Abstract
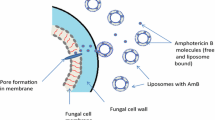
The pharmacokinetics and toxicity of liposomal amikacin in a patient treated for advanced pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis are described. A dose of 20 mg/kg of liposomal amikacin was given on alternate days for 14 days and weekly thereafter for 9 weeks, for a total dose of 20.1 g in 17 divided doses. Accumulation occurred with alternate-day, but not weekly, dosing. The serum levels of amikacin obtained with the liposomal preparation were considerably greater than those obtained with the conventional preparation (range, 81–457 mg/l vs. 4.1–37.7 mg/l). The liposomal amikacin was well tolerated and led to clinical improvement, but it failed to achieve a microbiological response. The patient's sputum remained smear- and culture-positive during the treatment period with liposomal amikacin and for 9 months afterward.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitehead, T., Lovering, A., Cropley, I. et al. Kinetics and Toxicity of Liposomal and Conventional Amikacin in a Patient with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. EJCMID 17, 794–797 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960050189