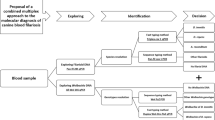
Abstract
Laboratory diagnosis of Strongyloides infections can be grouped into direct and indirect detection methods, and a combination of the two methods is often needed to reach an accurate and timely diagnosis. This review focuses on non-conventional direct detection via molecular and antigen detection assays. Conventional PCR is the most commonly used molecular diagnostic for Strongyloides. Real-time PCR is accurate and highly sensitive for quantitative and qualitative analysis. Meanwhile, PCR-RFLP can efficiently distinguish human and dog isolates of S. stercoralis, S. fuelleborni (from monkey), and S. ratti (from rodent). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) amplifies DNA isothermally with high specificity, efficiency, and rapidity, and has potential for point-of-care (POC) translation. As for antigen detection assay, coproantigen detection ELISAs for strongyloidiasis traditionally relied on raising rabbit polyclonal antibodies against the parasite antigens for use as capture or detection reagents. Subsequently, hybridoma technology using animals has enabled the discovery of monoclonal antibodies specific to Strongyloides antigens and was utilised to develop antigen detection assays. In recent times, phage display technology has facilitated the discovery of scFv antibody against Strongyloides protein that can accelerate the development of such assays. Improvements in both direct detection methods are being made. Strongyloides molecular diagnostics is moving from the detection of a single infection to the simultaneous detection of soil-transmitted helminths. Meanwhile, antigen detection assays can also be multiplexed and aptamers can be used as antigen binders. In the near future, these two direct detection methods may be more widely used as diagnostic tools for strongyloidiasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisoffi Z, Buonfrate D, Montresor A, Requena-Méndez A, Munoz J, Krolewiecki AJ et al (2013) Strongyloides stercoralis: a plea for action. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7(5):e2214
Taylor MJ, Garrard TA, O’Donahoo FJ, Ross KE (2014) Human strongyloidiasis: identifying knowledge gaps, with emphasis on environmental control. Res Rep Trop Med 3:55–63
Krolewiecki A, Nutman TB (2019) Strongyloidiasis: a neglected tropical disease. Infect Dis Clin 33(1):135–151
Keiser PB, Nutman TB (2004) Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev 17(1):208–217
Hartono C, Muthukumar T, Suthanthiran M (2013) Immunosuppressive drug therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3(9):a015487
Genta RM (1992) Dysregulation of strongyloidiasis: a new hypothesis. Clin Microbiol Rev 5(4):345–355
Ghosh K, Ghosh K (2007) Strongyloides stercoralis septicaemia following steroid therapy for eosinophilia: report of three cases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 101(11):1163–1165
Blaizot R, Simon S, Brottier J, Blanchet D, Brousse P, Boukhari R et al (2019) Utility of PCR in patients with Strongyloides stercoralis and HTLV-1 Coinfection in French Guiana. Am J Trop Med Hyg 101:848–850
Speare R, Durrheim D (2004) Strongyloides serology–useful for diagnosis and management of strongyloidiasis in rural indigenous populations, but important gaps in knowledge remain. Rural Remote Health 4(4):264
Rodrigues RM, de Oliveira MC, Sopelete MC, Silva DA, Campos DM, Taketomi EA et al (2007) IgG1, IgG4, and IgE antibody responses in human strongyloidiasis by ELISA using Strongyloides ratti saline extract as heterologous antigen. Parasitol Res 101(5):1209–1214
Biggs B-A, Caruana S, Mihrshahi S, Jolley D, Leydon J, Chea L et al (2009) Management of chronic strongyloidiasis in immigrants and refugees: is serologic testing useful? Am J Trop Med Hyg 80(5):788–791
Llewellyn S, Inpankaew T, Nery SV, Gray DJ, Verweij JJ, Clements AC et al (2016) Application of a multiplex quantitative PCR to assess prevalence and intensity of intestinal parasite infections in a controlled clinical trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(1):e0004380
Incani RN, Ferrer E, Hoek D, Ramak R, Roelfsema J, Mughini-Gras L et al (2017) Diagnosis of intestinal parasites in a rural community of Venezuela: advantages and disadvantages of using microscopy or RT-PCR. Acta Trop 167:64–70
Watts MR, Robertson G, Bradbury RS (2016) The laboratory diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis. Microbiol Aust 37(1):4–9
