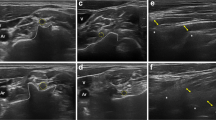
Abstract
Objectives
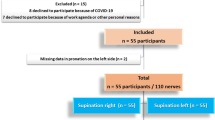
The objective of this study is to estimate the reference values of the brachial plexus roots at the interscalene groove. The physical and demographic characteristics of 59 healthy adult volunteers were studied. The CSA reference values and their correlations with weight, height, age, body mass index (BMI).
Methods
Fifty nine (27 males, 32 females) subjects were enrolled in the study. The mean cross sectional area of C5, C6 and C7 nerve roots were obtained.
Results
The mean CSA of the brachial plexus roots was as follows: C5 nerve root was 5.1 mm2 (range 1.7–11.1 ± 1.9 SD), C6 nerve root CSA 5.8 mm2 (range 1.7–12 ± 2.4 SD), and C7 nerve root 6.3 (range 1.6–19.6 ± 3.4 SD). There was a significant statistical difference between both sexes in our study. No statistical significant difference in tissue stiffness between dominant and nondominant hands. No statistical correlation was found between the CSA of the cervical nerve roots and different demographic factors. There was a positive statistical correlation between the CSA of C5 and both C6 and C7 nerve roots. Also positive significant statistical correlation was noted between the CSA of C6 and C7 nerve roots.
Conclusion
The CSA reference values of the C5-C7 nerve roots has been determined in asymptomatic individuals and can serve as a reference when studying pathological conditions of these structures.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSA:
-
Cross-sectional area
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
References
Haun DW, Cho JC, Clark TB, Kettner NW (2009 Sep) Normative cross-sectional area of the brachial plexus and subclavian artery using ultrasonography. J Manip Physiol Ther 32(7):564–570
Haun DW, Cho JC, Kettner NW (2010) Normative cross-sectional area of the C5-C8 nerve roots using ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med Biol 36(9):1422–1430
Orebaugh SL, Williams BA (2009) Brachial plexus anatomy: normal and variant. ScientificWorldJournal. 9:300–312
Johnson EO, Vekris M, Demesticha T, Soucacos PN (2010) Neuroanatomy of the brachial plexus: normal and variant anatomy of its formation. Surg Radiol Anat 32(3):291–297
Lapegue F, Faruch-Bilfeld M, Demondion X, Apredoaei C, Bayol MA, Artico H, Chiavassa-Gandois H, Railhac JJ, Sans N (2014) Ultrasonography of the brachial plexus, normal appearance and practical applications. Diagn Interv Imaging 95(3):259–275
Mattox R, Battaglia PJ, Welk AB, Maeda Y, Haun DW, Kettner NW (2016) Reference values for the scalene interval width during varying degrees of glenohumeral abduction using ultrasonography. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 39(9):662–667
Bedewi MA, Nissman D, Aldossary NM, Maetani TH, El Sharkawy MS, Koura H (2018 Sep) Shear wave elastography of the brachial plexus roots at the interscalene groove. Neurol Res 40(9):805–810
Griffith JF (2018) Ultrasound of the brachial plexus. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 22(3):323–333. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1645862Epub 2018 May 23. Review
Griffith JF, Lalam RK (2019) Top-ten tips for imaging the brachial plexus with ultrasound and MRI. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 23(4):405–418
Won SJ, Kim BJ, Park KS, Kim SH, Yoon JS (2012 Nov) Measurement of cross-sectional area of cervical roots and brachial plexus trunks. Muscle Nerve 46(5):711–716
Sugimoto T, Ochi K, Hosomi N, Mukai T, Ueno H, Takahashi T, Ohtsuki T, Kohriyama T, Matsumoto M (2013) Ultrasonographic reference sizes of the median and ulnar nerves and the cervical nerve roots in healthy Japanese adults. Ultrasound Med Biol 39(9):1560–1570
Kerasnoudis A, Pitarokoili K, Behrendt V, Gold R, Yoon MS (2013) Cross sectional area reference values for sonography of peripheral nerves and brachial plexus. Clin Neurophysiol 124(9):1881
Cartwright MS, Passmore LV, Yoon JS, Brown ME, Caress JB, Walker FO (2008) Cross-sectional area reference values for nerve ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve 37:566–571
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was obtained by local ethics commettee.
Informed consent
Proper informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bedewi, M.A., Kotb, M.A. Ultrasound reference values of C5, C6, and C7 brachial plexus roots at the interscalene groove. Neurol Sci 42, 2425–2429 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04836-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04836-1