Abstract
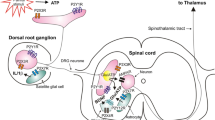
Prokineticins (PK) 1 and 2 belong to a new family of chemokines capable to interact with two different G coupled receptors: Prokineticin receptor (PKR)1 and 2. Both prokineticins and their receptors are widely distributed in different tissues and regulate several biological functions. In particular, a role of the PK system in inflammation and nociception has been established. PKRs are expressed in regions of the nervous system associated with pain and in primary sensitive neurons they colocalize with transient potential receptor vanilloid–TRPV1 providing an anatomical interaction in nociceptor sensitization. Moreover, PKs are strongly upregulated in immune and glial cells and sustain a proinflammatory loop in inflamed tissues. Recent evidences indicate that the block of the PK system represents a promising strategy to contrast inflammation and pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollay C, Wechselberger C, Mignogna G, Negri L, Melchiorri P, Barra D, Kreil G (1999) Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 374(2):189–196
Negri L, Lattanzi R, Giannini E, De Felice M, Colucci A, Melchiorri P (2004) Bv8, the amphibian homologue of the mammalian prokineticins, modulates ingestive behaviour in rats. Br J Pharmacol 142(1):181–191
Cheng MY, Bullock CM, Li C, Lee AG, Bermak JC, Belluzzi J, Weaver DR, Leslie FM, Zhou QY (2002) Prokineticin 2 transmits the behavioural circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nature 417(6887):405–410
Ferrara N, Frantz G, LeCouter J, Dillard-Telm L, Pham T, Draksharapu A, Giordano T, Peale F (2003) Differential expression of the angiogenic factor genes vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endocrine gland-derived VEGF in normal and polycystic human ovaries. Am J Pathol 162(6):1881–1893
Monnier J, Quillien V, Piquet-Pellorce C, Leberre C, Preisser L, Gascan H, Samson M (2008) Prokineticin 1 induces CCL4, CXCL1 and CXCL8 in human monocytes but not in macrophages and dendritic cells. Eur Cytokine Netw 19(4):166–175
LeCouter J, Zlot C, Tejada M, Peale F, Ferrara N (2004) Bv8 and endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor stimulate hematopoiesis and hematopoietic cell mobilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(48):16813–16818
Dorsch M, Qiu Y, Soler D, Frank N, Duong T, Goodearl A, O’Neil S, Lora J, Fraser CC (2005) PK1/EG-VEGF induces monocyte differentiation and activation. J Leukoc Biol 78(2):426–434
Martucci C, Franchi S, Giannini E, Tian H, Melchiorri P, Negri L, Sacerdote P (2006) Bv8, the amphibian homologue of the mammalian prokineticins, induces a proinflammatory phenotype of mouse macrophages. Br J Pharmacol 147(2):225–234
Franchi S, Giannini E, Lattuada D, Lattanzi R, Tian H, Melchiorri P, Negri L, Panerai AE, Sacerdote P (2008) The prokineticin receptor agonist Bv8 decreases IL-10 and IL-4 production in mice splenocytes by activating prokineticin receptor-1. BMC Immunol 9:60
Lin DC, Bullock CM, Ehlert FJ, Chen JL, Tian H, Zhou QY (2002) Identification and molecular characterization of two closely related G protein-coupled receptors activated by prokineticins/endocrine gland vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem 277(22):19276–19280
Ito H, Noda K, Yoshida K, Otani K, Yoshiga M, Oto Y, Saito S, Kurosaka D (2016) Prokineticin 2 antagonist, PKRA7 suppresses arthritis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:387
Abou-Hamdan M, Costanza M, Fontana E, Di Dario M, Musio S, Congiu C, Onnis V, Lattanzi R, Radaelli M, Martinelli V, Salvadori S, Negri L, Poliani PL, Farina C, Balboni G, Steinman L, Pedotti R (2015) Critical role for prokineticin 2 in CNS autoimmunity. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2(3):e95
He X, Shen C, Lu Q, Li J, Wei Y, He L, Bai R, Zheng J, Luan N, Zhang Z, Rong M, Lai R (2016) Prokineticin 2 plays a pivotal role in psoriasis. EBioMedicine 13:248–261
