Abstract
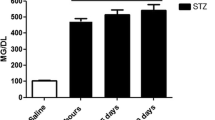
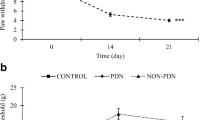
The temporal course of diabetic polyneuropathy in a rat model plays a critical role in studies on diabetic polyneuropathy treatment. In this study, the temporal course of neuropathic symptoms was investigated in diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin and evaluated by nerve conduction velocity and behavioral assays, including the von Frey test for mechanical allodynia and the hot plate test for hyperalgesia. The results revealed that both mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia started on the 2nd week, while nerve conduction velocity significantly decreased from the 1st week. In addition, the severity of allodynia did not change after the 3rd week. Hyperalgesia and nerve conduction velocity progressively aggravated even to the 8th week. Transmission electron microscopy showed that loss of unmyelinated axons, loosening of the myelin structure, and thickening of the perineurium layer were visible from the 4th week and worsened on the 8th week. Differences in the temporal course of neuropathic symptoms are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulton AJ, Malik RA (1998) Diabetic neuropathy. Med Clin N Am 82(4):909–929
Benbow SJ, Cossins L, MacFarlane IA (1999) Painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med: J Br Diabet Assoc 16(8):632–644
Gilliatt RW, Willison RG (1962) Peripheral nerve conduction in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 25:11–18
Dyck PJ, Albers JW, Andersen H, Arezzo JC, Biessels GJ, Bril V, Feldman EL, Litchy WJ, O’Brien PC, Russell JW, on behalf of the Toronto Expert Panel on Diabetic N (2011) Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes/Metabol Res Rev. doi:10.1002/dmrr.1226
Behse F, Buchthal F, Carlsen F (1977) Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40(11):1072–1082
Sharma AK, Thomas PK (1974) Peripheral nerve structure and function in experimental diabetes. J Neurol Sci 23(1):1–15 0022-510X(74)90136-1 [pii]
Coppey LJ, Davidson EP, Dunlap JA, Lund DD, Yorek MA (2000) Slowing of motor nerve conduction velocity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats is preceded by impaired vasodilation in arterioles that overlie the sciatic nerve. Int J Exp Diabet Res 1(2):131–143
Morrow TJ (2004) Animal models of painful diabetic neuropathy: the STZ rat model. Current protocols in neuroscience/editorial board, Jacqueline N Crawley [et al] Chapter 9:Unit 9 1 doi:10.1002/0471142301.ns0918s29
Bennett GJ, Chung JM, Honore M, Seltzer Z (2003) Models of neuropathic pain in the rat. Current protocols in neuroscience/editorial board, Jacqueline N Crawley [et al] Chapter 9:Unit 9 14. doi:10.1002/0471142301.ns0914s22
Moller KA, Johansson B, Berge OG (1998) Assessing mechanical allodynia in the rat paw with a new electronic algometer. J Neurosci Methods 84(1–2):41–47
Eddy NB, Leimbach D (1953) Synthetic analgesics. II. dithienylbutenyl- and dithienylbutylamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 107(3):385–393
Calcutt NA, Jorge MC, Yaksh TL, Chaplan SR (1996) Tactile allodynia and formalin hyperalgesia in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of insulin, aldose reductase inhibition and lidocaine. Pain 68(2–3):293–299
Ilnytska O, Lyzogubov VV, Stevens MJ, Drel VR, Mashtalir N, Pacher P, Yorek MA, Obrosova IG (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition alleviates experimental diabetic sensory neuropathy. Diabetes 55(6):1686–1694. doi:10.2337/db06-0067
Li F, Obrosova IG, Abatan O, Tian D, Larkin D, Stuenkel EL, Stevens MJ (2005) Taurine replacement attenuates hyperalgesia and abnormal calcium signaling in sensory neurons of STZ-D rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288(1):E29–E36. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00168.2004
Liu Y, Wang L, Li X, Lv C, Feng D, Luo Z (2010) Tanshinone IIA improves impaired nerve functions in experimental diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399(1):49–54. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.037
Kolta MG, Ngong JM, Rutledge LP, Pierzchala K, Van Loon GR (1996) Endogenous opioid peptide mediation of hypoalgesic response in long-term diabetic rats. Neuropeptides 30(4):335–344
Joharchi K, Jorjani M (2007) The role of nitric oxide in diabetes-induced changes of morphine tolerance in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 570(1–3):66–71. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.026
Cherian PV, Kamijo M, Angelides KJ, Sima AA (1996) Nodal Na(+)-channel displacement is associated with nerve-conduction slowing in the chronically diabetic BB/W rat: prevention by aldose reductase inhibition. J Diabetes Complicat 10(4):192–200
Misawa S, Kuwabara S, Kanai K, Tamura N, Hiraga A, Nakata M, Ogawara K, Hattori T (2005) Axonal potassium conductance and glycemic control in human diabetic nerves. Clin Neurophysiol: Off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol 116(5):1181–1187. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2004.12.019
Jakobsen J, Lundbaek K (1976) Neuropathy in experimental diabetes: an animal model. Br Med J 2(6030):278–279
Medori R, Autilio-Gambetti L, Monaco S, Gambetti P (1985) Experimental diabetic neuropathy: impairment of slow transport with changes in axon cross-sectional area. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82(22):7716–7720
Bestetti G, Rossi GL, Zemp C (1981) Changes in peripheral nerves of rats four months after induction of streptozotocin diabetes. A qualitative and quantitative study. Acta Neuropathologica 54(2):129–134
Zemp C, Bestetti G, Rossi GL (1981) Morphological and morphometric study of peripheral nerves from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Acta Neuropathol 53(2):99–106
Shim B, Kim DW, Kim BH, Nam TS, Leem JW, Chung JM (2005) Mechanical and heat sensitization of cutaneous nociceptors in rats with experimental peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience 132(1):193–201. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.036
Fuchs D, Birklein F, Reeh PW, Sauer SK (2010) Sensitized peripheral nociception in experimental diabetes of the rat. Pain 151(2):496–505. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.08.010
Bierhaus A, Fleming T, Stoyanov S, Leffler A, Babes A, Neacsu C, Sauer SK, Eberhardt M, Schnolzer M, Lasitschka F, Neuhuber WL, Kichko TI, Konrade I, Elvert R, Mier W, Pirags V, Lukic IK, Morcos M, Dehmer T, Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ, Edelstein D, Nau C, Forbes J, Humpert PM, Schwaninger M, Ziegler D, Stern DM, Cooper ME, Haberkorn U, Brownlee M, Reeh PW, Nawroth PP (2012) Methylglyoxal modification of Nav1.8 facilitates nociceptive neuron firing and causes hyperalgesia in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Med 18(6):926–933. doi:10.1038/nm.2750
Dyck PJ, Giannini C (1996) Pathologic alterations in the diabetic neuropathies of humans: a review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55(12):1181–1193
Hill RE, Williams PE (2004) Perineurial cell basement membrane thickening and myelinated nerve fibre loss in diabetic and nondiabetic peripheral nerve. J Neurol Sci 217(2):157–163
King RH, Llewelyn JG, Thomas PK, Gilbey SG, Watkins PJ (1989) Diabetic neuropathy: abnormalities of Schwann cell and perineurial basal laminae. Implications for diabetic vasculopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15(4):339–355
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the National Health Research Institutes (Project ME-101-PP-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G.-S. Chen and C.-C. K. Lin equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YF., Lin, CC.K. & Chen, GS. Temporal course of streptozotocin-induced diabetic polyneuropathy in rats. Neurol Sci 35, 1813–1820 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1848-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1848-8