Abstract
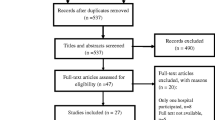
In Iran, patients showing rifampicin (RIF) resistance detected by the Xpert® MTB/RIF assay are considered as candidates for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) treatment. Despite the fact that RIF resistance has been used as a proxy for MDR-TB, little is known about the proportion of isoniazid (INH) resistance patterns in RIF-resistant TB. We systematically searched MEDLINE, Embase, and other databases up to March 2017 for studies addressing the proportion of INH resistance patterns in RIF-resistant TB in Iran. The data were pooled using a random effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q and I2 statistics. A total of 11 articles met the eligibility criteria. Data analysis demonstrated that 33.3% of RIF-resistant isolates from new TB cases and 14.8% of RIF-resistant isolates from previously treated cases did not display resistance to INH. The relatively high proportion of INH susceptibility among isolates with RIF resistance indicated that RIF resistance may no longer predict MDR-TB in Iran. Therefore, the detection of RIF resistance by the Xpert MTB/RIF assay will require complementary detection of INH resistance by other drug susceptibility testing (DST) methods in order to establish the diagnosis of MDR-TB.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (WHO) (2016) Global tuberculosis report 2016
Raviglione MC, Uplekar MW (2006) WHO’s new Stop TB Strategy. Lancet 367(9514):952–955
Daley CL, Caminero JA (2013) Management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 34(1):44–59
Zignol M, Hosseini MS, Wright A, Lambregts-van Weezenbeek C, Nunn P, Watt CJ, Williams BG, Dye C (2006) Global incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. J Infect Dis 194(4):479–485
Lynch JB (2013) Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Med Clin North Am 97(4):553–579
Van Rie A, Page-Shipp L, Scott L, Sanne I, Stevens W (2010) Xpert® MTB/RIF for point-of-care diagnosis of TB in high-HIV burden, resource-limited countries: hype or hope? Expert Rev Mol Diagn 10(7):937–946
Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, Allen J, Tahirli R, Blakemore R, Rustomjee R, Milovic A, Jones M, O’Brien SM, Persing DH, Ruesch-Gerdes S, Gotuzzo E, Rodrigues C, Alland D, Perkins MD (2010) Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med 363(11):1005–1015
Hillemann D, Rüsch-Gerdes S, Richter E (2007) Evaluation of the GenoType MTBDRplus assay for rifampin and isoniazid susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 45(8):2635–2640
Kurbatova EV, Cavanaugh JS, Shah NS, Wright A, Kim H, Metchock B, Van Deun A, Barrera L, Boulahbal F, Richter E, Martín-Casabona N, Arias F, Zemanova I, Drobniewski F, Santos Silva A, Coulter C, Lumb R, Cegielski JP (2012) Rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: susceptibility to isoniazid and other anti-tuberculosis drugs. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16(3):355–357
Velayati AA, Farnia P, Mozafari M, Sheikholeslami MF, Karahrudi MA, Tabarsi P, Hoffner S (2014) High prevelance of rifampin-monoresistant tuberculosis: a retrospective analysis among Iranian pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg 90(1):99–105
Nasiri MJ, Dabiri H, Darban-Sarokhalil D, Rezadehbashi M, Zamani S (2014) Prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Iran: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Infect Control 42(11):1212–1218
Nasiri MJ, Chirani AS, Amin M, Halabian R, Fooladi AAI (2016) Isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis in Iran: a systematic review. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 98:104–109
Munn Z, Moola S, Lisy K, Riitano D (2014) The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual 2014. The systematic review of prevalence and incidence data. The Joanna Briggs Institute, Adelaide
Nasiri MJ, Dabiri H, Darban-Sarokhalil D, Shahraki AH (2015) Prevalence of non-tuberculosis mycobacterial infections among tuberculosis suspects in Iran: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(6):e0129073
Mansoori S, Mirabolhasani Z, Farnia P, Velayati A (2003) The pattern of drug resistance among newly diagnosed and old cases of pulmonary tuberculosis in NRITLD. Arch Iranian Med 6(4):255–260
Bahrmand AR, Velayati AA, Bakayev VV (2000) Treatment monitoring and prevalence of drug resistance in tuberculosis patients in Tehran. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 4(6):544–549
Shamaei M, Marjani M, Chitsaz E, Kazempour M, Esmaeili M, Farnia P, Tabarsi P, Amiri MV, Mirsaeidi M, Mansouri D, Masjedi MR, Velayati AA (2009) First-line anti-tuberculosis drug resistance patterns and trends at the national TB referral center in Iran—eight years of surveillance. Int J Infect Dis 13(5):e236–e240
Namaei MH, Sadeghian A, Naderinasab M, Ziaee M (2006) Prevalence of primary drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Mashhad, Iran. Indian J Med Res 124(1):77–80
Mirsaeidi MS, Tabarsi P, Farnia P, Ebrahimi G, Morris MW, Masjedi MR, Velayati AA, Mansouri D (2007) Trends of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a tertiary tuberculosis center in Iran. Saudi Med J 28(4):544–550