Becker SL, Piraisoody N, Kramme S, Marti H, Silué KD, Panning M et al (2015) Real-time PCR for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in human stool samples from Côte d’Ivoire: diagnostic accuracy, inter-laboratory comparison and patterns of hookworm co-infection. Acta Trop 150:210–217
Kristanti H, Meyanti F, Wijayanti MA, Mahendradhata Y, Polman K, Chappuis F et al (2018) Diagnostic comparison of Baermann funnel, Koga agar plate culture and polymerase chain reaction for detection of human Strongyloides stercoralis infection in Maluku, Indonesia. Parasitol Res 117(10):3229–3235
Watts MR, James G, Sultana Y, Ginn AN, Outhred AC, Kong F et al (2014) A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for Strongyloides stercoralis in stool that uses a visual detection method with SYTO-82 fluorescent dye. Am J Trop Med Hyg 90(2):306–311
Zarlenga DS, Higgins J (2001) PCR as a diagnostic and quantitative technique in veterinary parasitology. Vet Parasitol 101(3–4):215–230
Gasser RB (2006) Molecular tools—advances, opportunities and prospects. Vet Parasitol 136(2):69–89
Barda B, Wampfler R, Sayasone S, Phongluxa K, Xayavong S, Keoduangsy K et al (2018) Evaluation of two DNA extraction methods for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. J Clin Microbiol 56(4):e01941–e01917
Fakhrieh-Kashan Z, Zahabiun F, Sharifdini M, Fotouhi-Ardakani R, Kia E (2019) Critical diagnosis of complicated strongyloidosis with nested-PCR and high resolution melting analysis (HRM). Ann Parasitol 65(4):333–9-–9
Sanprasert V, Kerdkaew R, Srirungruang S, Charuchaibovorn S, Phadungsaksawasdi K, Nuchprayoon S (2019) Development of conventional multiplex PCR: a rapid technique for simultaneous detection of soil-transmitted helminths. Pathogens 8(3):152
Nagayasu E, Htwe MPPTH, Hortiwakul T, Hino A, Tanaka T, Higashiarakawa M et al (2017) A possible origin population of pathogenic intestinal nematodes, Strongyloides stercoralis, unveiled by molecular phylogeny. Sci Rep 7(1):4844
Ramachandran S, Gam AA, Neva FA (1997) Molecular differences between several species of Strongyloides and comparison of selected isolates of S. stercoralis using a polymerase chain reaction-linked restriction fragment length polymorphism approach. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56(1):61–65
Hu P, Hegde M, Lennon PA (2012) Modern clinical molecular techniques. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Tong SY, Giffard PM (2012) Microbiological applications of high-resolution melting analysis. J Clin Microbiol 50(11):3418–3421
Erali M, Voelkerding KV, Wittwer CT (2008) High resolution melting applications for clinical laboratory medicine. Exp Mol Pathol 85(1):50–58
Mori Y, Kanda H, Notomi T (2013) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): recent progress in research and development. J Infect Chemother 19(3):404–411
Nakamura N, Ito K, Takahashi M, Hashimoto K, Kawamoto M, Yamanaka M et al (2007) Detection of six single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with rheumatoid arthritis by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method and an electrochemical DNA chip. Anal Chem 79(24):9484–9493
Fernández-Soto P, Sánchez-Hernández A, Gandasegui J, Santos CB, López-Abán J, Saugar JM et al (2016) Strong-LAMP: a LAMP assay for Strongyloides spp. detection in stool and urine samples. Towards the diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis starting from a rodent model. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(7):e0004836
Watts MR, Kim R, Ahuja V, Robertson GJ, Sultana Y, Wehrhahn M et al (2019) Comparison of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays for the detection of Strongyloides in different specimen matrices. J Clin Microbiol 57(4):e01173–01118
Buonfrate D, Requena-Mendez A, Angheben A, Cinquini M, Cruciani M, Fittipaldo A et al (2018) Accuracy of molecular biology techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection—a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 12(2):e0006229
Paula FMD, Malta FDM, Marques PD, Sitta RB, Pinho JRR, Gryschek RCB et al (2015) Molecular diagnosis of strongyloidiasis in tropical areas: a comparison of conventional and real-time polymerase chain reaction with parasitological methods. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 110(2):272–274
