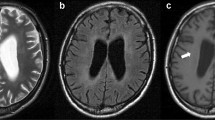
Abstract
Brain abscess represents a significant medical problem, despite recent advances made in detection and therapy. Streptococcus intermedius, a commensal organism, has the potential to cause significant morbidity. S. intermedius expresses one or more members of a family of structurally and antigenically related surface proteins termed antigen I/II, which plays a potential role in its pathogenesis. It is involved in binding to human fibronectin and laminin and in inducing IL-8 release from monocytes, which promotes neutrophil chemotaxis and activation. There are few published data on the role of this organism in brain abscess. This review focuses on the clinical evidence, pathogenic role, mechanism of predisposition, and currently employed strategies to fight against S. intermedius associated to brain abscess.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esen N, Kielian T (2009) Toll-like receptors in brain abscess. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 336:41–61
Khattak A, Rehman R, Anayatullah AW (2010) Etiological factors of brain abscess. J Med Sci 18(4):194–196
Lu CH, Chang WN, Lui CC (2006) Strategies for the management of bacterial brain abscess. J Clin Neurosci 13(10):979–985
Carpenter J, Stapleton S, Holliman R (2007) Retrospective analysis of 49 cases of brain abscess and review of the literature. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 26(1):1–11
Menon S, Bharadwaj R, Chowdhary A, Kaundinya DV, Palande DA (2008) Current epidemiology of intracranial abscesses: a prospective 5 year study. J Med Microbiol 57:1259–1268
Brook I (2009) Microbiology and antimicrobial treatment of orbital and intracranial complications of sinusitis in children and their management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1183–1186
Vajramani GV, Nagmoti MB, Patil CS (2005) Neurobrucellosis presenting as an intra-medullary spinal cord abscess. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 4:14–18
Jacobs JA, Pietersen HG, Stobberingh EE, Soeters PB (1995) Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus constellatus and Streptococcus intermedius. Clinical relevance, hemolytic and serologic characteristics. Am J Clin Pathol 104:547–553
Nagamune H, Whiley RA, Goto T, Inai Y, Maeda T, Hardie JM, Kourai H (2000) Distribution of the intermedilysin gene among the anginosus group Streptococci and correlation between intermedilysin production and deep-seated infection with Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Microbiol 38:220–226
Jacobs JA, Tjhie JH, Smeets MGJ, Schot CS, Schouls LM (2003) Genotyping by amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis reveals persistence and recurrence of infection with Streptococcus anginosus group organisms. J Clin Microbiol 41:2862–2866
Goto T, Nagamune H, Miyazaki A, Kawamura Y, Ohnishi O, Hattori K, Ohkura K, Miyamoto K, Akimoto S, Ezaki T, Hirota K, Miyake Y, Maeda T, Kourai H (2002) Rapid identification of Streptococcus intermedius by PCR with the ily gene as a species marker gene. J Med Microbiol 51:178–186
Parker MT, Ball LC (1976) Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol 9(3):275–302
Mirzanejad Y, Stratton CW (2005) Streptococcus anginosus group. In: Mandell GL, Douglas RG, Bennett JE, Dolin R (eds) Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6th edn. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, PA
Atiq M, Ahmed US, Allana SS, Chishti KN (2006) Brain abscess in children. Indian J Pediatr 73:401–404
Yamamoto M, Fukushima T, Ohshiro S, Go Y, Tsugu H, Kono K, Tomonaga M (1999) Brain abscess caused by Streptococcus intermedius: two case reports. Surg Neurol 51:219–222
Petti CA, Simmon KE, Bender J, Blaschke A, Webster KA, Conneely MF, Schreckenberger PC, Origitano TC, Challapalli M (2008) Culture-negative intracerebral abscesses in children and adolescents from Streptococcus anginosus group infection: a case series. Clin Infect Dis 46:1578–1580
