Abstract
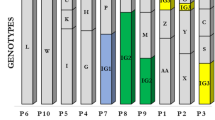
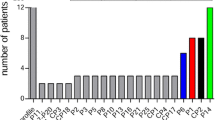
Pseudomonas aeruginosa accounts for about one half of all pulmonary infections of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. In this study, we analyzed 135 P. aeruginosa strains isolated from the expectorations of 55 CF adult patients attending a CF referral center over a period of five years. We assessed the genotype of the strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and analyzed some phenotypic characteristics, such as O serotype, enzyme and mucous production, antibiotics susceptibility, and motility. PFGE allowed the typification of 97.1% of strains, revealing the presence of nine different genomic patterns. The pattern indicated as B was the most frequent, whereas patterns H and I were the most uncommon. Serotyping failed to identify 37.8% of strains and 29 out of 55 patients harbored almost one non-typable (NT) strain. During the five years of the study, we observed a progressive reduction of O6 and O10 types, but an increase of the O1 type and of NT strains. Most strains produced protease, hemolysin, and gelatinase, and were mobile. Several patients harbored the same serotype or genotype in sequential isolates, though characterized by a different susceptibility to antimicrobials. We did not observe a relationship between bacterial genotype and phenotype. This could be due to the fact that PFGE is not sensitive enough to detect subtle genotypic differences. The epidemiological importance of the genotypic characterization of bacteria-colonizing CF subjects and the surveillance measures to be adopted in CF centers are briefly discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sener B, Köseoğlu O, Ozcelik U, Kocagöz T, Günalp A (2001) Epidemiology of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosis. Int J Med Microbiol 291:387–393
Juan C, Gutiérrez O, Oliver A, Ayerstarán JI, Borrell N, Pérez JL (2005) Contribution of clonal dissemination and selection of mutants during therapy to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial resistance in an intensive care unit setting. Clin Microbiol Infect 11:887–892
Van Daele SG, Franckx H, Verhelst R, Schelstraete P, Haerynck F, Van Simaey L, Claeys G, Vaneechoutte M, de Baets F (2005) Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis rehabilitation centre. Eur Respir J 25:474–481
Garaizar J, Latorre M, López-Molina N, Laconcha I, Alberdi L, Rementeria A, Audicana A, Uliarte R, Cisterna R (1997) Computerized restriction endonuclease analysis compared with O-serotype and phage type in the epidemiologic fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Clin Microbiol Infect 3:222–228
Renders N, Römling U, Verbrugh H, van Belkum A (1996) Comparative typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by random amplification of polymorphic DNA or pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA macrorestriction fragments. J Clin Microbiol 34:3190–3195
Ruiz L, Domínguez A, Ruiz N, Viñas M (2004) Relationship between clinical and environmental isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a hospital setting. Arch Med Res 35:251–257
Jelsbak L, Johansen HK, Frost A, Thøgersen R, Thomsen LE, Ciofu O, Yang L, Haagensen JA, Høiby N, Molin S (2007) Molecular epidemiology and dynamics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations in lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun 75:2214–2224
Johnson JK, Arduino SM, Stine OC, Johnson JA, Harris AD (2007) Multilocus sequence typing compared to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for molecular typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 45:3707–3712
Jones AM, Govan JRW, Doherty CJ, Dodd ME, Isalska BJ, Stanbridge TN, Webb K (2001) Spread of a multiresistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an adult cystic fibrosis clinic. Lancet 358:557–558
Armstrong DS, Nixon GM, Carzino R, Bigham A, Carlin JB, Robins-Browne RM, Grimwood K (2002) Detection of a widespread clone of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a pediatric cystic fibrosis clinic. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:983–987
Jones AM, Govan JRW, Doherty CJ, Dodd ME, Isalska BJ, Stanbridge TN, Webb AK (2003) Identification of airborne dissemination of epidemic multiresistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at a CF centre during a cross infection outbreak. Thorax 58:525–527
Römling U, Kader A, Sriramulu DD, Simm R, Kronvall G (2005) Worldwide distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clone C strains in the aquatic environment and cystic fibrosis patients. Environ Microbiol 7:1029–1038
Finnan S, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F, Boyd EF (2004) Genome diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients and the hospital environment. J Clin Microbiol 42:5783–5792
Fraser GM, Hughes C (1999) Swarming motility. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:630–635
Rashid MH, Kornberg A (2000) Inorganic polyphosphate is needed for swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4885–4890
Beatson SA, Whitchurch CB, Sargent JL, Levesque RC, Mattick JS (2002) Differential regulation of twitching motility and elastase production by Vfr in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:3605–3613