Negri L, Lattanzi R, Giannini E, Metere A, Colucci M, Barra D, Kreil G, Melchiorri P (2002) Nociceptive sensitization by the secreted protein Bv8. Br J Pharmacol 137(8):1147–1154
De Felice M, Melchiorri P, Ossipov MH, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Negri L (2012) Mechanisms of Bv8-induced biphasic hyperalgesia: increased excitatory transmitter release and expression. Neurosci Lett 521(1):40–45
Vellani V, Colucci M, Lattanzi R, Giannini E, Negri L, Melchiorri P, McNaughton PA (2006) Sensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 by the prokineticin receptor agonist Bv8. J Neurosci 26(19):5109–5116
de Novellis V, Negri L, Lattanzi R, Rossi F, Palazzo E, Marabese I, Giannini E, Vita D, Melchiorri P, Maione S (2007) The prokineticin receptor agonist Bv8 increases GABA release in the periaqueductal grey and modifies RVM cell activities and thermoceptive reflexes in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 26(11):3068–3078
Negri L, Lattanzi R, Giannini E, Colucci M, Margheriti F, Melchiorri P, Vellani V, Tian H, De Felice M, Porreca F (2006) Impaired nociception and inflammatory pain sensation in mice lacking the prokineticin receptor PKR1: focus on interaction between PKR1 and the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in pain behavior. J Neurosci 26(25):6716–6727
Hu WP, Zhang C, Li JD, Luo ZD, Amadesi S, Bunnett N, Zhou QY (2006) Impaired pain sensation in mice lacking prokineticin 2. Mol Pain 2:35
Austin PJ, Moalem-Taylor G (2010) The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. J Neuroimmunol 229(1–2):26–50
Giannini E, Lattanzi R, Nicotra A, Campese AF, Grazioli P, Screpanti I, Balboni G, Salvadori S, Sacerdote P, Negri L (2009) The chemokine Bv8/prokineticin 2 is up-regulated in inflammatory granulocytes and modulates inflammatory pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(34):14646–14651
Maftei D, Marconi V, Florenzano F, Giancotti LA, Castelli M, Moretti S, Borsani E, Rodella LF, Balboni G, Luongo L, Maione S, Sacerdote P, Negri L, Lattanzi R (2014) Controlling the activation of the Bv8/prokineticin system reduces neuroinflammation and abolishes thermal and tactile hyperalgesia in neuropathic animals. Br J Pharmacol 171(21):4850–4865
Guida F, Lattanzi R, Boccella S, Maftei D, Romano R, Marconi V, Balboni G, Salvadori S, Scafuro MA, de Novellis V, Negri L, Maione S, Luongo L (2015) PC1, a non-peptide PKR1-preferring antagonist, reduces pain behavior and spinal neuronal sensitization in neuropathic mice. Pharmacol Res 91:36–46
Castelli M, Amodeo G, Negri L, Lattanzi R, Maftei D, Gotti C, Pistillo F, Onnis V, Congu C, Panerai AE, Sacerdote P, Franchi S (2016) Antagonism of the prokineticin system prevents and reverses allodynia and inflammation in a mouse model of diabetes. PLoS One 11(1):e0146259
Hang LH, Luo H, Li SN, Shu WW, Chen Z, Chen YF, Yuan JF, Shi LL, Shao DH (2015) Involvement of spinal Bv8/prokineticin 2 in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 117(3):180–185
Schlereth T, Schukraft J, Krämer-Best HH, Geber C, Ackermann T, Birklein F (2016) Interaction of calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) in human skin. Neuropeptides 59:57–62
Hoffmann T, Negri L, Maftei D, Lattanzi R, Reeh PW (2016) The prokineticin Bv8 sensitizes cutaneous terminals of female mice to heat. Eur J Pain 20(8):1326–1334
Xiong YC, Li XM, Wang XJ, Liu YQ, Qiu F, Wu D, Gan YB, Wang BH, Hu WP (2010) Prokineticin 2 suppresses GABA-activated current in rat primary sensory neurons. Neuropharmacology 59(7–8):589–594
Panerai AE (2013) Is migraine a disorder of the central nervous system? Neurol Sci 34(Suppl 1):S33–S35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I certify that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franchi, S., Sacerdote, P. & Panerai, A. The prokineticin system: an interface between neural inflammation and pain. Neurol Sci 38 (Suppl 1), 27–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2875-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2875-z