Marjani M, Baghaei P, Tabarsi P, Shamaei M, Mansouri D, Masjedi MR, Velayati A (2012) Drug resistance pattern and outcome of treatment in recurrent episodes of tuberculosis. East Mediterr Health J 18(9):957–961
Livani S, Mirinargesi M, Nemati-Shoja E, Rafiei S, Taziki M, Tabarraei A, Ghaemi E (2011) Prevalence of multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by mycobacteria growth indicator tube in Golestan province, north of Iran (in Persian). Med Lab J 5(2):7–14
Nasiri MJ, Rezaei F, Zamani S, Darban-Sarokhalil D, Fooladi AAI, Shojaei H, Feizabadi MM (2014) Drug resistance pattern of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from patients of five provinces of Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Med 7(3):193–196
Mohajeri P, Norozi B, Atashi S, Farahani A (2014) Anti tuberculosis drug resistance in west of Iran. J Glob Infect Dis 6(3):114–117
Farazi A, Sofian M, Zarrinfar N, Katebi F, Hoseini SD, Keshavarz R (2013) Drug resistance pattern and associated risk factors of tuberculosis patients in the central province of Iran. Caspian J Intern Med 4(4):785–789
Tavanaee Sani A, Shakiba A, Salehi M, Bahrami Taghanaki HR, Ayati Fard SF, Ghazvini K (2015) Epidemiological characterization of drug resistance among Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from patients in northeast of Iran during 2012–2013. Biomed Res Int 2015:747085
Espinal MA, Laserson K, Camacho M, Fusheng Z, Kim SJ, Tlali RE, Smith I, Suarez P, Antunes ML, George AG, Martin-Casabona N, Simelane P, Weyer K, Binkin N, Raviglione MC (2001) Determinants of drug-resistant tuberculosis: analysis of 11 countries. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 5(10):887–893
Caws M, Duy PM, Tho DQ, Lan NTN, Hoa DV, Farrar J (2006) Mutations prevalent among rifampin- and isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from a hospital in Vietnam. J Clin Microbiol 44(7):2333–2337
Coovadia YM, Mahomed S, Pillay M, Werner L, Mlisana K (2013) Rifampicin mono-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: a significant phenomenon in a high prevalence TB-HIV region. PLoS One 8(11):e77712
Mukinda FK, Theron D, van der Spuy GD, Jacobson KR, Roscher M, Streicher EM, Musekiwa A, Coetzee GJ, Victor TC, Marais BJ, Nachega JB, Warren RM, Schaaf HS (2012) Rise in rifampicin-monoresistant tuberculosis in Western Cape, South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16(2):196–202
Sanders M, Van Deun A, Ntakirutimana D, Masabo JP, Rukundo J, Rigouts L, Fissette K, Portaelst F (2006) Rifampicin mono-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Bujumbura, Burundi: results of a drug resistance survey. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 10(2):178–183
Traore H, Fissette K, Bastian I, Devleeschouwer M, Portaels F (2000) Detection of rifampicin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from diverse countries by a commercial line probe assay as an initial indicator of multidrug resistance [technical note]. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 4(5):481–484
Rufai SB, Kumar P, Singh A, Prajapati S, Balooni V, Singh S (2014) Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF with line probe assay for detection of rifampin-monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 52(6):1846–1852
Kumar P, Balooni V, Sharma BK, Kapil V, Sachdeva KS, Singh S (2014) High degree of multi-drug resistance and hetero-resistance in pulmonary TB patients from Punjab state of India. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 94(1):73–80
Ayaz A, Hasan Z, Jafri S, Inayat R, Mangi R, Channa AA, Malik FR, Ali A, Rafiq Y, Hasan R (2012) Characterizing Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Karachi, Pakistan: drug resistance and genotypes. Int J Infect Dis 16(4):e303–e309
Zeka AN, Tasbakan S, Cavusoglu C (2011) Evaluation of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis and detection of rifampin resistance in pulmonary and extrapulmonary specimens. J Clin Microbiol 49(12):4138–4141
World Health Organization (WHO) (2014) Companion handbook to the WHO guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis
Ai J-W, Ruan Q-L, Liu Q-H, Zhang W-H (2016) Updates on the risk factors for latent tuberculosis reactivation and their managements. Emerg Microbes Infect 5(2):e10
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the “Clinical Research Development Center of Baqiyatallah Hospital” for their kind cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical approval
The manuscript is a systematic review, so ethical approval was not required for the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasiri, M.J., Zamani, S., Pormohammad, A. et al. The reliability of rifampicin resistance as a proxy for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review of studies from Iran. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37, 9–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3079-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3079-4