Abstract
Background
Clinical data on male neuromyelitis optica spectrum (NMO) patients remain limited to date.
Objective
To analyze clinical characteristics, therapeutic responses, and outcomes in Chinese male NMOSD patients.
Methods
We retrospectively assessed clinical, demographic, treatment, and outcome data of male patients with NMOSD.
Results
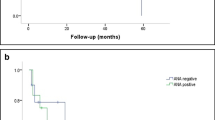
We identified 52 male patients among 471 NMOSD patients. Male patients had more frequent optic neuritis (ON) attacks and less frequent myelitis than female patients. No-remission rates of high-dose intravenous steroid therapy were higher in male patients than in female patients.
Conclusion
Male NMOSD patients had different clinical characteristics and worse response to high-dose intravenous steroid therapy than female patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wingerchuk DM, Banwell B, Bennett JL, Cabre P, Carroll W, Chitnis T, de Seze J, Fujihara K, Greenberg B, Jacob A, Jarius S, Lana-Peixoto M, Levy M, Simon JH, Tenembaum S, Traboulsee AL, Waters P, Wellik KE, Weinshenker BG, International Panel for NMO Diagnosis (2015) International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 85:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729
Banerjee A, Ng J, Coleman J, Ospina JP, Mealy M, Levy M (2019) Outcomes from acute attacks of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder correlate with severity of attack, age and delay to treatment. Mult Scler Relat Disord 28:60–63
Borisow N, Kleiter I, Gahlen A, Fischer K, Wernecke KD, Pache F, Ruprecht K, Havla J, Krumbholz M, Kümpfel T, Aktas O, Ringelstein M, Geis C, Kleinschnitz C, Berthele A, Hemmer B, Angstwurm K, Weissert R, Stellmann JP, Schuster S, Stangel M, Lauda F, Tumani H, Mayer C, Zeltner L, Ziemann U, Linker RA, Schwab M, Marziniak M, Then Bergh F, Hofstadt-van Oy U, Neuhaus O, Winkelmann A, Marouf W, Rückriem L, Faiss J, Wildemann B, Paul F, Jarius S, Trebst C, Hellwig K, NEMOS (Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group) (2017) Influence of female sex and fertile age on neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult. Scler. 23(8):1092–1103
Kim SM, Waters P, Woodhall M, Kim YJ, Kim JA, Cheon SY, Lee S, Jo SR, Kim DG, Jung KC, Lee KW, Sung JJ, Park KS (2017) Gender effect on neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with aquaporin4-immunoglobulin G. Mult. Scler. 23(8):1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458516674366
Kunchok A, Malpas C, Nytrova P, Havrdova EK, Alroughani R, Terzi M, Yamout B, Hor JY, Karabudak R, Boz C, Ozakbas S, Olascoaga J, Simo M, Granella F, Patti F, McCombe P, Csepany T, Singhal B, Bergamaschi R, Fragoso Y, Al-Harbi T, Turkoglu R, Lechner-Scott J, Laureys G, Oreja-Guevara C, Pucci E, Sola P, Ferraro D, Altintas A, Soysal A, Vucic S, Grand'Maison F, Izquierdo G, Eichau S, Lugaresi A, Onofrj M, Trojano M, Marriott M, Butzkueven H, Kister I, Kalincik T (2020) Clinical and therapeutic predictors of disease outcomes in AQP4-IgG+ neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult Scler Relat Disord 38:101868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2019.101868
Lin CW, Lin IH, Chen TC, Jou JR, Woung LC (2019) Clinical course and treatment response of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disease: an 8-year experience. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol 8(3):206–210. https://doi.org/10.22608/APO.2018247
Wingerchuk DM (2009) Neuromyelitis optica: effect of gender. J. Neurol. Sci. 286(1-2):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.045
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG (2006) Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 66(10):1485–1489
Kleiter I, Gahlen A, Borisow N, Fischer K, Wernecke KD, Wegner B, Hellwig K, Pache F, Ruprecht K, Havla J, Krumbholz M, Kümpfel T, Aktas O, Hartung HP, Ringelstein M, Geis C, Kleinschnitz C, Berthele A, Hemmer B, Angstwurm K, Stellmann JP, Schuster S, Stangel M, Lauda F, Tumani H, Mayer C, Zeltner L, Ziemann U, Linker R, Schwab M, Marziniak M, Bergh FT, Oy UH, Oliver Neuhaus 23, Alexander Winkelmann 24, Wael Marouf 25, Jürgen Faiss 3, Wildemann O, Paul F, Jarius S, Trebst C, Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group (2016) Neuromyelitis optica: evaluation of 871 attacks and 1153 treatment courses. Ann. Neurol. 79(2):206–216
Kleiter I, Gahlen A, Borisow N, Fischer K, Wernecke KD, Hellwig K, Pache F, Ruprecht K, Havla J, Kümpfel T, Aktas O, Hartung HP, Ringelstein M, Geis C, Kleinschnitz C, Berthele A, Hemmer B, Angstwurm K, Stellmann JP, Schuster S, Stangel M, Lauda F, Tumani H, Mayer C, Krumbholz M, Zeltner L, Ziemann U, Linker R, Schwab M, Marziniak M, Then Bergh F, Hofstadt-van Oy U, Neuhaus O, Zettl UK, Faiss J, Wildemann B, Paul F, Jarius S, Trebst C, NEMOS (Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group) (2016) Apheresis therapies for NMOSD attacks: a retrospective study of 207 therapeutic interventions. Neurol Neuroimunol Neuroinflamm 5(6):e504
Jeong IH, Kim HJ, Kim N-H, Jeong KS, Park CY (2016) Subclinical primary retinal pathology in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J. Neurol. 263(7):1343–1348
Cerghet M, Skoff RP, Swamydas M, Bessert D (2009) Sexual dimorphism in the white matter of rodents. J. Neurol. Sci. 286(1-2):76–80
Kitley J, Leite MI, Nakashima I, Waters P, McNeillis B, Brown R, Takai Y, Takahashi T, Misu T, Elsone L, Woodhall M, George J, Boggild M, Vincent A, Jacob A, Fujihara K, Palace J (2012) Prognostic factors and disease course in aquaporin-4 antibody positive patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder from the United Kingdom and Japan. Brain 135(Pt 6):1834–1849
Mao Z, Yin J, Zhong X, Zhao Z, Qiu W, Lu Z, Hu X (2015) Late-onset neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in AQP4-seropositive patients in a Chinese population. BMC Neurol. 15:160
Brotfain E, Gruenbaum SE, Boyko M, Kutz R, Zlotnik A, Klien M (2016) Neuroprotection by estrogen and progesterone in traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 14(6):641–653
Collongues N, Patte-Mensah C, De Seze J, Mensah-Nyagan AG, Derfuss T (2018) Testosterone and estrogen in multiple sclerosis: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 18(6):515–522
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Editage for the English language editing service.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81771300, 81971140, and 81901229), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (grant numbers 2017A030313853 and 2015A030310149), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (grant number 2019A1515010297), and Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (grant number 201904010444).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University approved this study. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Li, C., Mao, Z. et al. Male patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: different clinical characteristics and worse steroid treatment response. Neurol Sci 42, 3267–3274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04933-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04933-1