Abstract
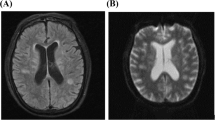
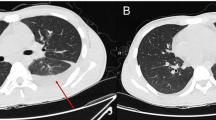
Presented here is the case of a 27-year-old male with atypical features of Lemierre’s syndrome in which a definitive diagnosis was achieved using molecular methods. While routine investigations, including bacterial cultures, were unhelpful, two real-time PCR assays demonstrated Fusobacterium necrophorum-specific DNA in aspirates from brain and renal abscesses. This is the first report demonstrating that a laboratory diagnosis can be made using molecular methods in suspected cases of Lemierre’s syndrome. Use of these methods can thus resolve diagnostic confusion, prevent unnecessary investigation, and direct specific antimicrobial treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lemierre A (1936) On certain septicaemias due to anaerobic organisms. Lancet 1:701–703
Sinave CP, Hardy GJ, Fardy PW (1989). The Lemierre syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 68:85–94
Brazier JS (2002) Fusobacterium necrophorum infections in man. Rev Med Microbiol 13:141–149
Hodgson AL, Nicholson LA, Doran TJ, Corner LA (1993) Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of Fusobacterium necrophorum using a novel repeat DNA sequence and a 16S rRNA gene probe. FEMS Microbiol Lett 107:205–210
Narayanan S, Nagaraja TG, Okwumabua O, Staats J, Chengappa MM, Oberst RD (1997) Ribotyping to compare Fusobacterium necrophorum isolates from bovine liver abscesses, ruminal walls, and ruminal contents. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4671–4678
Nicholson LA, Morrow CJ, Corner LA, Hodgson AL (1994) Phylogenetic relationship of Fusobacterium necrophorum A, AB, and B biotypes based upon 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:315–319
Narongwanichgarn W, Misawa N, Jin JH, Amoako KK, Kawaguchi E, Shinjo T, Haga T, Goto Y (2003) Specific detection and differentiation of two subspecies of Fusobacterium necrophorum by PCR. Vet Microbiol 91:183–195
Aliyu SH, Marriott RK, Curran MD, Parmar S, Bentley N, Brown NM, Brazier JS, Ludlam H (2004) Real-time PCR investigation into the importance of Fusobacterium necrophorum as a cause of acute pharyngitis in general practice. J Med Microbiol 53:1029–1035
Fredricks DN, Relman DA (1998) Improved amplification of microbial DNA from blood cultures by removal of the PCR inhibitor sodium polyanetholesulfonate. J Clin Microbiol 36:2810–2816
Harris KA, Hartley JC (2003) Development of broad-range 16S rDNA PCR for use in the routine diagnostic clinical microbiology service. J Med Microbiol 52:685–691
Brazier JS, Hall V, Yusuf E, Duerden BI (2002) Fusobacterium necrophorum infections in England and Wales 1990-2000. J Med Microbiol 51:269–272
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to Dr. J. Brazier of the Anaerobe Reference Laboratory, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff, Wales, UK, for the help and advice he offered in the preparation of this manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliyu, S.H., Yong, P.F.K., Newport, M.J. et al. Molecular diagnosis of Fusobacterium necrophorum infection (Lemierre’s syndrome). Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 24, 226–229 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-005-1298-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-005-1298-6