Abstract
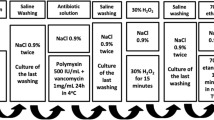
Bone allografts retrieved from multi-organ donors can be decontaminated with minimally aggressive methods. Therefore, we evaluated the efficacy of antibiotics and antiseptics in the decontamination of bone fragments actively contaminated with coagulase-negative staphylococci. Gentamicin (512/1,024 μg/mL), rifampicin (400/1,000 μg/mL), chlorhexidine in alcohol and chlorhexidine soap were tested with different contact times and temperatures and a delay in starting decontamination. Gentamicin-susceptible strains dried on bone could be removed by gentamicin 512 μg/mL after 19 h of contact, while strains not dried on bone could be eliminated by soaking bone for 60 min in gentamicin 512 μg/mL. Rifampicin-susceptible strains could be eliminated by soaking bone for 60 min in rifampicin 1,000 μg/mL. In none of the experimental conditions could gentamicin/rifampicin-resistant staphylococci be eliminated. Antiseptics could not eliminate staphylococci from bone. Different antibiotics need different protocols in order to decontaminate bone allografts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Commission Directive 2006/17/EC of 8 February 2006 implementing Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards certain technical requirements for the donation, procurement and testing of human tissues and cells. Official Journal of the European Union 9.2.2006. Available online at: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/site/en/oj/2006/l_038/l_03820060209en00400052.pdf
Deijkers RLM, Bloem RM, Petit PLC et al (1997) Contamination of bone allografts: analysis of incidence and predisposing factors. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:161–166. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.79B1.7137
Veen MR (1994) Decontamination of bacterially contaminated bone grafts. In: Veen MR (ed) Bone allografts. A study into bacterial contamination, sensitivity of cultures, decontamination, and contribution to postoperative infection. PhD thesis, Leiden, The Netherlands, pp 73–89
Eastlund T, Strong DM (2004) Infectious disease transmission through tissue transplantation. In: Phillips G (ed) Advances in tissue banking, vol. 7, 1st edn. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp 51–133
Lord CF, Gebhardt MC, Tomford WW, Mankin HJ (1988) Infection in bone allografts. Incidence, nature, and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:369–376
Hirn M, Laitinen M, Pirkkalainen S, Vuento R (2004) Cefuroxime, rifampicin and pulse lavage in decontamination of allograft bone. J Hosp Infect 56:198–201. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2003.12.014
Burd T, Conroy BP, Meyer SC, Allen WC (2000) The effects of chlorhexidine irrigation solution on contaminated bone-tendon allografts. Am J Sports Med 28:241–244
Peters G, Locci R, Pulverer G (1982) Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis 146:479–482
Craig WA, Gudmundsson S (1996) Postantibiotic effect. In: Lorian V (ed) Antibiotics in laboratory medicine, 4th edn. Williams and Wilkins, New York, p 304
Cremieux A, Freney J, Davin-Regli A (2001) Methods of testing disinfectants. In: Block SS (ed) Disinfection, sterilization, and preservation, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1305–1329
Acknowledgement
This study was granted by the Research Foundation—Flanders.
There are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
V.S.M. Saegeman is an Aspirant Researcher of the Fund for Scientific Research—Flanders.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saegeman, V.S.M., Ectors, N.L., Lismont, D. et al. Effectiveness of antibiotics and antiseptics on coagulase-negative staphylococci for the decontamination of bone allografts. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28, 813–816 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0715-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0715-7