Sharifdini M, Mirhendi H, Ashrafi K, Hosseini M, Mohebali M, Khodadadi H et al (2015) Comparison of nested polymerase chain reaction and real-time polymerase chain reaction with parasitological methods for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in human fecal samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg 93(6):1285–1291
Amor A, Rodriguez E, Saugar JM, Arroyo A, López-Quintana B, Abera B et al (2016) High prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis in school-aged children in a rural highland of North-Western Ethiopia: the role of intensive diagnostic work-up. Parasit Vectors 9(1):617
Buonfrate D, Perandin F, Formenti F, Bisoffi Z (2017) A retrospective study comparing agar plate culture, indirect immunofluorescence and real-time PCR for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Parasitology 144(6):812–816
Meurs L, Polderman AM, Melchers NVV, Brienen EA, Verweij JJ, Groosjohan B et al (2017) Diagnosing polyparasitism in a high-prevalence setting in Beira, Mozambique: detection of intestinal parasites in fecal samples by microscopy and real-time PCR. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11(1):e0005310
Lodh N, Caro R, Sofer S, Scott A, Krolewiecki A, Shiff C (2016) Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis: detection of parasite-derived DNA in urine. Acta Trop 163:9–13
Mas-Coma S, Bargues M (2009) Populations, hybrids and the systematic concepts of species and subspecies in Chagas disease triatomine vectors inferred from nuclear ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA. Acta Trop 110(2–3):112–136
Labes E, Wijayanti N, Deplazes P, Mathis A (2011) Genetic characterization of Strongyloides spp. from captive, semi-captive and wild Bornean orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus) in Central and East Kalimantan, Borneo, Indonesia. Parasitology 138(11):1417–1422
Laymanivong S, Hangvanthong B, Insisiengmay B, Vanisaveth V, Laxachack P, Jongthawin J et al (2016) First molecular identification and report of genetic diversity of Strongyloides stercoralis, a current major soil-transmitted helminth in humans from Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Parasitol Res 115(8):2973–2980
Terashima A, Canales M, Tello R, Mas-Coma S, Esteban G, Bargues M et al (2000) Strongyloides fuelleborni: reporte del primer caso clínico en el Perú. Diagnóstico 39:199–203
Van De N, Minh PN, Mas-Coma S (2019) Strongyloidiasis in northern Vietnam: epidemiology, clinical characteristics and molecular diagnosis of the causal agent. Parasit Vectors 12(1):515
Verweij JJ, Canales M, Polman K, Ziem J, Brienen EA, Polderman AM et al (2009) Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in faecal samples using real-time PCR. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 103(4):342–346
Formenti F, La Marca G, Perandin F, Pajola B, Romano M, Santucci B et al (2019) A diagnostic study comparing conventional and real-time PCR for Strongyloides stercoralis on urine and on faecal samples. Acta Trop 190:284–287
Basso W, Grandt L-M, Magnenat A-L, Gottstein B, Campos M (2019) Strongyloides stercoralis infection in imported and local dogs in Switzerland: from clinics to molecular genetics. Parasitol Res 118(1):255–266
Gorgani-Firouzjaee T, Kalantari N, Javanian M, Ghaffari S (2018) Strongyloides stercoralis: detection of parasite-derived DNA in serum samples obtained from immunosuppressed patients. Parasitol Res 117(9):2927–2932
Weerakoon KG, McManus DP (2016) Cell-free DNA as a diagnostic tool for human parasitic infections. Trends Parasitol 32(5):378–391
Bosqui LR, Marques PD, de Melo GB, Maria do Rosário F, Malta FM, Pavanelli WR et al (2018) Molecular and immnune diagnosis: further testing for human strongyloidiasis. Mol Diagn Ther 22(4):485–491
Al-Mekhlafi HM, Nasr NA, Lim YA, Elyana FN, Sady H, Atroosh WM et al (2019) Prevalence and risk factors of Strongyloides stercoralis infection among Orang Asli schoolchildren: new insights into the epidemiology, transmission and diagnosis of strongyloidiasis in Malaysia. Parasitology 146(12):1602–1614
Ahmad AF, Hadip F, Ngui R, Lim YA, Mahmud R (2013) Serological and molecular detection of Strongyloides stercoralis infection among an Orang Asli community in Malaysia. Parasitol Res 112(8):2811–2816
Sahimin N, Lim YA, Noordin R, Yunus MH, Arifin N, Behnke JM et al (2019) Epidemiology and immunodiagnostics of Strongyloides stercoralis infections among migrant workers in Malaysia. Asian Pac J Trop Med 12(6):250
