Abstract
Background and objective
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are relatively common in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Many studies have revealed that striatal monoamine availability is associated with specific neuropsychiatric symptoms. This study was aimed to investigate the association between comprehensive neuropsychiatric symptoms and striatal monoamine availability in patients with early PD without dementia.
Methods
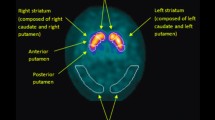
A total of 156 newly diagnosed patients with PD without dementia were included. All patients’ mental and behavioral problems were assessed with the 12-item Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI). They underwent positron emission tomography (PET) with 18F-N-(3-fluoropropyl)-2beta-carbon ethoxy-3beta-(4-iodophenyl) nortropane and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Patients were divided into no neuropsychiatric symptoms and neuropsychiatric symptoms groups according to total NPI score. After normalizing the PET images to spatially normalized MRI, regional standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) with a volume of interest template were analyzed for the two groups.
Results
Ninety-eight patients had more than one neuropsychiatric symptom. The SUVR of the thalamus in neuropsychiatric symptoms group was significantly lower than the SUVR in no neuropsychiatric symptoms group independent of age, sex, disease duration, or severity of motor symptoms.
Conclusion
Patients with early PD who have neuropsychiatric symptoms had a lower monoamine availability in the thalamus than those with no neuropsychiatric symptoms. This finding suggests that decreased monoamine transporter availability in the thalamus may be an imaging biomarker of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with PD.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 November 2020
The originally figure 1 was published online in black and white.
References
Aarsland D, Bronnick K, Alves G, Tysnes OB, Pedersen KF, Ehrt U, Larsen JP (2009) The spectrum of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with early untreated Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(8):928–930. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2008.166959
Aarsland D, Larsen JP, Lim NG, Janvin C, Karlsen K, Tandberg E, Cummings JL (1999) Range of neuropsychiatric disturbances in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67(4):492–496. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.67.4.492
Aarsland D, Bronnick K, Ehrt U, De Deyn PP, Tekin S, Emre M, Cummings JL (2007) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease and dementia: frequency, profile and associated care giver stress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2005.083113
Kulisevsky J, Pagonabarraga J, Pascual-Sedano B, Garcia-Sanchez C, Gironell A, Trapecio Group Study (2008) Prevalence and correlates of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Mov Disord 23(13):1889–1896. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22246
Wen MC, Chan LL, Tan LC, Tan EK (2016) Depression, anxiety, and apathy in Parkinson’s disease: insights from neuroimaging studies. Eur J Neurol 23(6):1001–1019. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13002.
Erro R, Pappata S, Amboni M, Vicidomini C, Longo K, Santangelo G, Picillo M, Vitale C, Moccia M, Giordano F, Brunetti A, Pellecchia MT, Salvatore M, Barone P (2012) Anxiety is associated with striatal dopamine transporter availability in newly diagnosed untreated Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(9):1034–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.05.022
Vriend C, Raijmakers P, Veltman DJ, van Dijk KD, van der Werf YD, Foncke EM, Smit JH, Berendse HW, van den Heuvel OA (2014) Depressive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease are related to reduced [123I]FP-CIT binding in the caudate nucleus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85(2):159–164. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-304,811
Di Giuda D, Camardese G, Bentivoglio AR, Cocciolillo F, Guidubaldi A, Pucci L, Bruno I, Janiri L, Giordano A, Fasano A (2012) Dopaminergic dysfunction and psychiatric symptoms in movement disorders: a 123I-FP-CIT SPECT study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39(12):1937–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2232-7
Santangelo G, Vitale C, Picillo M, Cuoco S, Moccia M, Pezzella D, Erro R, Longo K, Vicidomini C, Pellecchia MT, Amboni M, Brunetti A, Salvatore M, Barone P, Pappata S (2015) Apathy and striatal dopamine transporter levels in de-novo, untreated Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21(5):489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.02.015
Park SB, Kwon KY, Lee JY, Im K, Sunwoo JS, Lee KB, Roh H, Ahn MY, Park S, Kim SJ, Oh JS, Kim JS (2019) Lack of association between dopamine transporter loss and non-motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a detailed PET analysis of 12 striatal subregions. Neurol Sci 40(2):311–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3632-7
Koch W, Unterrainer M, Xiong G, Bartenstein P, Diemling M, Varrone A, Dickson JC, Tossici-Bolt L, Sera T, Asenbaum S, Booij J, Kapucu OL, Kluge A, Ziebell M, Darcourt J, Nobili F, Pagani M, Hesse S, Vander Borght T, Van Laere K, Tatsch K, la Fougère C (2014) Extrastriatal binding of [(1)(2)(3)I]FP-CIT in the thalamus and pons: gender and age dependencies assessed in a European multicentre database of healthy controls. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(10):1938–1946. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2785-8.
