Abstract
Background
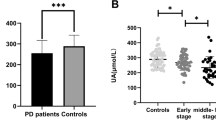
Uric acid is a natural antioxidant and it has been shown that low levels of uric acid may be a risk factor for the development of Parkinson’s disease. We aimed to investigate the relationship between uric acid and improvement of motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation.
Methods
We analyzed the correlation between serum uric acid levels in 64 patients with Parkinson’s disease and the rate of improvement of motor symptoms 2 years after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation.
Results
A non-linear correlation was observed between uric acid levels and the rate of motor symptom improvement after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation, during both the drug-off and drug-on periods.
Conclusions
Uric acid is positively associated with the rate of motor symptom improvement in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation within a certain range.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okun MS (2012) Deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 367:1529–1538
Habets JGV, Heijmans M, Kuijf ML, Janssen MLF, Temel Y, Kubben PL (2018) An update on adaptive deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 33:1834–1843
Jahanshahi M, Leimbach F, Rawji V. Short and long-term cognitive effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease and identification of relevant factors. J Parkinsons Dis 2022 Online ahead of print.
Seifar F, Dinasarapu AR, Jinnah HA. Uric acid in Parkinson’s disease: what is the connection? Mov Disord 2022 Online ahead of print.
Shi X, Zheng J, Ma J, Wang Z, Sun W, Li M, Huang S, Hu S (2022) Low serum uric acid levels are associated with the nonmotor symptoms and brain gray matter volume in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 43:1747–1754
Zhang LL, Zhang L, Dong J, Zhao Y, Wang XP (2022) Factors contributing to malnutrition in Parkinson’s disease patients with freezing of gait. Front Neurol 13:816315
Kwok OM, Underhill AT, Berry JW, Luo W, Elliott TR, Yoon M (2008) Analyzing longitudinal data with multilevel models: an example with individuals living with lower extremity intra-articular fractures. Rehabil Psychol 53:370–386
Shek DT, Ma CM (2011) Longitudinal data analyses using linear mixed models in SPSS: concepts, procedures and illustrations. Sci World J 11:42–76
Dănău A, Dumitrescu L, Lefter A, Popescu BO (2022) Serum uric acid levels in Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional electronic medical record database study from a tertiary referral centre in Romania. Medicina (Kaunas) 58(2):245
Chang KH, Chen CM (2020) The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(7):597
Dionísio PA, Amaral JD, Rodrigues CMP (2021) Oxidative stress and regulated cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 67:101263
Tönnies E, Trushina E (2017) Oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 57:1105–1121
Lee YH, Chung SJ, Yoo HS, Lee Y, Sohn YH et al (2020) Gender-specific effect of urate on white matter integrity in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 75:41–47
Lee Y, Park YH, Lee JJ, Sohn YH, Lee JM, Lee PH (2018) Gender-specific effect of uric acid on resting-state functional networks in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 52:49–54
Prent N, Potters WV, Boon LI, Caan MWA, de Bie RMA, van den Munckhof P et al (2019) Distance to white matter tracts is associated with deep brain stimulation motor outcome in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosurg 26:1–10
Huang LC, Chen LG, Wu PA, Pang CY, Lin SZ, Tsai ST, Chen SY (2022) Effect of deep brain stimulation on brain network and white matter integrity in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 28:92–104
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all authors for this study.
Funding
This paper is supported by the Special Fund Project for Guiding Local Science and Technology Development by the Central Government (No.: 2019b07030001) and Doctoral Research Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of USTC (No.: RC2021121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BWC and CN jointly completed the experiment and the writing; CX, JMM, PC, and MLJ assisted in the writing and followed up patients. CSN took the overall control of the whole study. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
None.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, B., Ni, C., Mei, J. et al. Relationship between serum uric acid levels and the outcome of STN-DBS in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 44, 3913–3917 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06911-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06911-9