Abstract
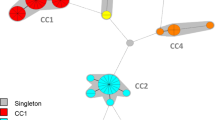
The usefulness and performance of repetitive-sequence-based polymerase chain reaction (rep-PCR), the DiversiLab system, in the epidemiological surveillance for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain typing was assessed. MRSA isolates from five distinct outbreaks with precise epidemiological data (n = 69) and from the culture collection of well-characterized MRSA strains (n = 132) consisting of 35 spa and 23 pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) types were analyzed. The typing results of the DiversiLab system in outbreak analysis were compared to the spa and PFGE typing methods. The DiversiLab system proved to be a reliable tool for the rapid first-line typing of MRSA isolates, showing a good reliability in distinguishing MRSA strains in an area where several MRSA types were causing epidemics. This, however, required that the automatic clustering was combined with manual interpretation using the pattern overlay function when the strain types showing high similarity were clustered together. All outbreaks were distinguished with the DiversiLab system and the PFGE method, but not with the spa typing method. The overall discriminatory power of the DiversiLab system in differentiating diverse MRSA strains proved to be good. We also demonstrated that, in addition to the genetic relatedness analysis of MRSA strains, it is important to obtain accurate epidemiological information in order to perform reliable epidemiological surveillance studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolkewitz M, Frank U, Philips G, Schumacher M, Davey P; BURDEN Study Group (2011) Mortality associated with in-hospital bacteraemia caused by Staphylococcus aureus: a multistate analysis with follow-up beyond hospital discharge. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:381–386. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq424
Shurland S, Zhan M, Bradham DD, Roghmann MC (2007) Comparison of mortality risk associated with bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 28:273–279. doi:10.1086/512627
Kerttula AM, Lyytikäinen O, Salmenlinna S, Vuopio-Varkila J (2004) Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Finland. J Hosp Infect 58:109–114. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2004.05.019
March A, Aschbacher R, Dhanji H, Livermore DM, Böttcher A, Sleghel F, Maggi S, Noale M, Larcher C, Woodford N (2010) Colonization of residents and staff of a long-term-care facility and adjacent acute-care hospital geriatric unit by multiresistant bacteria. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:934–944. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03024.x
Ichiyama S, Ohta M, Shimokata K, Kato N, Takeuchi J (1991) Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 29:2690–2695
Prevost G, Jaulhac B, Piemont Y (1992) DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is more effective than ribotyping in distinguishing among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol 30:967–973
Murchan S, Kaufmann ME, Deplano A, de Ryck R, Struelens M, Zinn CE, Fussing V, Salmenlinna S, Vuopio-Varkila J, El Solh N, Cuny C, Witte W, Tassios PT, Legakis N, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Vindel A, Laconcha I, Garaizar J, Haeggman S, Olsson-Liljequist B, Ransjo U, Coombes G, Cookson B (2003) Harmonization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for epidemiological typing of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a single approach developed by consensus in 10 European laboratories and its application for tracing the spread of related strains. J Clin Microbiol 41:1574–1585. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.4.1574-1585.2003
Frénay HME, Bunschoten AE, Schouls LM, van Leeuwen WJ, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE, Verhoef J, Mooi FR (1996) Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on the basis of protein A gene polymorphism. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 15:60–64. doi:10.1007/BF01586186
Shopsin B, Gomez M, Montgomery SO, Smith DH, Waddington M, Dodge DE, Bost DA, Riehman M, Naidich S, Kreiswirth BN (1999) Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol 37:3556–3563
Tang YW, Waddington MG, Smith DH, Manahan JM, Kohner PC, Highsmith LM, Li H, Cockerill FR 3rd, Thompson RL, Montgomery SO, Persing DH (2000) Comparison of protein A gene sequencing with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and epidemiologic data for molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 38:1347–1351
Vainio A, Kardén-Lilja M, Ibrahem S, Kerttula AM, Salmenlinna S, Virolainen A, Vuopio-Varkila J (2008) Clonality of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in Finland as defined by several molecular methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27:545–555. doi:10.1007/s10096-008-0470-1
van der Zee A, Verbakel H, van Zon JC, Frenay I, van Belkum A, Peeters M, Buiting A, Bergmans A (1999) Molecular genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus strains: comparison of repetitive element sequence-based PCR with various typing methods and isolation of a novel epidemicity marker. J Clin Microbiol 37:342–349
Shutt CK, Pounder JI, Page SR, Schaecher BJ, Woods GL (2005) Clinical evaluation of the DiversiLab microbial typing system using repetitive-sequence-based PCR for characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol 43:1187–1192. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.3.1187-1192.2005
