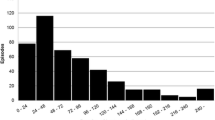
Abstract
Infective endocarditis (IE) has been increasingly recognized as an important complication of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB), leading to a low threshold for echocardiography and extended treatment with anti-staphylococcal agents. However, outside of IE, many indications for prolonged anti-staphylococcal therapy courses are present. We sought to determine the frequency in which findings from a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) changed clinical SAB management in a large Canadian health region. Residents (> 18 years) with SAB from 2012 to 2014 who underwent transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and TEE were assessed. Patients potentially benefiting from an extended course of anti-staphylococcal agents were defined a priori. Patient demographics, treatment (including surgical), and clinical outcomes were extracted and evaluated. Of the 705 episodes of SAB that underwent a screening echocardiogram, 203 episodes underwent both a TTE and TEE, of which 92.1% (187/203) contained an a priori indication for extended anti-staphylococcal therapy. Regardless of TEE results, actual duration of therapy did not differ in SAB episodes that had ≥ 1 extended anti-staphylococcal therapy criteria (36.7 days, IQR 23.4–48.6 vs. 43.8 days, IQR 33.3–49.5, p = 0.17). Additionally, there were no cases in which TEE was utilized as the sole reason to shorten duration of therapy or proceed to surgery for those with SAB. Routine performance of TEE may be unnecessary in all SAB as many patients have pre-existing indications for extended anti-staphylococcal therapy independent of TEE findings. An algorithm to selectively identify cases of SAB that would benefit from TEE can reduce resource and equipment expenditure and patient risks associated with TEE.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG (2015) Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 28(3):603–661
Lam JC, Gregson DB, Robinson S, Somayaji R, Conly JM, Parkins MD (2019) Epidemiology and outcome determinants of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia revisited: a population-based study. Infection 47(6):961–971
Laupland KB, Lyytikäinen O, Søgaard M, Kennedy KJ, Knudsen JD, Ostergaard C, Galbraith JC, Valiquette L, Jacobsson G, Collignon P, Schønheyder HC, Collaborative IBS (2013) The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection: a multinational population-based surveillance study. Clin Microbiol Infect 19(5):465–471
Incani A, Hair C, Purnell P, O'Brien DP, Cheng AC, Appelbe A, Athan E (2013) Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: evaluation of the role of transoesophageal echocardiography in identifying clinically unsuspected endocarditis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(8):1003–1008
Remadi JP, Habib G, Nadji G, Brahim A, Thuny F, Casalta JP, Peltier M, Tribouilloy C (2007) Predictors of death and impact of surgery in Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis. Ann Thorac Surg 83(4):1295–1302
Røder BL, Wandall DA, Frimodt-Møller N, Espersen F, Skinhøj P, Rosdahl VT (1999) Clinical features of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a 10-year experience in Denmark. Arch Intern Med 159(5):462–469
Asgeirsson H, Thalme A, Weiland O (2018) Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia and endocarditis - epidemiology and outcome: a review. Infect Dis (Lond) 50(3):175–192
Bayer AS, Lam K, Ginzton L, Norman DC, Chiu CY, Ward JI (1987) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clinical, serologic, and echocardiographic findings in patients with and without endocarditis. Arch Intern Med 147(3):457–462
Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK (1994) New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med 96(3):200–209
Rasmussen RV, Høst U, Arpi M, Hassager C, Johansen HK, Korup E, Schønheyder HC, Berning J, Gill S, Rosenvinge FS, Fowler VG, Møller JE, Skov RL, Larsen CT, Hansen TF, Mard S, Smit J, Andersen PS, Bruun NE (2011) Prevalence of infective endocarditis in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: the value of screening with echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(6):414–420
Habib G, Badano L, Tribouilloy C, Vilacosta I, Zamorano JL, Galderisi M, Voigt JU, Sicari R, Cosyns B, Fox K, Aakhus S, Echocardiography EAo (2010) Recommendations for the practice of echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Eur J Echocardiogr 11(2):202–219
Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, Rybak MJ, Talan DA, Chambers HF, America IDSo (2011) Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 52(3):e18–e55
Sullenberger AL, Avedissian LS, Kent SM (2005) Importance of transesophageal echocardiography in the evaluation of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Heart Valve Dis 14(1):23–28
Reynolds HR, Jagen MA, Tunick PA, Kronzon I (2003) Sensitivity of transthoracic versus transesophageal echocardiography for the detection of native valve vegetations in the modern era. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16(1):67–70
Holland TL, Arnold C, Fowler VG (2014) Clinical management of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a review. JAMA 312(13):1330–1341
Sekar P, Johnson JR, Thurn JR, Drekonja DM, Morrison VA, Chandrashekhar Y, Adabag S, Kuskowski MA, Filice GA (2017) Comparative sensitivity of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography in diagnosis of infective endocarditis among veterans with. Open Forum Infect Dis 4(2):ofx035
