Abstract
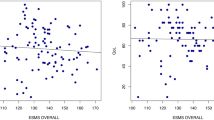
This study was conducted to determine the self-efficacy of patients diagnosed with epilepsy. This descriptive-correlational study was conducted between November-December 2020 with individuals diagnosed with epilepsy and living in the eastern province of Turkey. The sample of the study consisted of individuals diagnosed with epilepsy (101 persons) who were living in this province and agreed to participate in the study. According to the findings obtained from the study, the Epilepsy Self-efficacy Scale Total Mean Score of the individuals was found to be 226.38 ± 45.23. The scale does not have a cut-off point, and the total score that can be obtained from the scale varies between 0 and 310. An increase in the score obtained indicates high self-efficacy. It can be said that the self-efficacy levels of the sampled individuals are also high. It was found that there was a negative correlation between the first diagnosis age and the seizure management sub-dimension, and a positive statistically significant correlation between the age of the individuals and the age of the first seizure. The Epilepsy Self-efficacy Scale Total Mean Score of the individuals was found to be statistically high in those who received information regarding the disorder and used their drug/drugs regularly. It is suggested to conduct the study in larger groups. It is recommended to carry out studies to increase epilepsy self-efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirtz D, Thurman D, Gwinn HK, Mohamed M, Chaudhuri A, Zalutsky R (2007) How common are the “common” neurologic disorders? Neurology 68(5):326–337. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000252807.38124.a3
Gorgulu U, Fesci H (2011) Life with epilepsy: psychosocial effects of epilepsy. Med J 26:27–32. https://doi.org/10.5222/j.goztepetrh.2011.27
Elliott JO, Jacobson MP, Seals BF (2006) Self-efficacy, knowledge, health beliefs, quality of life, and stigma in relation to osteoprotective behaviors in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 9(3):478–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2006.07.007
Chen HF, Tsai YF, Lin YP, Shih MS, Chen JC (2010) The relationships among medicine symptom distress, self-efficacy, patient–provider relationship, and medication compliance in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 19(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.06.007
DiIorio C, Faherty B, Manteuffel B (1992a) The development and testing of an instrument to measure self-efficacy in individuals with epilepsy. J Neurosci Nurs 24(1):9–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/01376517-199202000-00004
Dogan N, Goris S, Demir H (2006) Pain and self-efficacy levels of individuals with osteoarthritis. J Pain 28(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.5505/agri.2015.30085
Unsal A, Kasikci M (2010) Effect of education on perceived self-efficacy for individuals with arthritis. Int J Caring Sci 3(1):3–11
Yanik YT, Erol O (2016) Evaluation of self-efficacy levels of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Anatolia Nursing Health Sci 19(3):166-174. 10.17049/ahsbd.22818
Bandura A (2004) Health promotion by social cognitive means. Health Educ Behav 31(2):143–164. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090198104263660
Kulakci H, Ayyildiz KT, Emiroglu ON, Koroglu E (2012) Evaluation of self-efficacy perceptions and healthy lifestyle behaviors of the elderly living in nursing home. Dokuz Eylul University Faculty of Nursing Electronic Journal 5:53–64
Bandura A (1995) Self-efficacy in changing societies. New York, NY, US. Cambridge University Press 1-45. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511527692
Gramstad A, Iversen E, Engelsen BA (2001) The impact of affectivity dispositions, self-efficacy and locus of control on psychosocial adjustment in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 46(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-1211(01)00261-3
Bandura A (1989) Regulation of cognitive processes through perceived self-efficacy. Developmental Psychology 25(5):729. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.25.5.729
Bandura A (1986) The explanatory and predictive scope of self-efficacy theory. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology 4(3):359–373. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.1986.4.3.359
DiIorio C, Faherty B, Manteuffel B (1992b) The relationship of self-efficacy and social support in self-management of epilepsy. West J Nurs Res 14(3):292–303. https://doi.org/10.1177/019394599201400303
DiIorio C, Shafer P, Letz R, Henry T, Schomer D, Yeager K (2003) The association of stigma with self-management and perceptions of health care among adults with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 4:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1525-5050(03)00103-3
Adadioglu O (2019) Determination of self-efficiency of patients with epilepsy. Dissertation, University of Marmara
Büyüköztürk Ş (2012) Testlerin geçerlik ve güvenirlik analizlerinde kullanılan bazı istatistikler. Sosyal bilimler için veri analizi el kitabı, 16. Baskı Pegem Akademi Yayıncılık, Ankara, sy. 167-171
Adadioglu O, Oguz S (2019) Impact of self-efficacy on epilepsy management. Int J Health Sci Res 8(5):393–397
Smith KW, McGraw SA, Costa LA, McKinley JB (1996) A self-efficacy scale for HIV risk behaviors: development and evaluation. AIDS Educ Prev 8(2):97–105
Şireci E, Karabulutlu EY (2017) Diabetes mellitus type II patients’ acceptance of illness and determination of self-efficacy levels for their care. Journal of Anatolian Nursing and Health Sciences 20(1):48–55
Dirik G, Sertel P, Kartal M (2011) The relationship of social support, self-efficacy and disability with psychological distress experienced by patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Duzce Med J 13(1):45–52
Abdelsalam Z, Abdel Rahman A, El Sayed Y, Mossa F (2010) Psychosocial stressors and self efficacy among adults diagnosed with epilepsy in Egypt. Egypt Nurs J 1(1July2010).
Ko JO, Lee MH (2017) Structural equation modeling on health-related quality of life in adults with epilepsy. J Korean Acad Nurs 47(5):624–637. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.624
Mollaoğlu M (2016) Epilepsy and care. Turkey Clinics J Intern Med Nurs-Special Topics 2(2):47–55
Aydemir N, Unsal P, Ozkara Ç (2011) Epilepsy-related attitudes, knowledge and information sources of individuals with epilepsy. Epilepsy 17(3):90–96
Senol MG, Gun I, Saracoglu M (2011) Patient’s viewpoint: information and understanding about epilepsy. Nobel Medicus 7(1):94–101
Lee SA, Lee BI, Group KQIES (2015) Association of knowledge about epilepsy with mood and self-efficacy in Korean people with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 52:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.08.027
Guven ST, Dalgic AI (2017) Antiepileptic medications used for children with epilepsy and the importance of nursing approach in medication administration. Int Ref J Nurs Res 9:188–207
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Agri Ibrahim Cecen University and conformed to the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
All patients signed informed consent forms
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yildirim, M.S., Yildiz, E. Determination of self-efficacy of patients diagnosed with epilepsy. Neurol Sci 43, 2709–2715 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05661-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05661-w