Abstract
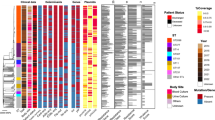
The purpose of the study was to analyze the distribution of the macrolide-resistance genes in 134 erythromycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus blood-culture isolates collected at 15 German university hospitals. The most prevalent resistance gene was ermC (68/134; 50.7%), followed by ermA (52/134; 38.8%), ereB (10/134; 7.5%), and mrsA/msrB (4/134; 6%). The least common genes were ermB (3/134; 2.2%) and ereA (1/134; 0.7%). Overall, resistance to erythromycin was predominantly due to the presence of two erm genes, although with different distributions, depending on the methicillin-resistance pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, FJ., Petridou, J., Fluit, A. et al. Distribution of Macrolide-Resistance Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Blood-Culture Isolates from Fifteen German University Hospitals. EJCMID 19, 385–387 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050500
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050500