Overhage J, Bains M, Brazas MD, Hancock RE (2008) Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a complex adaptation leading to increased production of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance. J Bacteriol 190:2671–2679
Deretic V, Schurr MJ, Yu H (1995) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, mucoidy and the chronic infection phenotype in cystic fibrosis. Trends Microbiol 3:351–356
Yagci A, Tuc Y, Soyletir G (2002) Elastase and alkaline protease production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: comparison of two procedures. New Microbiol 25:223–229
Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS, Christmas JW, Prince AS (2005) Pathogen-host interactions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 171:1209–1223
Burke V, Robinson JO, Richardson CJ, Bundell CS (1991) Longitudinal studies of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Pathology 23:145–148
Rust L, Messing CR, Iglewski BH (1994) Elastase assays. Methods Enzymol 235:554–562
Allice T, Scutera S, Chirillo MG, Savoia D (2006) Burkholderia respiratory tract infections in Italian patients with cystic fibrosis: molecular characterization. J Infect 53:159–165
Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, Swaminathan B (1995) Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol 33:2233–2239
Hunter PR, Gaston MA (1988) Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol 26:2465–2466
Merlo CA, Boyle MP, Diener-West M, Marshall BC, Goss CH, Lechtzin N (2007) Incidence and risk factors for multiple antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Chest 132:562–568
Lambiase A, Raia V, Del Pezzo M, Sepe A, Carnovale V, Rossano F (2006) Microbiology of airway disease in a cohort of patients with cystic fibrosis. BMC Infect Dis 6:4
Valenza G, Tappe D, Turnwald D, Frosch M, König C, Hebestreit H, Abele-Horn M (2008) Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from sputa of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros 7:123–127
Millesimo M, de Intinis G, Chirillo MG, Musso T, Savoia D (1996) Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates: serotypes, resistance phenotypes and plasmid profiles. Eur J Epidemiol 12:123–129
Fonseca AP, Correia P, Sousa JC, Tenreiro R (2007) Association patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates as revealed by virulence traits, antibiotic resistance, serotype and genotype. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51:505–516
Tingpej P, Smith L, Rose B, Zhu H, Conibear T, Al Nassafi K, Manos J, Elkins M, Bye P, Willcox M, Bell S, Wainwright C, Harbour C (2007) Phenotypic characterization of clonal and nonclonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from lungs of adults with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol 45:1697–1704
Lee B, Haagensen JA, Ciofu O, Andersen JB, Høiby N, Molin S (2005) Heterogeneity of biofilms formed by nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol 43:5247–5255
Fluit AC, Verhoef J, Schmitz F-J; European SENTRY Participants (2000) Antimicrobial resistance in European isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 19:370–374
Vosahlikova S, Drevinek P, Cinek O, Pohunek P, Maixnerova M, Urbaskova P, van den Reijden TJK, Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A (2007) High genotypic diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis in the Czech Republic. Res Microbiol 158:324–329
Golini G, Favari F, Marchetti F, Fontana R (2004) Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of levofloxacin against clinical isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:798–800
Struelens MJ; Members of the ESGEM of the ESCMID (1996) Consensus guidelines for appropriate use and evaluation of microbial epidemiologic typing system. Clin Microbiol Infect 2:1–11
Agodi A, Sciacca A, Campanile F, Messina C, Barchitta M, Sciacca S, Stefani S (2000) Molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis in Sicily: genome macrorestriction analysis and rapid PCR-ribotyping. New Microbiol 23:319–327
Ciofu O, Riis B, Pressler T, Poulsen HE, Høiby N (2005) Occurrence of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients is associated with the oxidative stress caused by chronic lung inflammation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:2276–2282
Foweraker JE, Laughton CR, Brown DFJ, Bilton D (2005) Phenotypic variability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sputa from patients with acute infective exacerbation of cystic fibrosis and its impact on the validity of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:921–927
Römling U, Schmidt KD, Tümmler B (1997) Large genome rearrangements discovered by the detailed analysis of 21 Pseudomonas aeruginosa clone C isolates found in environment and disease habitats. J Mol Biol 271:386–404
Saiman L, Siegel J (2004) Infection control in cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:57–71
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca (MIUR; ex-60% funds) and the Piemonte Region, Italy (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leone, I., Chirillo, M.G., Raso, T. et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27, 1093–1099 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-008-0551-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-008-0551-1