Fowler VG, Miro JM, Hoen B, Cabell CH, Abrutyn E, Rubinstein E, Corey GR, Spelman D, Bradley SF, Barsic B, Pappas PA, Anstrom KJ, Wray D, Fortes CQ, Anguera I, Athan E, Jones P, van der Meer JT, Elliott TS, Levine DP, Bayer AS, Investigators I (2005) Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a consequence of medical progress. JAMA 293(24):3012–3021
Holden E, Bashir A, Das I, Morton H, Steadman CD, Nightingale P, Steeds RP, David MD (2014) Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in a UK tertiary referral Centre: a ‘transoesophageal echocardiogram for all’ policy. J Antimicrob Chemother 69(7):1960–1965
Kaasch AJ, Fowler VG, Rieg S, Peyerl-Hoffmann G, Birkholz H, Hellmich M, Kern WV, Seifert H (2011) Use of a simple criteria set for guiding echocardiography in nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 53(1):1–9
Van Hal SJ, Mathur G, Kelly J, Aronis C, Cranney GB, Jones PD (2005) The role of transthoracic echocardiography in excluding left sided infective endocarditis in Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J Inf Secur 51(3):218–221
Joseph JP, Meddows TR, Webster DP, Newton JD, Myerson SG, Prendergast B, Scarborough M, Herring N (2013) Prioritizing echocardiography in Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J Antimicrob Chemother 68(2):444–449
Khatib R, Sharma M (2013) Echocardiography is dispensable in uncomplicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Medicine (Baltimore) 92(3):182–188
Freitas-Ferraz AB, Bernier M, Vaillancourt R, Ugalde PA, Nicodème F, Paradis JM, Champagne J, O'Hara G, Junquera L, Del Val D, Muntané-Carol G, O'Connor K, Beaudoin J, Rodés-Cabau J (2020) Safety of transesophageal echocardiography to guide structural cardiac interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol 75(25):3164–3173
Hilberath JN, Oakes DA, Shernan SK, Bulwer BE, D'Ambra MN, Eltzschig HK (2010) Safety of transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 23(11):1115–1127 quiz 1220-1111
Petti CA, Fowler VG (2003) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis. Cardiol Clin 21(2):219–233 vii
Chong YP, Moon SM, Bang KM, Park HJ, Park SY, Kim MN, Park KH, Kim SH, Lee SO, Choi SH, Jeong JY, Woo JH, Kim YS (2013) Treatment duration for uncomplicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia to prevent relapse: analysis of a prospective observational cohort study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(3):1150–1156
Alberta Health Services Annual Report 2015-2016. Alberta Health Services. Accessed 31 Dec 2017
Fowler VG, Olsen MK, Corey GR, Woods CW, Cabell CH, Reller LB, Cheng AC, Dudley T, Oddone EZ (2003) Clinical identifiers of complicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med 163(17):2066–2072
Wilson R, Hambuger M (1957) Fifteen years’ experience with staphylococcus septicemia in a large city hospital; analysis of fifty-five cases in the Cincinnati General Hospital 1940 to 1954. Am J Med 22(3):437–457
Heriot GS, Tong SYC, Cheng AC, Liew D (2018) Benefit of echocardiography in patients with. Open forum Infect Dis 5(12):ofy303
Buitron de la Vega P, Tandon P, Qureshi W, Nasr Y, Jayaprakash R, Arshad S, Moreno D, Jacobsen G, Ananthasubramaniam K, Ramesh M, Zervos M (2016) Simplified risk stratification criteria for identification of patients with MRSA bacteremia at low risk of infective endocarditis: implications for avoiding routine transesophageal echocardiography in MRSA bacteremia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35(2):261–268
Evangelista A, Gonzalez-Alujas MT (2004) Echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Heart 90(6):614–617
Bai AD, Agarwal A, Steinberg M, Showler A, Burry L, Tomlinson GA, Bell CM, Morris AM (2017) Clinical predictors and clinical prediction rules to estimate initial patient risk for infective endocarditis in Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 23(12):900–906
Humpl T, McCrindle BW, Smallhorn JF (2003) The relative roles of transthoracic compared with transesophageal echocardiography in children with suspected infective endocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol 41(11):2068–2071
Sochowski RA, Chan KL (1993) Implication of negative results on a monoplane transesophageal echocardiographic study in patients with suspected infective endocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol 21(1):216–221
Robles P (2003) Judicious use of transthoracic echocardiography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Heart 89(11):1283–1284
Siadecki SD, Frasure SE, Lewiss RE, Saul T (2016) High body mass index is strongly correlated with decreased image quality in focused bedside echocardiography. J Emerg Med 50(2):295–301
Danner RL, Hartman BJ (1987) Update on spinal epidural abscess: 35 cases and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis 9(2):265–274
Côté G, Denault A (2008) Transesophageal echocardiography-related complications. Can J Anaesth 55(9):622–647
Code availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SR, DBG, MDP; investigation: JCL, DBG, SR, MDP; formal analysis: JCL, MDP; data curation: JCL, DBG, SR, MDP; writing—original draft: JCL; writing—review and editing: JCL, DBG, SR, RS, LW, JMC, MDP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board at the University of Calgary (REB14_1456).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lam, J.C., Gregson, D.B., Somayaji, R. et al. Forgoing transesophageal echocardiogram in selected patients with complicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 40, 623–631 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-04097-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-04097-y