
Demoulin G, Goronszy IC, Wutscher K, Forsthuber E (1997) Co-current nitrification/denitrification and biological P-removal in cyclic activated sludge plants by redox controlled cycle operation. Water Sci Technol 35:215–224
Keller J, Subramaniam K, Gösswein J, Greenfield PF (1997) Nutrient removal from industrial wastewater using single tank sequencing batch reactors. Water Sci Technol 35:137–144
Metcalf, Eddy (1991) Wastewater engineering:treatment, disposal, reuse, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Pastorelli G, Canziani R, Pedrazzi L, Rozzi A (1999) Phosphorus and nitrogen removal in moving-bed sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Water Sci Technol 40:169–176
Ramirez CN, Martinez SG (2000) Phosphorus uptake kinetics in a biofilm sequencing batch reactor. Bioprocess Eng 23:143–147
Sang-Ill L, Jong-Ho P, Kwang-Baik K, Ben K (1997) Effect of fermented swine wastes on biological nutrient removal in sequencing batch reactors. Water Res 31:1807–1812
Tasli R, Artan N, Orhon D (1997) The influence of different substrates on enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 35:75–80
Umble AK, Ketchum AL (1997) A strategy for coupling municipal wastewater treatment using the sequencing batch reactor with effluent nutrient recovery through aquaculture. Water Sci Technol 35:177–184
Zuniga MAG, Martinez SG (1996) Biological phosphate and nitrogen removal in a biofilm sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 34:293–301
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the research funds of Uludag University, Bursa and Dokuz Eylul University, Izmir, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kargı, F., Uygur, A. Biological nutrient removal in sequencing batch reactor with different number of steps. Clean Techn Environ Policy 6, 61–65 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-003-0190-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-003-0190-2