Abstract
Purpose
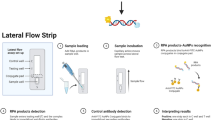
This article aims to establish a rapid visual method for the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS) based on recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and lateral flow strip (LFS).
Methods
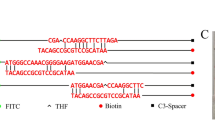
Utilizing speB of GAS as a template, RPA primers were designed, and basic RPA reactions were performed. To reduce the formation of primer dimers, base mismatch was introduced into primers. The probe was designed according to the forward primer, and the RPA-LFS system was established. According to the color results of the reaction system, the optimum reaction temperature and time were determined. Thirteen common clinical standard strains and 14 clinical samples of GAS were used to detect the selectivity of this method. The detection limit of this method was detected by using tenfold gradient dilution of GAS genome as template. One hundred fifty-six clinical samples were collected and compared with qPCR method and culture method. Kappa index and clinical application evaluation of the RPA-LFS were carried out.
Results
The enhanced RPA-LFS method demonstrates the ability to complete the amplification process within 6 min at 33 °C. This method exhibits a high analytic sensitivity, with the lowest detection limit of 0.908 ng, and does not exhibit cross-reaction with other pathogenic bacteria.
Conclusions
The utilization of RPA and LFS allows for efficient and rapid testing of GAS, thereby serving as a valuable method for point-of-care testing.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Wilkening RV, Federle MJ (2017) Evolutionary constraints shaping streptococcus pyogenes-host interactions. Trends Microbiol 25(7):562–572
Dale JB, Walker MJ (2020) Update on group A streptococcal vaccine development. Curr Opin Infect Dis 33(3):244–250
Nakamura A, Sugimoto Y, Ohishi K, Sugawara Y, Fujieda A, Monma F, Suzuki K, Masuya M, Nakase K, Matsushima Y, Wada H, Katayama N, Nobori T (2010) Diagnostic value of PCR analysis of bacteria and fungi from blood in empiric-therapy-resistant febrile neutropenia. J Clin Microbiol 48(6):2030–2036
Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, Gerber MA, Kaplan EL, Lee G, Martin JM, Van Beneden C (2012) Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis an official Public Infect Dis Soc Am 55(10):e86-102
Pritt BS, Patel R, Kirn TJ, Thomson RB Jr (2016) Point-counterpoint: a nucleic acid amplification test for streptococcus pyogenes should replace antigen detection and culture for detection of bacterial pharyngitis. J Clin Microbiol 54(10):2413–2419
Lobato IM, O’Sullivan CK (2018) Recombinase polymerase amplification: basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Anal Chem : TRAC 98:19–35
Li J, Macdonald J, von Stetten F (2018) Review: a comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 144(1):31–67
Liu X, Yan Q, Huang J, Chen J, Guo Z, Liu Z, Cai L, Li R, Wang Y, Yang G, Lan Q (2019) Influence of design probe and sequence mismatches on the efficiency of fluorescent RPA. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(6):95
Li J, Ma B, Fang J, Zhi A, Chen E, Xu Y, Yu X, Sun C, Zhang M (2019) Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) combined with lateral flow immunoassay for rapid detection of salmonella in food. Foods 9(1):27
Zhu B, Wang L, Lu Y, Chen C, Wang K, Zhang L (2023) Recombinase polymerase amplification assay with lateral flow strips for rapid detection of candidiasis due to Candida parapsilosis. Curr Microbiol 80(7):217
Wang F, Ge D, Wang L, Li N, Chen H, Zhang Z, Zhu W, Wang S, Liang W (2021) Rapid and sensitive recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips for detecting Candida albicans. Anal Biochem 633:114428
Wang F, Wang Y, Liu X, Wang L, Wang K, Xu C, Huang G, Gao X (2022) Rapid, simple, and highly specific detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae with visualized recombinase polymerase amplification. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:878881
Wang YL, Zhang X, Wang Q, Liu PX, Tang W, Guo R, Zhang HY, Chen ZG, Han XG, Jiang W (2022) Rapid and visual detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk using a recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow assay combined with immunomagnetic separation. J Appl Microbiol 133(6):3741–3754
Jiang X, Lin A, Li S, Shi Y, Zhou F, Felix Gomez GG, Gregory RL, Zhang C, Chen S, Huang R (2022) Effects of artificial honey and epigallocatechin-3-gallate on streptococcus pyogenes. BMC Microbiol 22(1):207
S. Hamada, S. Kawabata, I. Nakagawa, (2015) Molecular and genomic characterization of pathogenic traits of group A Streptococcus pyogenes, Proceedings of the Japan Academy. Series B, Physical and biological sciences 91(10) 539–59.
Nakagawa I (2013) Streptococcus pyogenes escapes from autophagy. Cell Host Microbe 14(6):604–606
Mustafa Z, Ghaffari M (2020) Diagnostic methods, clinical guidelines, and antibiotic treatment for group A streptococcal pharyngitis: a narrative review. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:563627
Fan X, Li L, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Liu C, Wang Q, Dong Y, Wang S, Chi T, Song F, Sun C, Wang Y, Ha D, Zhao Y, Bao J, Wu X, Wang Z (2020) Clinical validation of two recombinase-based isothermal amplification assays (RPA/RAA) for the rapid detection of african swine fever virus. Front Microbiol 11:1696
Yu CE, Ferretti JJ (1991) Frequency of the erythrogenic toxin B and C genes (speB and speC) among clinical isolates of group A streptococci. Infect Immun 59(1):211–215
Daher RK, Stewart G, Boissinot M, Boudreau DK, Bergeron MG (2015) Influence of sequence mismatches on the specificity of recombinase polymerase amplification technology. Mol Cell Probes 29(2):116–121
Zhao M, Wang X, Wang K, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou P, Wang L, Zhu W (2022) Recombinant polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips for the detection of deep-seated Candida krusei infections. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:958858
Funding
The project was supported by the Science Foundation of Kangda College of Nanjing Medical University (grant number KD2023KYJJ061), the Health and Wellness Surface Science and Technology Project of Lianyungang City (grant number 202217), the Science and Technology Bureau Key R&D Program (Social Development) Project of Lianyungang City (grant number SF2224), the “521 Project” scientific research funding project of Lianyungang City (grant number LYG06521202157), and the 2023 Jiangsu Province Preventive Medicine Research Project (grant number Yl2023028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation: Yuzhi Gao; funding acquisition: XuZhu Gao and Tuo Ji; methodology: XuZhu Gao and YuDie Cao; project administration: XuZhu Gao; resources: Juan Hu; writing—original draft: XuZhu Gao; writing—review and editing: Tuo Ji.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second People’s Hospital of Lianyungang (protocol code 2023K021). We confirm that all experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Second People’s Hospital of Lianyungang. We confirm that all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all the individuals included in this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Detection of Streptococcus pyogenes using a combination of recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow strips.
2. The combined specific probe and primer exhibited high selectivity and analytic sensitivity for the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes.
3. Simple processing for the rapid (6 min) diagnosis of Streptococcus pyogenes infection.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, XZ., Cao, YD., Gao, YZ. et al. Efficient detection of Streptococcus pyogenes based on recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow strip. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 43, 735–745 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-024-04780-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-024-04780-4