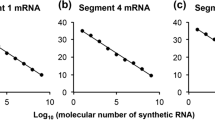
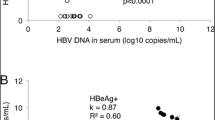
Abstract
The replication of hepatitis A virus (HAV) is via a complementary negative-strand RNA. Each negative strand may serve as a template for the synthesis of many positive strands. The aim of this study was to detect the intermediate replicative (negative strand) of HAV in order to monitor its replication in vitro and in vivo. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was standardized to detect the intermediate replicative of HAV in cell culture and liver from non-human primates infected experimentally. HAV primers from the 5′ non-translated region and VP3 were used in the cDNA synthesis of negative-strand RNA. The negative strand was detected in the infected cell lines and liver by highly strand-specific rTth recombinant Thermus thermophilus DNA polymerase reverse transcription followed by quantitative PCR. The results indicate that the negative-strand HAV RNA can be detected in vivo and in vitro. This model is an approach for assessing the dynamic patterns of replication and should represent a valuable tool for the monitoring of HAV replications in cell cultures and for the evaluation of experimental infections in animal models.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujiwara K, Yokosuka O, Fukai K, Imazeki F, Saisho H, Omata M (2001) Analysis of full-length hepatitis A virus genome in sera from patients with fulminant and self-limited acute type A hepatitis. J Hepatol 35:112–119. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(01)00074-5
Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C, Cainelli F, Casali F, Ghironzi G, Ferraro T, Concia E (1998) Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med 338:286–290. doi:10.1056/NEJM199801293380503
Gamarnik AV, Andino R (1998) Switch from translation to RNA replication in a positive-stranded RNA virus. Genes Dev 12:2293–2304. doi:10.1101/gad.12.15.2293
Kräusslich HG, Wimmer E (1988) Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem 57:701–754. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413
Carrasco L, Otero MJ, Castrillo JL (1989) Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther 40:171–212. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-X
Palmenberg AC (1990) Proteolytic processing of picornaviral polyprotein. Annu Rev Microbiol 44:603–623. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003131
Wimmer E, Kuhn RJ, Pincus S, Yang CF, Toyoda H, Nicklin MJ, Takeda N (1987) Molecular events leading to picornavirus genome replication. J Cell Sci Suppl 7:251–276
Semler BL, Kuhn RJ, Wimmer E (1988) Replication of the poliovirus genome. In: Domingo E, Holland JJ, Ahlquist P (eds) RNA genetics. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 23–48
Bishop NE, Anderson DA (2000) Uncoating kinetics of hepatitis A virus virions and provirions. J Virol 74:3423–3426. doi:10.1128/JVI.74.7.3423-3426.2000
Daemer RJ, Feinstone SM, Gust ID, Purcell RH (1981) Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun 32:388–393
Pinto MA, Marchevsky RS, Baptista ML, de Lima MA, Pelajo-Machado M, Vitral CL, Kubelka CF, Pissurno JW, Franca MS, Schatzmayr HG, Gaspar AM (2002) Experimental hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection in Callithrix jacchus: early detection of HAV antigen and viral fate. Exp Toxicol Pathol 53:413–420. doi:10.1078/0940-2993-00212
Hammitt LL, Bulkow L, Hennessy TW, Zanis C, Snowball M, Williams JL, Bell BP, McMahon BJ (2008) Persistence of antibody to hepatitis A virus 10 years after vaccination among children and adults. J Infect Dis 15:1776–1782. doi:10.1086/593335
Jiang YJ, Liao GY, Zhao W, Sun MB, Qian Y, Bian CX, Jiang SD (2004) Detection of infectious hepatitis A virus by integrated cell culture/strand-specific reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J Appl Microbiol 97:1105–1112. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02413.x
Jothikumar N, Cromeans TL, Sobsey MD, Robertson BH (2005) Development and evaluation of a broadly reactive TaqMan assay for rapid detection of hepatitis A virus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3359–3363. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.6.3359-3363.2005
Sánchez G, Populaire S, Butot S, Putallaz T, Joosten H (2006) Detection and differentiation of human hepatitis A strains by commercial quantitative real-time RT-PCR tests. J Virol Methods 132:160–165. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.10.010
Yuki N, Matsumoto S, Tadokoro K, Mochizuki K, Kato M, Yamaguchi T (2006) Significance of liver negative-strand HCV RNA quantitation in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 44:302–309. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.10.014
Gaspar AM, Vitral CL, Yoshida CF, Schatzmayr HG (1992) Primary isolation of a Brazilian strain of hepatitis A virus (HAF-203) and growth in a primate cell line (FRhK-4). Braz J Med Biol Res 25:697–705
De Paula VS, Diniz-Mendes L, Villar LM, Luz SL, Silva LA, Jesus MS, da Silva NM, Gaspar AMC (2007) Hepatitis A virus in environmental water samples from the Amazon Basin. Water Res 41:1169–1176. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.11.029
De Chastonay J, Siegl G (1987) Replicative events in hepatitis A virus-infected MRC-5 cells. Virology 157:268–275. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(87)90269-8
Anderson DA, Ross BC, Locarnini SA (1988) Restricted replication of hepatitis A virus in cell culture: encapsidation of viral RNA depletes the pool of RNA available for replication. J Virol 62:4201–4206
Agnès F, Crance JM, Lévêque F (1994) Separate detection of the two complementary RNA strands of hepatitis A virus. J Virol Methods 49:323–330. doi:10.1016/0166-0934(94)90147-3
Chaves RL, Graff J, Normann A, Flehmig B (1994) Specific detection of minus strand hepatitis A virus RNA by Tail-PCR following reverse transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 25:1919–1920. doi:10.1093/nar/22.10.1919
Takeda Y, Ashida M, Hamada C (1996) Growth of hepatitis A virus in murine cells. Acta Virol 40:201–208
Schmitz G, Dotzauer A (1998) Proof of hepatitis A virus negative-sense RNA by RNA/DNA-hybrid detection: a method for specific detection of both viral negative- and positive-strand RNA species. Nucleic Acids Res 26:5230–5232. doi:10.1093/nar/26.22.5230
Giachetti C, Semler BL (1991) Role of a viral membrane polypeptide in strand-specific initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis. J Virol 65:2647–2654
Novak JE, Kirkegaard K (1991) Improved method for detecting poliovirus negative strands used to demonstrate specificity of positive-strand encapsidation and the ratio of positive to negative strands in infected cells. J Virol 65:3384–3387
Barton DJ, Morasco BJ, Flanegan JB (1999) Translating ribosomes inhibit poliovirus negative-strand RNA synthesis. J Virol 73:10104–10112
Racaniello VR (2001) Picornaviridae: their viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE (eds) Fields virology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 796–838
Mourani S, Dobbs SM, Genta RM, Tandon AK, Yoffe B (1994) Hepatitis A virus-associated cholecystitis. Ann Intern Med 120:398–400
Cho MW, Ehrenfeld E (1991) Rapid completion of the replication cycle of hepatitis A virus subsequent to reversal of guanidine inhibition. Virology 180:770–780. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(91)90090-X
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Financiadora de Estudos e Projeto (FINEP). We thank Heloisa Maria Nogueira Diniz of the Serviço de Produção e Tratamento de Imagem, IOC/Fiocruz, for the PCR schematic drawing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Paula, V.S., Perse, A.S., Amado, L.A. et al. Kinetics of hepatitis A virus replication in vivo and in vitro using negative-strand quantitative PCR. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28, 1167–1176 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0759-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0759-8