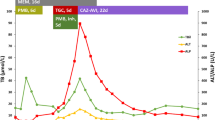
Abstract
Fulminant hepatic failure is an uncommon but life-threatening adverse reaction to antibiotic therapy. Reported here is a case of severe liver injury associated with ciprofloxacin administered for treatment of a gram-negative infection in a 79-year-old female. The patient presented with metabolic acidosis 48 hours after the first ciprofloxacin intake. Symptoms resolved after cessation of ciprofloxacin therapy. This report highlights an uncommon side effect of a commonly used antimicrobial agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfson JS, Hooper DC (1991) Overview over fluoroquinolone safety. Am J Med 91:153–161
Contreras MA, Luna R, Mulero J, Andreu JL (2001) Severe ciprofloxacin-induced acute hepatitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 20:434–435
Hautekeete ML, Kockx MM, Naegels S, Holvoet JK, Hubens H, Klöppel G (1995) Cholestatic hepatitis related to quinolones: a report of two cases. J Hepatol 23:759–760
Fuchs S, Simon Z, Brezis M (1994) Fatal hepatic failure associated with ciprofloxacin. Lancet 343:738–739
Grassmick BK, Lehr VT, Sundareson AS (1992) Fulminant hepatic failure possibly related to ciprofloxacin. Ann Pharmacother 26:636–639
Gruchalla RS (2000) Clinical assessment of drug-induced disease. Lancet 356:1505–1511
Benichou C (1990) Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol 11:272–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goetz, M., Galle, P.R. & Schwarting, A. Non-Fatal Acute Liver Injury Possibly Related to High-Dose Ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22, 294–296 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-0914-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-0914-6