Abstract
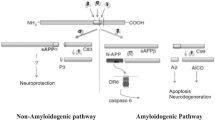
Amyloid-β (Aβ) as a crucial factor in pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is derived from amyloid precursor protein (APP) through a proteolytic process catalyzing by β- and γ-secretase—in amyloidogenesis pathway. Products of α-secretase cleavage also have protective effects against Aβ toxicity. According to existing evidences, microRNAs (miRNAs) show a unique pattern of expression in AD. Moreover, miRNAs regulatory effects on expression of secretases and their main components have been demonstrated in AD. The miRNAs levels may be changed in preclinical conditions and may be considered as diagnostic biomarkers in AD. Therefore, in this paper, we review the miRNAs involved in APP cleavage pathways and the formation of Aβ in order to evaluate the potential diagnostic biomarkers in AD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schonrock N, Matamales M, Ittner LM, Gotz J (2012) MicroRNA networks surrounding APP and amyloid-β metabolism—implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 235:447–454
Povova J, Ambroz P, Bar M, Pavulova V, Sery O, Tomaskova H, Janout V (2012) Epidemiological of and risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Biomed Pep Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 156(2):108–114
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (2007) Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(2):101–112
Kuhn P, Wang H, Dislich B, Colombo A, Zeitschel U, Ellwart JW, Kremmer E, RoBner S, Lichtenthaler SF (2010) ADAM10 is the physiologically relevant, constitutive alpha-secretase of the amyloid precursor protein in primary neurons. EMBO J 29(17):3020–3032
Femminella GD, Ferrara N, Rengo G (2015) The emerging role of microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Physiol 6(40)
Berti V, Polito C, Lombardi G, Ferrari C, Sorbi S, Pupi A (2016) Rethinking on the concept of biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 37:663–672
Geekiyanage H, Jicha GA, Nelson PT, Chan C (2012) Blood serum miRNA: non-invasive biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 235(2):491–496
During EH, Osorio RS, Elahi FM, Mosconi L, de Leon MJ (2011) The concept of FDG-PET endophenotype in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 32:559–569
Toledo JB, Show LM, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Plasma amyloid beta measurements - a desired but elusive Alzheimer’s disease biomarker. Alzheimers res Ther 5(2):8
Jin XF, Wu N, Wang L, Li J (2013) Circulating microRNAs: a novel class of potential biomarkers for diagnosing and prognosing central nervous system diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33(5):601–613
Hebert SS, Horré K, Nicolai L, Papadopoulou AS, Mandemakers W, Silahtaroglu NA, Kauppinen S, Delacourte A, Strooper BD (2008) Loss of microRNA cluster miR-29a/b-1 in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease correlates with increased BACE1/ -secretase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(17):6415–6420
Rooij EV, Kauppinen S (2014) Development of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med 8(12):1361–1471
Haass C (2004) Take five-BACE and the gamma-secretase quartet conduct Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide generation. EMBO J 23(3):483–488
He G, Luo W, Li P, Remmers C, Netzer WJ, Hendrick J, Bettayeb K, Flajolet M, Gorelick F, Greengard W, Greengard P (2010) Gamma-secretase activating protein is a therapeutictarget for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 467:95–98
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K, Kosik KS (2003) A microRNA array reveals extensive regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA 9:1274–1281
Ikeda K, Urakami K, Arai H, Wada K, Ji Y, Adachi Y, Okada A, Kowa H, Sasaki H, Ohno K, Ohtsuka Y, Ishikawa Y, Nakashima K (2000) The expression of Presenilin 1 mRNA in skin fibroblasts and brains from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 11:245–250
Jayadev S, Case A, Alajajian B, Moller ET, Garden GA (2013) Presenilin 2 influences miR146 level and activity in microglia. J Neurochem 127(5):592–599
Galimberti D, Villa C, Fenoglio C, Serpente M, Ghezzi L, Cioffi S, Arighi A, Fumagalli G, Scarpini E (2014) Circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 42(4):1261–1267
Sorbi S, Nacmias B, Forleo P, Latorraca S, Gobbini I, Bracco L, Piacentini S, Amaducci L (1994) ApoE allele frequencies in Italian sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 177(1–2):100–102