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51(6):745–752. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.51.6.745
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(12):1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26424
Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, Na DL (2010) Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci 25(7):1071–1076. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.7.1071
Litvan I, Goldman JG, Tröster AI, Schmand BA, Weintraub D, Petersen RC, Mollenhauer B, Adler CH, Marder K, Williams-Gray CH, Aarsland D, Kulisevsky J, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Burn DJ, Barker RA, Emre M (2012) Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force guidelines. Mov Disord 27(3):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.24893
Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, Broe GA, Cummings J, Dickson DW, Gauthier S, Goldman J, Goetz C, Korczyn A, Lees A, Levy R, Litvan I, McKeith I, Olanow W, Poewe W, Quinn N, Sampaio C, Tolosa E, Dubois B (2007) Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22(12):1689–1707. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21507
Kim JS, Cho H, Choi JY, Lee SH, Ryu YH, Lyoo CH, Lee MS (2015) Feasibility of computed tomography-guided methods for spatial normalization of dopamine transporter positron emission tomography image. PLoS One 10(7):e0132585. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132585
Weintraub D, Simuni T, Caspell-Garcia C, Coffey C, Lasch S, Siderowf A, Aarsland D, Barone P, Burn D, Chahine LM, Eberling J, Espay AJ, Foster ED, Leverenz JB, Litvan I, Richard I, Troyer MD, Hawkins KA, Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (2015) Cognitive performance and neuropsychiatric symptoms in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(7):919–927. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26170
Getz SJ, Levin B (2017) Cognitive and neuropsychiatric features of early Parkinson’s disease. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 32(7):769–785. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acx091
Remy P, Doder M, Lees A, Turjanski N, Brooks D (2005) Depression in Parkinson’s disease: loss of dopamine and noradrenaline innervation in the limbic system. Brain 128(6):1314–1322. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh445
Felicio AC, Moriyama TS, Godeiro-Junior C, Shih MC, Hoexter MQ, Borges V, Silva SM, Amaro-Junior E, Andrade LA, Ferraz HB, Bressan RA (2010) Higher dopamine transporter density in Parkinson’s disease patients with depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 211(1):27–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1867-y
Yoo SW, Oh YS, Hwang EJ, Ryu DW, Lee KS, Lyoo CH, Kim JS (2019) “Depressed” caudate and ventral striatum dopamine transporter availability in de novo Depressed Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 132:104563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104563
Ceravolo R, Frosini D, Poletti M, Kiferle L, Pagni C, Mazzucchi S, Volterrani D, Bonuccelli U (2013) Mild affective symptoms in de novo Parkinson’s disease patients: relationship with dopaminergic dysfunction. Eur J Neurol 20(3):480–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2012.03878.x
Joling M, van den Heuvel OA, Berendse HW, Booij J, Vriend C (2018) Serotonin transporter binding and anxiety symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-316,193.
Picillo M, Santangelo G, Erro R, Cozzolino A, Amboni M, Vitale C, Barone P, Pellecchia MT (2017) Association between dopaminergic dysfunction and anxiety in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 37:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.02.010
Price JL, Drevets WC (2010) Neurocircuitry of mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(1):192–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.104
Spies M, Knudsen GM, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S (2015) The serotonin transporter in psychiatric disorders: insights from PET imaging. Lancet Psychiatry 2(8):743–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00232-1
Politis M, Wu K, Loane C, Kiferle L, Molloy S, Brooks DJ, Piccini P (2010) Staging of serotonergic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: an in vivo 11C-DASB PET study. Neurobiol Dis 40(1):216–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.05.028
Strecker K, Wegner F, Hesse S, Becker GA, Patt M, Meyer PM, Lobsien D, Schwarz J, Sabri O (2011) Preserved serotonin transporter binding in de novo Parkinson’s disease: negative correlation with the dopamine transporter. J Neurol 258(1):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5666-5
Maillet A, Krack P, Lhommée E, Météreau E, Klinger H, Favre E, Le Bars D, Schmitt E, Bichon A, Pelissier P, Fraix V, Castrioto A, Sgambato-Faure V, Broussolle E, Tremblay L, Thobois S (2016) The prominent role of serotonergic degeneration in apathy, anxiety and depression in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Brain 139(9):2486–2502. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww162.
Monastero R, Di Fiore P, Ventimiglia GD, Camarda R, Camarda C (2013) The neuropsychiatric profile of Parkinson’s disease subjects with and without mild cognitive impairment. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 120(4):607–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-0988-y.
Leroi I, Pantula H, McDonald K, Harbishettar V (2012) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment and dementia. Parkinsons Dis 2012:308097. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/308097
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT (NRF-2017R1D1A1B06028086 and NRF-2019R1G1A1099554), and by the financial support of the Catholic Medical Center Research Foundation made in the program year of 2019. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval and Informed consent
Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital ethics committee approved the study and all participants signed informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, YS., Kim, J.H., Yoo, SW. et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and striatal monoamine availability in early Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Neurol Sci 42, 711–718 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04859-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04859-8