Abstract
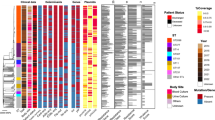
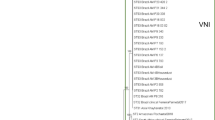
Bacteremia with Streptococcus bovis/equinus complex strains is associated with hepatobiliary disease, colorectal lesions (CL), and infective endocarditis (IE). This study addressed the clinical significance of subspecies distinction of previously designated S. bovis blood culture isolates according to the updated nomenclature. During 2002–2013, all blood culture isolates previously designated as S. bovis were recultured and identified using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and MALDI-TOF (Bruker BioTyper and Vitek MS, bioMérieux). Clinical data of patients aged ≥18 years were reviewed. A review of four recent case series was performed as well. Forty blood isolates were identified using 16S rRNA sequencing. Twenty-six bacteremic patients had S. gallolyticus ssp. pasteurianus, six had S. gallolyticus ssp. gallolyticus, two had S. gallolyticus ssp. macedonicus, and six had S. infantarius bacteremia. Species diagnosis using Vitek and bioMérieux MALDI-TOF technology was applicable in 37 and 36 samples, respectively, and was successful in all samples (100 %). Subspecies identification was confirmed in 30 (83 %) samples (as compared with 16S rRNA sequencing detection). IE was diagnosed in 22 (59 %) patients and CL in 8 (20 %) patients. Both complications were associated with all subspecies. Combining our results with those of four recent series resulted in, overall, 320 bacteremic cases, of which 88 (28 %) had CL and 66 (21 %) had IE. All ‘bovis/equinus’ complex subspecies were associated with CL or IE. From a clinical point of view, species diagnosis using MALDI-TOF MS should suffice to warrant consideration of transesophageal echocardiography and colonoscopy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jans C, Meile L, Lacroix C, Stevens MJ (2015) Genomics, evolution, and molecular epidemiology of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC). Infect Genet Evol 33:419–436
Klein RS, Recco RA, Catalano MT, Edberg SC, Casey JI, Steigbigel NH (1977) Association of Streptococcus bovis with carcinoma of the colon. N Engl J Med 297:800–802
Zarkin BA, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, Effron PN, Magnuson TH, Pitt HA (1990) The triad of Streptococcus bovis bacteremia, colonic pathology, and liver disease. Ann Surg 211:786–792
Cohen LF, Dunbar SA, Sirbasku DM, Clarridge JE 3rd (1997) Streptococcus bovis infection of the central nervous system: report of two cases and review. Clin Infect Dis 25:819–823
Facklam RR (1972) Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol 23:1131–1139
Schlegel L, Grimont F, Ageron E, Grimont PA, Bouvet A (2003) Reappraisal of the taxonomy of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex and related species: description of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus subsp. nov., S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus subsp. nov. and S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:631–645
Poyart C, Quesne G, Trieu-Cuot P (2002) Taxonomic dissection of the Streptococcus bovis group by analysis of manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase gene (sodA) sequences: reclassification of ‘Streptococcus infantarius subsp. coli’ as Streptococcus lutetiensis sp. nov. and of Streptococcus bovis biotype 11.2 as Streptococcus pasteurianus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1247–1255
Ruoff KL, Miller SI, Garner CV, Ferraro MJ, Calderwood SB (1989) Bacteremia with Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus salivarius: clinical correlates of more accurate identification of isolates. J Clin Microbiol 27:305–308
Beck M, Frodl R, Funke G (2008) Comprehensive study of strains previously designated Streptococcus bovis consecutively isolated from human blood cultures and emended description of Streptococcus gallolyticus and Streptococcus infantarius subsp. coli. J Clin Microbiol 46:2966–2972
Romero B, Morosini MI, Loza E, Rodríguez-Baños M, Navas E, Cantón R, Campo RD (2011) Reidentification of Streptococcus bovis isolates causing bacteremia according to the new taxonomy criteria: still an issue? J Clin Microbiol 49:3228–3233
Lazarovitch T, Shango M, Levine M, Brusovansky R, Akins R, Hayakawa K et al (2013) The relationship between the new taxonomy of Streptococcus bovis and its clonality to colon cancer, endocarditis, and biliary disease. Infection 41:329–337
Sheng WH, Chuang YC, Teng LJ, Hsueh PR (2014) Bacteraemia due to Streptococcus gallolyticus subspecies pasteurianus is associated with digestive tract malignancies and resistance to macrolides and clindamycin. J Infect 69:145–153
Hinse D, Vollmer T, Erhard M, Welker M, Moore ER, Kleesiek K, Dreier J (2011) Differentiation of species of the Streptococcus bovis/equinus-complex by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in comparison to sodA sequence analyses. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:52–57
Megged O, Assous MV, Miskin H, Peleg U, Schlesinger Y (2013) Neurologic manifestations of Fusobacterium infections in children. Eur J Pediatr 172:77–83
Baker GC, Cowan DA (2004) 16 S rDNA primers and the unbiased assessment of thermophile diversity. Biochem Soc Trans 32:218–221
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11030–11035
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Corredoira J, Alonso MP, Coira A, Casariego E, Arias C, Alonso D, Pita J, Rodriguez A, López MJ, Varela J (2008) Characteristics of Streptococcus bovis endocarditis and its differences with Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27:285–291
Herrero IA, Rouse MS, Piper KE, Alyaseen SA, Steckelberg JM, Patel R (2002) Reevaluation of Streptococcus bovis endocarditis cases from 1975 to 1985 by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol 40:3848–3850
Malkin J, Kimmitt PT, Ou HY, Bhasker PS, Khare M, Deng Z et al (2008) Identification of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus as the etiological agent in a case of culture-negative multivalve infective endocarditis by 16S rDNA PCR analysis of resected valvular tissue. J Heart Valve Dis 17:589–592
De Vuyst L, Tsakalidou E (2008) Streptococcus macedonicus, a multi-functional and promising species for dairy fermentations. Int Dairy J 18(5):476–485
Papadimitriou K, Anastasiou R, Mavrogonatou E, Blom J, Papandreou NC, Hamodrakas SJ et al (2014) Comparative genomics of the dairy isolate Streptococcus macedonicus ACA-DC 198 against related members of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex. BMC Genomics 15:272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the Mirsky Research Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
E. Ben-Chetrit and Y. Wiener-Well contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Chetrit, E., Wiener-Well, Y., Kashat, L. et al. Streptococcus bovis new taxonomy: does subspecies distinction matter?. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36, 387–393 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2814-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2814-6