Orlacchio A, Kawarai T, Polidoro M, Stefani A, Orlacchio A, George-Hyslpo PH, Bernardi G (2002) Association analysis between Alzheimer’s disease and the Nicastrin gene polymorphisms. Neurosci Lett 333(2):115–118
Delay C, Dorval V, Fok A, Grenier-Boley LJC, Hsiung GY, Hebert SS (2014) MicroRNAs targeting Nicastrin regulate Aβ production and areaffected by target site polymorphisms. Front Mol Neurosci 7:67
Paris S, Smith PY, Goupil C, Dorval V, Hebert SS (2015) Preclinical evaluation of miR-15/107 family members as multifactorial drug targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4(10):e256
Liu W, Liu C, Zhu J, Shu P, Yin B, Gong Y, Qiang B, Yuan J, Peng X (2012) MicroRNA-16 targets amyloid precursor protein to potentially modulate Alzheimer’s-associated pathogenesis in SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol Aging 33(3):522–534
Mallick B, Ghosh Z (2011) A complex crosstalk between polymorphic microRNA target sites and AD prognosis. RNA Biol 8(4):665–673
Fatica A, Bozzoni I (2014) Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Neurol 15(1):7–21
Kim J, Yoon H, Chung D, Brown JL, Belmonte K, Kim J (2016) miR-186 is decreased in aged brain and suppresses BACE1 expression. J Neurochem 137(3):436–445
Yang G, Song Y, Zhou X, Deng Y, Liu T, Weng G, Yu D, Pan S (2015) MicroRNA-29c targets β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and has a neuroprotective role in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep 12(2):3081–3088
Lei X, Lei L, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Cheng Y (2015) Downregulated miR-29c correlates with increased BACE1 expression in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(2):1565–1574
Muller M, Jakel L, Bruinsma IB, Claassen JA, Kuiperij HB, Verbeek MM (2016) MicroRNA-29a is a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Neurobiol 53(5):2894–2899
Tan L, Yu JT, Liu QY, Tan MS, Zhang W, Hu N, Wang YL, Sun L, Jiang T, Tan L (2014) Circulating miR-125b as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 336(1–2):52–56
Dangla-Valls A, Molinuevo JL, Altirriba J, Sanchez-Valle R, Alcolea D, Fortea J, Rami L, Balasa M, Munoz-Garcia C, Ezquerra M, Fernandez-Santiago R, Lleo A, Antonell A (2016) CSF microRNA profiling in Alzheimer’s disease: a screening and validation study. Mol Neurobiol:1–8
Chen Y, Huang X, Zhang YW, Rockenstein E, Bu G, Golde TE, Masliah E, Xu H (2012) Alzheimer’s β-secretase (BACE1) regulates the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway independently of β-amyloid. J Neurosci 32(33):11390–11395
Zhu HC, Wang LM, Wang M, Song B, Tan S, Teng JF, Duan DX (2012) MicroRNA-195 downregulates Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-β production by targeting BACE1. Brain Res Bull 88(6):596–601
Ai J, Sun LH, Che H, Zhang R, Zhang TZ, Wu WC, Su XL, Chen X, Yang G, Li K, Wang N, Ban T, Bao YN, Guo F, Niu HF, Zhu YL, Zhu XY, Zhao SG, Yang BF (2013) MicroRNA-195 protects against dementia induced by chronic brain hypoperfusion via its anti-amyloidogenic effect in rats. J Neurosci 33(9):3989–4001
Geekiyanage H, Jicha GA, Nelson PT, Chan C (2012) Blood serum miRNA: non-invasive biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 235(2):491–496
Sørensen SS, Nygaard AB, Christensen T (2016) miRNA expression profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia - an exploratory study. Transl Neurodegener 5:6
Fang M, Wang J, Zhang X, Geng Y, Hu Z, Rudd JA, Ling S, Chen W, Hun S (2012) The miR-124 regulates the expression of BACE1/ -secretase correlated with cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicol Lett 209(1):94–105
Smith P, Hashimi AA, Girard J, Delay C, Hebert SS (2010) In vivo regulation of amyloid precursor protein neuronal splicing by microRNAs. J Neurochem 116(2):240–247
Liu CG, Wang JL, Li L, Wang PC (2014) MicroRNA-384 regulates both amyloid precursor protein and β-secretase expression and is a potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Med 34(1):160–166
Endres K, Fahrenholz F (2012) Regulation of alpha-secretase ADAM10 expression and activity. Exp Brain Res 217(3):343–352
Augustin R, Endres K, Reinhardt S, Kuhn P, Lichtenthaler SF, Hansen J, Wurst W, Trumbach D (2012) Computational identification and experimental validation of microRNAs binding to the Alzheimer-related gene ADAM10. BMC Med Genet 13(1):35–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajjari, S.N., Mehdizadeh, M., Sadigh-Eteghad, S. et al. Secretases-related miRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: new approach for biomarker discovery. Neurol Sci 38, 1921–1926 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-3086-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-3086-3