Tenover FC, Gay EA, Frye S, Eells SJ, Healy M, McGowan JE Jr (2009) Comparison of typing results obtained for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates with the DiversiLab system and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol 47:2452–2457. doi:10.1128/JCM.00476-09
Healy M, Huong J, Bittner T, Lising M, Frye S, Raza S, Schrock R, Manry J, Renwick A, Nieto R, Woods C, Versalovic J, Lupski JR (2005) Microbial DNA typing by automated repetitive-sequence-based PCR. J Clin Microbiol 43:199–207. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.1.199-207.2005
Baum C, Haslinger-Löffler B, Westh H, Boye K, Peters G, Neumann C, Kahl BC (2009) Non-spa-typeable clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains are naturally occurring protein A mutants. J Clin Microbiol 47:3624–3629. doi:10.1128/JCM.00941-09
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) (2012) Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters, version 2.0. Available online at: http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/. Last accessed 2 Jan 2012
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2007) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 17th informational supplement. Approved standard MS100-S17. CLSI, Wayne, PA
Pasanen T, Korkeila M, Mero S, Tarkka E, Piiparinen H, Vuopio-Varkila J, Vaara M, Tissari P (2010) A selective broth enrichment combined with real-time nuc-mecA-PCR in the exclusion of MRSA. APMIS 118:74–80. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02562.x
Ibrahem S, Salmenlinna S, Kerttula AM, Virolainen-Julkunen A, Kuusela P, Vuopio-Varkila J (2005) Comparison of genotypes of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus in Finland. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 24:325–328. doi:10.1007/s10096-005-1328-4
Kerttula AM, Lyytikäinen O, Kardén-Lilja M, Ibrahem S, Salmenlinna S, Virolainen A, Vuopio-Varkila J (2007) Nationwide trends in molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Finland, 1997–2004. BMC Infect Dis 7:94–101. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-7-94
Salmenlinna S, Lyytikäinen O, Kotilainen P, Scotford R, Siren E, Vuopio-Varkila J (2000) Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Finland. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 19:101–107. doi:10.1007/s100960050438
Kanerva M, Salmenlinna S, Vuopio-Varkila J, Lehtinen P, Möttönen T, Virtanen MJ, Lyytikäinen O (2009) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Finland in 2004 to 2006. J Clin Microbiol 47:2655–2657. doi:10.1128/JCM.00771-09
Ross TL, Merz WG, Farkosh M, Carroll KC (2005) Comparison of an automated repetitive sequence-based PCR microbial typing system to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for analysis of outbreaks of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 43:5642–5647. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.11.5642-5647.2005
Babouee B, Frei R, Schultheiss E, Widmer AF, Goldenberger D (2011) Comparison of the DiversiLab repetitive element PCR system with spa typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for clonal characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 49:1549–1555. doi:10.1128/JCM.02254-10
Petersson AC, Olsson-Liljequist B, Miörner H, Haeggman S (2010) Evaluating the usefulness of spa typing, in comparison with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, for epidemiological typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a low-prevalence region in Sweden 2000–2004. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:456–462. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02881.x
Grisold AJ, Zarfel G, Strenger V, Feierl G, Leitner E, Masoud L, Hoenigl M, Raggam RB, Dosch V, Marth E (2010) Use of automated repetitive-sequence-based PCR for rapid laboratory confirmation of nosocomial outbreaks. J Infect 60:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2009.10.045
Pasanen T, Kotila SM, Horsma J, Virolainen A, Jalava J, Ibrahem S, Antikainen J, Mero S, Tarkka E, Vaara M, Tissari P (2011) Comparison of repetitive extragenic palindromic sequence-based PCR with PCR ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in studying the clonality of Clostridium difficile. Clin Microbiol Infect 17:166–175. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03221.x
Acknowledgments
Sointu Mero is gratefully acknowledged for her help in performing the reproducibility studies described in this paper and participating in the DiversiLab strain typing process. Additionally, we thank Nina Elomaa for her help in the epidemiological data analysis. This study was supported by the EVO Fund and the Emil Aaltonen Foundation. The results were presented, in part, at the 1st International Conference on Prevention and Infection Control (ICPIC), June/July 2011, Geneva, Switzerland, Poster no. 176.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirvonen, J.J., Pasanen, T., Tissari, P. et al. Outbreak analysis and typing of MRSA isolates by automated repetitive-sequence-based PCR in a region with multiple strain types causing epidemics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31, 2935–2942 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1644-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1644-4