Al Masalma M, Armougom F, Scheld WM, Dufour H, Roche PH, Drancourt M, Raoult D (2009) The expansion of the microbiological spectrum of brain abscesses with use of multiple 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing. Clin Infect Dis 48:1169–1178
Jan F, Hafiz AM, Gupta S, Meidl J, Allaqaband S (2009) Brain abscesses in a patient with a patent foramen ovale: a case report. J Med Case Rep 3(1):9299
Wong CA, Donald F, Macfarlane JT (1995) Streptococcus milleri pulmonary disease: a review and clinical description of 25 patients. Thorax 50:1093–1096
Melo JC, Raff MJ (1978) Brain abscess due to Streptococcus MG-intermedius (Streptococcus milleri). J Clin Microbiol 7:529–532
Khatib R, Ramanathan J, Baran J Jr (2000) Streptococcus intermedius: a cause of lobar pneumonia with meningitis and brain abscesses. Clin Infect Dis 30(2):396–397
Weightman NC, Barnham MRD, Dove M (2004) Streptococcus milleri group bacteraemia in North Yorkshire, England (1989–2000). Indian J Med Res 119:164–167
Mehnaz A, Syed AU, Saleem AS, Khalid CN (2006) Clinical features and outcome of cerebral abscess in congenital heart disease. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 18:21–24
Osawa R, Whiley RA (1995) Effects of different acidulants on growth of ‘Streptococcus milleri group’ strains isolated from various sites of the human body. Lett Appl Microbiol 20:263–267
Brochu V, Greinier D, Mayrand D (1998) Human transferrin as a source of iron for Streptococcus intermedius. FEMS Microbiol Lett 166:127–133
Shinzato T, Saito A (1995) The Streptococcus milleri group as a cause of pulmonary infections. Clin Infect Dis 21:S238–S243
Baddour LM (1994) Virulence factors among gram-positive bacteria in experimental endocarditis. Infect Immun 62:2143–2148
Petersen FC, Pasco S, Ogier J, Klein JP, Assev S, Scheie AA (2001) Expression and functional properties of the Streptococcus intermedius surface protein antigen I/II. Infect Immun 69:4647–4653
Kielian T, Barry B, Hickey WF (2001) CXC chemokine receptor-2 ligands are required for neutrophil-mediated host defense in experimental brain abscesses. J Immunol 166:4634–4643
Wessels MR (1997) Biology of streptococcal capsular polysaccharides. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser 26:20S–31S
Kanamori S, Kusano N, Shinzato T, Saito A (2004) The role of the capsule of the Streptococcus milleri group in its pathogenicity. J Infect Chemother 10(2):105–109
Brook I, Walker RI (1985) The role of encapsulation in the pathogenesis of anaerobic gram-positive cocci. Can J Microbiol 31:176–180
Ruoff KL, Ferraro MJ (1987) Hydrolytic enzymes of “Streptococcus milleri”. J Clin Microbiol 25:1645–1647
Willcox MDP, Patrikakis M, Knox KW (1995) Degradative enzymes of oral streptococci. Aust Dent J 40:121–128
Takao A, Nagashima H, Usui H, Sasaki F, Maeda N, Ishibashi K, Fujita H (1997) Hyaluronidase activity in human pus from which Streptococcus intermedius was isolated. Microbiol Immunol 41:795–798
Homer K, Shain H, Beighton D (1997) The role of hyaluronidase in growth of Streptococcus intermedius on hyaluronate. Adv Exp Med Biol 418:681–683
Shain H, Homer KA, Beighton D (1996) Degradation and utilisation of chondroitin sulphate by Streptococcus intermedius. J Med Microbiol 44:372–380
Faber V, Rosendal K (1954) Streptococcal hyaluronidase. II. Studies on the production of hyaluronidase and hyaluronic acid by representatives of all types of hemolytic streptococci belonging to group A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 35:159–164
Hynes WL, Walton SL (2000) Hyaluronidases of Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 183:201–207
Pecharki D, Petersen FC, Scheie AA (2008) Role of hyaluronidase in Streptococcus intermedius biofilm. Microbiology 154:932–938