Knopp S, Salim N, Schindler T, Karagiannis Voules DA, Rothen J, Lweno O et al (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of Kato-Katz, FLOTAC, Baermann, and PCR methods for the detection of light-intensity hookworm and Strongyloides stercoralis infections in Tanzania. Am J Trop Med Hyg 90(3):535–545
Taniuchi M, Verweij JJ, Noor Z, Sobuz SU, van Lieshout L, Petri WA Jr et al (2011) High throughput multiplex PCR and probe-based detection with Luminex beads for seven intestinal parasites. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84(2):332–337
Basuni M, Muhi J, Othman N, Verweij JJ, Ahmad M, Miswan N et al (2011) A pentaplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of four species of soil-transmitted helminths. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84(2):338–343
Mejia R, Vicuña Y, Broncano N, Sandoval C, Vaca M, Chico M et al (2013) A novel, multi-parallel, real-time polymerase chain reaction approach for eight gastrointestinal parasites provides improved diagnostic capabilities to resource-limited at-risk populations. Am J Trop Med Hyg 88(6):1041–1047
Zueter AM, Mohamed Z, Abdullah AD, Mohamad N, Arifin N, Othman N et al (2014) Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis infection among cancer patients in a major hospital in Kelantan, Malaysia. Singap Med J 55(7):367
Sultana Y, Jeoffreys N, Watts MR, Gilbert GL, Lee R (2013) Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in stool. Am J Trop Med Hyg 88(6):1048–1051
Campo-Polanco LF, Sarmiento JMH, Mesa MA, Franco CJV, López L, Botero LE et al (2018) Strongyloidiasis in humans: diagnostic efficacy of four conventional methods and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 51(4):493–502
Cunningham LJ, Stothard JR, Osei-Atweneboana M, Armoo S, Verweij JJ, Adams ER (2018) Developing a real-time PCR assay based on multiplex high-resolution melt-curve analysis: a pilot study in detection and discrimination of soil-transmitted helminth and schistosome species. Parasitology 145(13):1733–1738
Krolewiecki AJ, Koukounari A, Romano M, Caro NN, Scott AL, Fleitas P et al (2018) Transrenal DNA-based diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis (Grassi, 1879) infection: Bayesian latent class modeling of test accuracy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 12(6):e0006550
Javanian M, Gorgani-Firouzjaee T, Kalantrai N (2019) Comparison of ELISA and PCR of the 18S rRNA gene for detection of human strongyloidiasis using serum sample. Infect Dis Ther 51(5):360–367
Repetto SA, Alba Soto CD, Cazorla SI, Tayeldin ML, Cuello S, Lasala MB et al (2013) An improved DNA isolation technique for PCR detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in stool samples. Acta Trop 126(2):110–114
Bretagne S, Costa JM (2006) Towards a nucleic acid-based diagnosis in clinical parasitology and mycology. Clin Chim Acta 363(1–2):221–228
Levenhagen MA, Costa-Cruz JM (2014) Update on immunologic and molecular diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis. Acta Trop 135:33–43
Papaiakovou M, Wright J, Pilotte N, Chooneea D, Schär F, Truscott JE et al (2019) Pooling as a strategy for the timely diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminths in stool: value and reproducibility. Parasit Vectors 12:443
Gyorkos TW, Genta RM, Viens P, Maclean JD (1990) Seroepidemiology of Strongyloides infection in the Southeast Asian refugee population in Canada. Am J Epidemiol 132(2):257–264
Sykes AM, McCarthy JS (2011) A coproantigen diagnostic test for Strongyloides infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5(2):e955
El-Badry AA (2009) ELISA-based coproantigen in human strongyloidiaisis: a diagnostic method correlating with worm burden. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 39(3):757–768
Gonçalves ALR, Silva CV, Ueta MT, Costa-Cruz JM (2010) A new faecal antigen detection system for Strongyloides venezuelensis diagnosis in immunosuppressed rats. Exp Parasitol 125(4):338–341
Nageswaran C, Craig P, Devaney E (1994) Coproantigen detection in rats experimentally infected with Strongyloides ratti. Parasitology 108(3):335–342
Gonçalves A, Nunes D, Gonçalves-Pires M, Ueta M, Costa-Cruz J (2012) Use of larval, parasitic female and egg antigens from Strongyloides venezuelensis to detect parasite-specific IgG and immune complexes in immunodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis. Parasitology 139(7):956–961
