Abstract
Introduction
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is one of the common autosomal recessive disorders with global heterozygous carrier frequency of 1:50. Due to high carrier frequency, significant morbidity associated with the infantile onset disease and prohibitive cost of recently approved therapy, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) recommends population based screening for SMA carrier status in eligible individuals in the reproductive age group. CODE-SEQ is a novel proprietary next generation sequencing (NGS) based assay, which is capable of detecting homozygous as well as heterozygous SMN1 exon 7 deletions. Along with the copy number estimation, this assay is capable of detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with silent SMA carrier status or “2+0” genotype.
Methods
We have validated a proprietary CODE-SEQ technology in a blinded cohort of 80 clinically well characterized samples from Turkish population for the detection of SMA carriers as well as affected cases. The results were correlated with gold standard MLPA assay.
Results
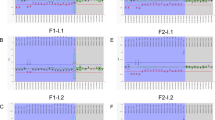
The copy numbers in exon 7 of SMN1 gene matched with MLPA results in all 80 samples giving 100% correlation. The assay accurately detected the presence/ absence of SNPs associated with “2+0” genotype in the reference samples. None of the tested clinical samples had these SNPs.
Conclusion
The results of this study support the notion that CODE-SEQ will be extremely useful in detecting SMA genotypes in large-scale population-based screening studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prior TW, Finanger E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. 2000 Feb 24 [Updated 2016 Dec 22]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1352/
Oskoui M, Levy G, Garland CJ, Gray JM, O'Hagen J, De Vivo DC, Kaufmann P (2007) The changing natural history of spinal muscular atrophy type 1. Neurology. 69:1931–1936
Prior TW, Nagan N, Sugarman EA, Batish SD, Braastad C (2011 Jul) Technical standards and guidelines for spinal muscular atrophy testing. Genet Med. 13(7):686–694
Wurster CD, Ludolph AC (2018) Nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 11:1756285618754459
Aartsma-Rus A (2017 Apr) FDA approval of nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy makes 2016 the year of splice modulating oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther 27(2):67–69
Prior TW (2008 Nov) Professional practice and guidelines committee. Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet Med 10(11):840–842
Muralidharan K, Wilson RB, Ogino S, Nagan N, Curtis C, Schrijver I (2011) Population carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy a position statement of the association for molecular pathology. J Mol Diagn. 13(1):3–6
Gitlin JM, Fischbeck K, Crawford TO, Cwik V, Fleischman A, Gonye K, Heine D, Hobby K, Kaufmann P, Keiles S, MacKenzie A, Musci T, Prior T, Lloyd-Puryear M, Sugarman EA, Terry SF, Urv T, Wang C, Watson M, Yaron Y, Frosst P, Howell RR (2010 Oct) Carrier testing for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet Med. 12(10):621–622
Wirth B (2000) An update of the mutation spectrum of the survival motor neuron gene (SMN1) in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Hum Mutat 15(3):228–237
Luo M, Liu L, Peter I, Zhu J, Scott SA, Zhao G, Eversley C, Kornreich R, Desnick RJ, Edelmann L (2014 Feb) An Ashkenazi Jewish SMN1 haplotype specific to duplication alleles improves pan-ethnic carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet Med. 16(2):149–156
Alías L, Bernal S, Calucho M, Martínez E, March F, Gallano P, Fuentes-Prior P, Abuli A, Serra-Juhe C, Tizzano EF (2018 Oct) Utility of two SMN1 variants to improve spinal muscular atrophy carrier diagnosis and genetic counselling. Eur J Hum Genet 26(10):1554–1557
Serra-Juhe C, Tizzano EF (2019 May) Perspectives in genetic counseling for spinal muscular atrophy in the new therapeutic era: early pre-symptomatic intervention and test in minors. Eur J Hum Genet 3
Lee TM, Kim SW, Lee KS, Jin HS, Koo SK, Jo I, Kang S, Jung SC (2004 Dec) Quantitative analysis of SMN1 gene and estimation of SMN1 deletion carrier frequency in Korean population based on real-time PCR. J Korean Med Sci 19(6):870–873
Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G (2002 Jun 15) Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 30(12):e57
Stuppia L, Antonucci I, Palka G, Gatta V Use of the MLPA assay in the molecular diagnosis of gene copy number alterations in human genetic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):3245–3276