Vendeville A, Winzer K, Heurlier K, Tang CM, Hardie KR (2005) Making ‘sense’ of metabolism: autoinducer-2, luxS and pathogenic bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:383–396
Streit JM, Steenbergen JN, Thorne GM, Alder J, Jones RN (2005) Daptomycin tested against 915 bloodstream isolates of viridans group streptococci (eight species) and Streptococcus bovis. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:574–578
Shain H, Homer KA, Beighton D (1996) Purification and properties of a novel glycosaminoglycan depolymerase from Streptococcus intermedius strain UNS 35. J Med Microbiol 44:381–389
Byers HL, Homer KA, Beighton D (1997) Sialic acid utilisation by viridans streptococci. Adv Exp Med Biol 418:713–716
Proft T, Fraser J (1998) Superantigens: just like peptides only different. J Exp Med 187(6):819–821
Arala-Chaves MP, Higerd TB, Porto MT, Munoz J, Goust JM, Fudenberg HH, Loadholt CB (1979) Evidence for the synthesis and release of strongly immunosuppressive, noncytotoxic substances by Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Invest 64(4):871–883
Liu D, Yumoto H, Hirota K, Murakami K, Takahashi K, Hirao K, Matsuo T, Ohkura K, Nagamune H, Miyake Y (2008) Histone-like DNA binding protein of Streptococcus intermedius induces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human monocytes via activation of ERK1/2 and JNK pathways. Cell Microbiol 10(1):262–276
Nagamune H, Ohnishi C, Katsuura A, Fushitani K, Whiley RA, Tsuji A, Matsuda Y (1996) Intermedilysin, a novel cytotoxin specific for human cells secreted by Streptococcus intermedius UNS46 isolated from a human liver abscess. Infect Immun 64(8):3093–3100
Sukeno A, Nagamune H, Whiley RA, Jafar SI, Aduse-Opoku J, Ohkura K, Maeda T, Hirota K, Miyake Y, Kourai H (2005) Intermedilysin is essential for the invasion of hepatoma HepG2 cells by Streptococcus intermedius. Microbiol Immunol 49:681–694
Tomoyasu T, Tabata A, Hiroshima R, Imaki H, Masuda S, Whiley RA, Aduse-Opoku J, Kikuchi K, Hiramatsu K, Nagamune H (2010) Role of catabolite control protein A in the regulation of intermedilysin production by Streptococcus Intermedius. Infect Immun 78(9):4012–4021
Kowlessar PI, O’Connell NH, Mitchell RD, Elliott S, Elliott TS (2006) Management of patients with Streptococcus milleri brain abscesses. J Infect 52(6):443–450
Haley EC Jr, Costello GT, Rodeheaver GT, Winn HR, Scheld WM (1983) Treatment of experimental brain abscess with penicillin and chloramphenicol. J Infect Dis 148(4):737–744
Jacobs JA, Stobberingh EE (1996) In-vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of the “Streptococcus milleri” group (Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus constellatus and Streptococcus intermedius). J Antimicrob Chemother 37:371–375
Limia A, Jiménez ML, Alarcón T, López-Brea M (1999) Five-year analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility of the Streptococcus milleri group. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 18:440–444
Aracil B, Gomez-Garces JL, Alos JI (1999) A study of susceptibility of 100 clinical isolates belonging to the Streptococcus milleri group to 16 cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother 43:399–402
Jansson AK, Enblad P, Sjölin J (2004) Efficacy and safety of cefotaxime in combination with metronidazole for empirical treatment of brain abscess in clinical practice: a retrospective study of 66 consecutive cases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:7–14
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A.K., Fournier, PE. The role of Streptococcus intermedius in brain abscess. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32, 477–483 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1782-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1782-8