Abstract
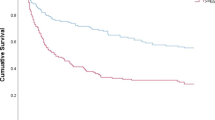
The aim of this study was to describe the epidemiology of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) bacteremia in a diabetic and a non-diabetic population of the University Hospital of Charleroi and to analyze medical outcomes, including risk of metastatic infection and mortality. Descriptive and multivariable analyses were performed using MedCalc 18.9 (MedCalc Software bvba, Ostend, Belgium). A total of 248 patients with MSSA bacteremia were identified between 1st January 2012 and 28th June 2017 out of which 32.7% were diabetic. Within the diabetic patients, we observed more prolonged hospital duration of stay (p = 0.034), more secondary bacteremia of cutaneous sources (including cellulitis, diabetic foot and ulcer) (p = 0.037), and more metastatic infection (p = 0.002). The overall 30-day mortality was 24.2% with no difference between the two groups. With a logistic regression analysis, it was demonstrated that age ≥ 60 years (odds ratio (OR), 2.20 (95% CI, 1.03–4.67)) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) ≥ 3 (OR, 2.95 (95% CI, 1.51–5.79)) were the only independent risk factors of mortality, while removal of the primary site of infection was a protective factor (OR, 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.62)). Risk of developing metastatic infection was increased with diabetes (OR, 2.08 (95% CI, 1.12–3.90)), while early empirical antibiotic therapy (OR, 0.38 (95% CI, 0.20–0.71)) decreased this risk. Diabetes was not associated with increased 30-day mortality after MSSA bacteremia. However, diabetes increased significantly the risk of metastatic infection. An aggressive treatment of MSSA bacteremia seems crucial to improve the outcome of diabetic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smit J (2017) Community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: studies of risk and prognosis with special attention to diabetes mellitus and chronic heart failure. Dan Med J 64:5
Kaasch AJ, Barlow G, Edgeworth JD, Fowler VG, Hellmich M, Hopkins S et al (2014) Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection: a pooled analysis of five prospective, observational studies. J Inf Secur 68(3):242–251
Kaech C, Elzi L, Sendi P, Frei R, Laifer G, Bassetti S et al (2006) Course and outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a retrospective analysis of 308 episodes in a Swiss tertiary-care centre. Clin Microbiol Infect 12(4):345–352
Hansen M-LU, Gotland N, Mejer N, Petersen A, Larsen AR, Benfield T et al (2017) Diabetes increases the risk of disease and death due to Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. A matched case-control and cohort study. Infect Dis (Lond) 49(9):689–697
Smit J, Søgaard M, Schønheyder HC, Nielsen H, Frøslev T, Thomsen RW (2016) Diabetes and risk of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a population-based case-control study. Eur J Endocrinol 174(5):631–639
User S. IDF diabetes atlas - across the globe [Internet]. [cited 2018 Feb 24]. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/across-the-globe.html
Thwaites GE, Scarborough M, Szubert A, Nsutebu E, Tilley R, Greig J et al (2018) Adjunctive rifampicin for Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia (ARREST): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 391(10121):668–678
Bassetti M, Trecarichi EM, Mesini A, Spanu T, Giacobbe DR, Rossi M et al (2012) Risk factors and mortality of healthcare-associated and community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin Microbiol Infect 18(9):862–869
Kanafani ZA, Kourany WM, Fowler VG, Levine DP, Vigliani GA, Campion M et al (2009) Clinical characteristics and outcomes of diabetic patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28(12):1477–1482
Turnidge JD, Kotsanas D, Munckhof W, Roberts S, Bennett CM, Nimmo GR et al (2009) Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a major cause of mortality in Australia and New Zealand. Med J Aust 191(7):368–373
Altas socio-économique de Charleroi et Sud Hainaut (3ème édition, 2017), Intercommunal pour la Gestion et la Réalisation d’Etudes Techniques et Economiques - IGRETEC
van Hal SJ, Jensen SO, Vaska VL, Espedido BA, Paterson DL, Gosbell IB (2012) Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev 25(2):362–386
Libert M, Elkholti M, Massaut J, Karmali R, Mascart G, Cherifi S (2008) Risk factors for meticillin resistance and outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection in a Belgian university hospital. J Hosp Infect 68(1):17–24
del Rio A, Cervera C, Moreno A, Moreillon P, Miró JM (2009) Patients at risk of complications of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Clin Infect Dis 48(Suppl 4):S246–S253
Smit J, Thomsen RW, Schønheyder HC, Nielsen H, Frøslev T, Søgaard M (2016) Outcome of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in patients with diabetes: a historical population-based cohort study. PLoS One 11(4):e0153766
Rieg S, Peyerl-Hoffmann G, de With K, Theilacker C, Wagner D, Hübner J et al (2009) Mortality of S. aureus bacteremia and infectious diseases specialist consultation--a study of 521 patients in Germany. J Inf Secur 59(4):232–239
Fowler VG, Olsen MK, Corey GR, Woods CW, Cabell CH, Reller LB et al (2003) Clinical identifiers of complicated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med 163(17):2066–2072
Lesens O, Methlin C, Hansmann Y, Remy V, Martinot M, Bergin C et al (2003) Role of comorbidity in mortality related to Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a prospective study using the Charlson weighted index of comorbidity. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 24(12):890–896
Bertoni AG, Saydah S, Brancati FL (2001) Diabetes and the risk of infection-related mortality in the U.S. Diabetes Care 24(6):1044–1049
Mylotte JM, Tayara A (2000) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: predictors of 30-day mortality in a large cohort. Clin Infect Dis 31(5):1170–1174
Shah BR, Hux JE (2003) Quantifying the risk of infectious diseases for people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(2):510–513
Big C, Malani PN (2010) Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections in older adults: clinical outcomes and risk factors for in-hospital mortality. J Am Geriatr Soc 58(2):300–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethic committee of the University Hospital of Charleroi on 27th September 2017 (CCB: B325201733405).
Informed consent
There was no informed consent because the author conducted a retrospective study with de-identified data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanderschelden, A., Lelubre, C., Richard, T. et al. Outcome of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) bacteremia: impact of diabetes. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 38, 2215–2220 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03659-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03659-z