Mahmuda A, Bande F, Abdulhaleem N, Majid RA, Hamat RA, Abdullah WO et al (2018) Investigations for the possible use of a monoclonal antibody produced against Strongyloides ratti antigen as an immunodiagnostic reagent for active Strongyloidiasis. Iran J Parasitol 13(2):204
Abduhaleem N, Mamuda A, Mustapha T, Abd Majid R, Lung LTT, Unyah NZ (2019) Evaluation of monoclonal antibody (IgG2bMAb) for detection of coproantigen from experimentally infected rats with Strongyloides ratti. Annu Res Rev Biol 32(2):1–9
Taweethavonsawat P, Chaicumpa W, Chaisri U, Chuenbal U, Sakolvaree Y, Tapchaisri P et al (2002) Specific monoclonal antibodies to Strongyloides stercoralis: a potential diagnostic reagent for strongyloidiasis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 20(4):247
Pasqualini R, Arap W (2004) Hybridoma-free generation of monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(1):257–259
Siegel D (2002) Recombinant monoclonal antibody technology. Transfus Clin Biol 9(1):15–22
Hoogenboom HR (2005) Selecting and screening recombinant antibody libraries. Nat Biotechnol 23(9):1105
Sepulveda J, Tremblay JM, DeGnore JP, Skelly PJ, Shoemaker CB (2010) Schistosoma mansoni host-exposed surface antigens characterized by sera and recombinant antibodies from schistosomiasis-resistant rats. Int J Parasitol 40(12):1407–1417
da Silva RV, Araújo TG, Gonzaga HT, Nascimento R, Goulart LR, Costa-Cruz JM (2013) Development of specific scFv antibodies to detect neurocysticercosis antigens and potential applications in immunodiagnosis. Immunol Lett 156(1–2):59–67
Rahumatullah A, Lim TS, Yunus MH, Noordin R (2019) Development of an antigen detection ELISA for bancroftian filariasis using BmSXP-specific recombinant monoclonal antibody. Am J Trop Med Hyg 101(2):436–440
Levenhagen MA, Santos FAA, Fujimura PT, Carneiro AP, Costa-Cruz JM, Goulart LR (2015) Structural and functional characterization of a novel scFv anti-HSP60 of Strongyloides sp. Sci Rep 5:10447
Miguel CB, Levenhagen MA, Costa-Cruz JM, Goulart LR, Alves PT, Ueira-Vieira C et al (2020) scFv against HSP60 of Strongyloides sp. and its application in the evaluation of parasite frequency in the elderly. Dis Markers 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4086929
Ravi V, Ramachandran S, Thompson RW, Andersen JF, Neva FA (2002) Characterization of a recombinant immunodiagnostic antigen (NIE) from Strongyloides stercoralis L3-stage larvae. Mol Biochem Parasitol 125(1):73–81
Ramanathan R, Burbelo PD, Groot S, Iadarola MJ, Neva FA, Nutman TB (2008) A luciferase immunoprecipitation systems assay enhances the sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. J Infect Dis 198(3):444–451
Krolewiecki AJ, Ramanathan R, Fink V, McAuliffe I, Cajal SP, Won K et al (2010) Improved diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis using recombinant antigen-based serologies in a community-wide study in northern Argentina. Clin Vaccine Immunol 17(10):1624–1630
Arifin N, Yunus MH, Nolan JT, Lok BJ, Noordin R (2018) Identification and preliminary evaluation of novel recombinant protein for serodiagnosis of strongyloidiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 98(4):1165–1170
Masoori L, Falak R, Mokhtarian K, Bandehpour M, Razmjou E, Jalallou N et al (2019) Production of recombinant 14-3-3 protein and determination of its immunogenicity for application in serodiagnosis of strongyloidiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 113(6):326–331
Momčilović S, Cantacessi C, Arsić-Arsenijević V, Otranto D, Tasić-Otašević S (2019) Rapid diagnosis of parasitic diseases: current scenario and future needs. Clin Microbiol Infect 25(3):290–309
Paulos S, Saugar JM, de Lucio A, Fuentes I, Mateo M, Carmena D (2019) Comparative performance evaluation of four commercial multiplex real-time PCR assays for the detection of the diarrhoea-causing protozoa Cryptosporidium hominis/parvum, Giardia duodenalis and Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS One 14(4):e0215068
Funding
Some of the authors are supported by funding from the Malaysian Ministry of Education through the Higher Institution Centre of Excellence (HICoE) Program (Grant No. 311/CIPPM/4401005) and FRGS Grant (No. 203/CIPPM/6711636).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balachandra, D., Ahmad, H., Arifin, N. et al. Direct detection of Strongyloides infection via molecular and antigen detection methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 40, 27–37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03949-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03949-x