Abstract.
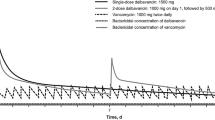
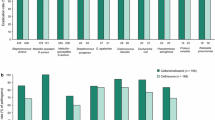
The vast majority of community-acquired skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) are caused by gram-positive cocci or are polymicrobial in nature. Hospital-acquired SSTIs are caused by gram-positive cocci in more than 50% of patients. Multidrug-resistant gram-positive cocci are rarely associated with community-acquired SSTIs but are frequently found in hospital-acquired SSTIs. Linezolid is the first member of a new class of antibiotics, the oxazolidinones. These antimicrobial agents have a unique mechanism of action and exhibit excellent activity against a variety of gram-positive organisms, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Linezolid is 100% orally absorbed, allowing for easy intravenous-to-oral continuation therapy. There is considerable clinical experience with the use of linezolid in SSTIs in phase II and III clinical trials. In comparative trials, linezolid was as effective as oxacillin-dicloxacillin or flucloxacillin in patients with complicated SSTIs caused by gram-positive organisms. Linezolid was also associated with significantly earlier hospital discharge than comparator agents among patients with SSTIs. It was equally effective as vancomycin in patients with SSTIs caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and has also demonstrated efficacy in patients with SSTIs caused by vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Linezolid is well tolerated: the most common adverse events (gastrointestinal effects, headache) are reported in frequencies similar to those reported for comparator agents. Myelosuppression has been reported after prolonged administration but is reversible after discontinuation of the drug. Overall, linezolid has favorable efficacy and safety profiles and will be an increasingly useful option for the treatment of SSTIs, particularly those due to multidrug-resistant, gram-positive organisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hau, .T. Efficacy and Safety of Linezolid in the Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 21, 491–498 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0753-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0753-x