Abstract
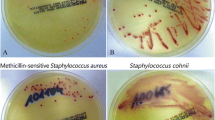
The absence of a reliable method to distinguish among coagulase negative staphylococcal strains in mixed culture hinders elucidation of colonization traits and precise tracking of colonization. This study examined whether colonial morphology could be used to correctly identify coagulase negative staphylococcal strains in mixed cultures. Staphylococci were isolated from nasal and hand cultures of ten subjects at 0 and 3 months. Samples were initially screened for the predominant coagulase negative staphylococcal strain by colonial morphology. The strains were subsequently identified by phenotypic and biochemical testing. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis demonstrated that the morphologic criteria correctly grouped the strains in 91.1% (41/45) of samples. This study suggests that colonial morphology is a reliable method for the initial characterization of coagulase negative staphylococcal strains. This approach has potential value for epidemiological studies that involve establishing links between commensal flora and their potential role as pathogens in subsequent clinical infections.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kloos WE, Bannerman TL (1994) Update on clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev 7:117–140
von Eiff C, Peters G, Heilmann C (2002) Pathogenesis of infections due to coagulase-negative staphylococci. Lancet Infect Dis 2:677–685
Seo SK, Venkataraman L, DeGirolami PC, Samore MH (2000) Molecular typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci from blood cultures does not correlate with clinical criteria for true bacteremia. Am J Med 109:697–704
Hu L, Umeda A, Kondo S, Amako K (1995) Typing of Staphylococcus aureus colonizing human nasal carriers by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Med Microbiol 42:127–132
Van Wijngaerden E, Peetermans WE, Van Lierde S, Van Eldere J (1997) Polyclonal staphylococcus endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 25:69–71
Van Eldere J, Peetermans WE, Struelens M, Deplano A, Bobbaers H (2000) Polyclonal staphylococcal endocarditis caused by genetic variability. Clin Infect Dis 31:24–30
Sharma M, Riederer K, Johnson LB, Khatib R (2001) Molecular analysis of coagulase-negative staphylococcus isolates from blood cultures: prevalence of genotypic variation and polyclonal bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 33:1317–1323
Huebner J, Goldmann DA (1999) Coagulase-negative staphylococci: role as pathogens. Annu Rev Med 50:223–236
Qamer S, Sandoe JA, Kerr KG (2003) Use of colony morphology to distinguish different enterococcal strains and species in mixed culture from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 41:2644–2646
Silva FR, Mattos EM, Coimbra MV, Ferreira-Carvalho BT, Figueiredo AM (2001) Isolation and molecular characterization of methicillin resistant coagulase negative staphylococci from nasal flora of healthy humans at three community institutions in Rio de Janeiro City. Epidemiol Infect 127:57–62
Tacconelli E, Carmeli Y, Aizer A, Ferreira G, Foreman MG, D’Agata EM (2003) Mupirocin prophylaxis to prevent Staphylococcus aureus infection in patients undergoing dialysis: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 37:1629–1638
Hanssen AM, Kjeldsen G, Sollid JU (2004) Local variants of Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in sporadic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci: evidence of horizontal gene transfer? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:285–296
Wisplinghoff H, Rosato AE, Enright MC, Noto M, Craig W, Archer GL (2003) Related clones containing SCCmec type IV predominate among clinically significant Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3574–3579
Gustafsson I, Cars O, Andersson DI (2003) Fitness of antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis assessed by competition on the skin of human volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother 52(2):258–263
Larson E, Aiello A, Lee LV, Della-Latta P, Gomez-Duarte C, Lin S (2003) Short- and long-term effects of handwashing with antimicrobial or plain soap in the community. J Commun Health 28:139–150
Cespedes C, Miller M, Quagliarello B, Vavagiakis P, Klein RS, Lowy FD (2002) Differences between Staphylococcus aureus isolates from medical and nonmedical hospital personnel. J Clin Microbiol 40:2594–2597
Koneman E (1997) Color atlas and textbook of diagnostic microbiology, 5th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Hebert GA, Crowder CG, Hancock GA, Jarvis WR, Thornsberry C (1988) Characteristics of coagulase-negative staphylococci that help differentiate these species and other members of the family Micrococcaceae. J Clin Microbiol 26:1939–1949
Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, Swaminathan B (1995) Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol 33:2233–2239
Kloos W (1997) Taxonomy and systematics of staphylococci indigenous to humans. In: Crossley KB, Archer G (eds) The staphylococci in human disease. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 113–137
Villari P, Sarnataro C, Iacuzio L (2000) Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus epidermidis in a neonatal intensive care unit over a three-year period. J Clin Microbiol 38:1740–1746
de Silva GD, Justice A, Wilkinson AR, Buttery J, Herbert M, Day NP, Peacock SJ (2001) Genetic population structure of coagulase-negative staphylococci associated with carriage and disease in preterm infants. Clin Infect Dis 33:1520–1528
Monsen T, Karlsson C, Wistrom J (2005) Spread of clones of multidrug-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci within a university hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 26:76–80
Miragaia M, Couto I, Pereira SF, Kristinsson KG, Westh H, Jarlov JO, Carrico J, Almeida J, Santos-Sanches I, de Lencastre H (2002) Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis clones: evidence of geographic dissemination. J Clin Microbiol 40:430–438
Ben-Ami R, Navon-Venezia S, Schwartz D, Carmeli Y (2003) Infection of a ventriculoatrial shunt with phenotypically variable Staphylococcus epidermidis masquerading as polymicrobial bacteremia due to various coagulase-negative Staphylococci and Kocuria varians. J Clin Microbiol 41:2444–2447
Ziebuhr W, Heilmann C, Gotz F, Meyer P, Wilms K, Straube E, Hacker J (1997) Detection of the intercellular adhesion gene cluster (ica) and phase variation in Staphylococcus epidermidis blood culture strains and mucosal isolates. Infect Immun 65:890–896
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Public Health Grants DA-09655 and DA-15018 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)—Specialized Center for Clinically Oriented Research (SCCOR) grant HL 077096-01 named “The Biology of Human Long-Term Mechanical Circulatory Support”.
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Phil Gialanella, Heather Cook, and Peter Vavagiakis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Locke, B.J., Lowy, F.D. Use of colony morphology to characterize carriage profiles of coagulase negative staphylococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 26, 895–899 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-007-0387-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-007-0387-0