Abstract
Background
Imaging indicators of early neurological deterioration (END) in patients with acute isolated pontine infarctions (AIPI) remained ambiguous. We aimed to find more specific neuroimaging markers for the development of END in patients with AIPI.
Methods
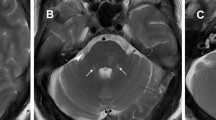
Patients with AIPI within 72 h of stroke onset were screened from a stroke database from January 2018 to July 2021 in the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. Clinical characteristics, laboratory tests, and imaging parameters were collected. The layers having the largest infarct area on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2 sequences were chosen. On the transverse plane of DWI and sagittal plane of T2-Flair images, the maximum length (a, m) and maximum width (b, n) vertical to the length of the infarcted lesions were measured respectively. On the sagittal plane of T2-Flair image, the maximum ventrodorsal length (f) and rostrocaudal thickness (h) were measured. On the sagittal plane, lesions were evenly split into upper, middle, and lower types based on the lesion’s location in the pons. The ventral and dorsal types of location were separated based on whether the ventral borders of the pons were involved on transvers plane. END was defined as a ≥2 point increase in the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) total score or a ≥1 point increase in the motor items within 72 h after admission. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to explore risk factors associated with END. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and the area under the curve (AUC) was performed to estimate the discriminative power and determine the optimal cut-off points of imaging parameters on the prediction of END.
Results
A total of 218 patients with AIPI were included in the final analysis. END occurred in 61 cases (28.0%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the ventral type of lesion location was associated with END in all models adjusted. In addition, in Model 1, b (odds ratio (OR) 1.145, 95% confidence interval (95% CI), 1.007–1.301) and n (OR 1.163, 95% CI 1.012–1.336); in Model 2, b*n (OR 1.010, 95% CI 1.002–1.018); in Model 3, n (OR 1.179, 95% CI, 1.028–1.353); and in Model 4, b (OR 1.143, 95% CI 1.006–1.298) and n (OR 1.167, 95% CI 1.016–1.341) were found to be associated with END respectively after different adjustments. ROC curve analysis with END showed that the AUC, the optimal cut-off value, and its sensitivity and specificity were 0.743 (0.671–0.815), 9.850 mm, and 68.9% and 79.0% for b; 0.724 (0.648–0.801), 10.800 mm, and 57.4% and 80.9% for n; and 0.772 (0.701–0.842), 108.274 mm2, and 62.3% and 85.4% for b*n, respectively (b*n vs b: P =0.213; b*n vs n: P =0.037; b vs n: P =0.645).
Conclusions
Our study revealed that besides the ventral type of lesion location, the maximum width of lesion on the transverse plane of DWI and sagittal plane of T2 image (b, n) may be imaging markers for the development of END in AIPI patients, and the product of the two (b*n) showed a better prediction value on the risks of END.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Dai Y, Wu H, Luo L, Wei L, Zhou L et al (2020) Predictors of early neurologic deterioration in acute pontine infarction. Stroke 51(2):637–640
Kato H, Takeda T, Ohara K, Tei H, Nishizawa E (2015) Rostrocaudal thickness on sagittal diffusion-weighted imaging as a predictor of motor deficits in an acute isolated pontine infarction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24(3):622–628
Gökçal E, Niftaliyev E, Baran G, Deniz Ç, Asil T (2017) Progressive deficit in isolated pontine infarction: the association with etiological subtype, lesion topography and outcome. Acta Neurol Belg 117(3):649–654
Oh S, Bang OY, Chung CS, Lee KH, Chang WH, Kim GM (2012) Topographic location of acute pontine infarction is associated with the development of progressive motor deficits. Stroke 43(3):708–713
Nakase T, Sasaki M, Ikeda Y, Suzuki A (2014) Progressing small vessel pontine infarction includes different etiologies. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 1(2):75–79
Song B, Fang H, Zhao L, Gao Y, Tan S, Lu J et al (2013) Validation of the ABCD3-I score to predict stroke risk after transient ischemic attack. Stroke 44(5):1244–1248
Kim JS, Lee JH, Im JH, Lee MC (1995) Syndromes of pontine base infarction. Clin-Radiol Correlation Study Stroke 26(6):950–955
Kim SK, Song P, Hong JM, Pak CY, Chung CS, Lee KH et al (2008) Prediction of progressive motor deficits in patients with deep subcortical infarction. Cerebrovasc Dis 25(4):297–303
Jeong HG, Kim BJ, Yang MH, Han MK, Bae HJ (2015) Neuroimaging markers for early neurologic deterioration in single small subcortical infarction. Stroke 46(3):687–691
Mattle HP, Arnold M, Lindsberg PJ, Schonewille WJ, Schroth G (2011) Basilar artery occlusion. Lancet Neurol 10(11):1002–1014
Catani M, Thiebaut de Schotten M (2008) A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex 44(8):1105–1132
Bodle JD, Feldmann E, Swartz RH, Rumboldt Z, Brown T, Turan TN (2013) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: an emerging tool for evaluating intracranial arterial disease. Stroke 44(1):287–292
Jang SH, Bai D, Son SM, Lee J, Kim DS, Sakong J et al (2008) Motor outcome prediction using diffusion tensor tractography in pontine infarct. Ann Neurol 64(4):460–465
Yinglin Liu, Hongmei Peng,etal.Risk factors for early neurological deterioration in acute isolated pontine infarction without any causative artery stenosis[J]. BMC Neurol (2022) 22:332.
Funding
This work was funded by the NHC Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cerebrovascular Disease, Henan Key Laboratory of Cerebrovascular Diseases Zhengzhou University, the Non-profit Central Research Institute and Major Science (2020-PT310-01), and Technology Projects of Henan Province in 2020 (Grant No. 201300310300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Project development: Yuan Gao, Yusheng Li, Bo Song, and Yuming Xu. Writing: Hongxun Yang. Data collection: Hongxun Yang, Ce Zong, Ke Zhang, and Hongbing Liu. Data analysis: Yapeng Li, Kai Liu, and Lulu Pei. Figures and tables: Anran Wang, Yunchao Wang, and Yan Ji. English editing help: Lu Zhao.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Our study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Ethics Review Number:2022-KY-1334-002).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary informations
ESM 1
(DOCX 461 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Liu, H., Zhang, K. et al. Neuroimaging markers of early neurological deterioration in acute isolated pontine infarction. Neurol Sci 44, 3607–3614 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06837-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06837-2