Feng Y, Ge X, Meng L, Scull J, Li J, Tian X, Zhang T, Jin W, Cheng H, Wang X, Tokita M, Liu P, Mei H, Wang Y, Li F, Schmitt ES, Zhang WV, Muzny D, Wen S, Chen Z, Yang Y, Beaudet AL, Liu X, Eng CM, Xia F, Wong LJ, Zhang J (2017 Aug) The next generation of population-based spinal muscular atrophy carrier screening: comprehensive pan-ethnic SMN1 copy-number and sequence variant analysis by massively parallel sequencing. Genet Med. 19(8):936–944
Larson JL, Silver AJ, Chan D, Borroto C, Spurrier B, Silver LM. Validation of a high resolution NGS method for detecting spinal muscular atrophy carriers among phase 3 participants in the 1000 Genomes Project. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:100. Published 2015 Oct 29
Hasanzad M, Azad M, Kahrizi K, Saffar BS, Nafisi S, Keyhanidoust Z, Azimian M, Refah AA, Also E, Urtizberea JA, Tizzano EF, Najmabadi H (2010 Jan) Carrier frequency of SMA by quantitative analysis of the SMN1 deletion in the Iranian population. Eur J Neurol 17(1):160–162
Vidal-Folch N, Gavrilov D, Raymond K, Rinaldo P, Tortorelli S, Matern D, Oglesbee D (2018 Dec) Multiplex droplet digital PCR method applicable to newborn screening, carrier status, and assessment of spinal muscular atrophy. Clin Chem 64(12):1753–1761
Product Description SALSA® MLPA® Probemix P460-A1 SMA, available at https://www.mrcholland.com/product/P460/4127. Accessed on March 16th, 2020
Kerkhof J, Schenkel LC, Reilly J, McRobbie S, Aref-Eshghi E, Stuart A, Rupar CA, Adams P, Hegele RA, Lin H, Rodenhiser D, Knoll J, Ainsworth PJ, Sadikovic B (2017 Nov) Clinical validation of copy number variant detection from targeted next-generation sequencing panels. J Mol Diagn. 19(6):905–920
Zhao M, Wang Q, Wang Q, Jia P, Zhao Z. Computational tools for copy number variation (CNV) detection using next-generation sequencing data: features and perspectives. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 11:S1
Yao R, Yu T, Qing Y, Wang J, Shen Y (2019) Evaluation of copy number variant detection from panel-based next-generation sequencing data. Mol Genet Genomic Med 7(1):e00513
Zhang L, Bai W, Yuan N, Du Z (2019 May 28) Comprehensively benchmarking applications for detecting copy number variation. PLoS Comput Biol 15(5):e1007069
Ellingford JM, Campbell C, Barton S, Bhaskar S, Gupta S, Taylor RL, Sergouniotis PI, Horn B, Lamb JA, Michaelides M, Webster AR, Newman WG, Panda B, Ramsden SC, Black GC (2017 Jun) Validation of copy number variation analysis for next-generation sequencing diagnostics. Eur J Hum Genet 25(6):719–724
Biros I, Forrest S (1999 Jan) Spinal muscular atrophy: untangling the knot? J Med Genet 36(1):1–8
Larson JL, Silver AJ, Chan D, Borroto C, Spurrier B, Silver LM (2015 Oct 29) Validation of a high resolution NGS method for detecting spinal muscular atrophy carriers among phase 3 participants in the 1000 Genomes Project. BMC Med Genet 16:100
Benard-Slagter A, Zondervan I, de Groot K, Ghazavi F, Sarhadi V, Van Vlierberghe P, De Moerloose B, Schwab C, Vettenranta K, Harrison CJ, Knuutila S, Schouten J, Lammens T, Savola S (2017 Sep) Digital multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification for detection of key copy number alterations in T- and B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. J Mol Diagn 19(5):659–672
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Nikhil Phadke, Karthik Ganesan, Shatakshi Ranade, Kunal Patil, Gülşah Sönmez, Zeynep Demirel, Günce Bayram, and Hilmi Tok for helping in performing the lab experiments and analysis of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MA (MD, DM) is a clinical geneticist and is an employee of GenePath Diagnostics, the organization who has applied patent for this novel CODE-SEQ platform. MA was not involved in the performing the wet lab experiments, analysis of the data, and correlation with gold standards.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethical committee of the Ankara Yıldırım Beyazıt University, School of Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1208 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceylan, A.C., Erdem, H.B., Şahin, İ. et al. SMN1 gene copy number analysis for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in a Turkish cohort by CODE-SEQ technology, an integrated solution for detection of SMN1 and SMN2 copy numbers and the “2+0” genotype. Neurol Sci 41, 2575–2584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04365-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04365-x