Abstract
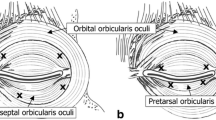
Blepharospasm (BS) is a focal dystonia involving involuntary contractions of muscles around the eyes. Botulinum toxin (BoNT) is the most effective treatment for BS and the technique of injection changes depending on the clinical picture. Usually typical BS benefits from the injection in the orbital part of the orbicularis oculi (OOc) muscle (orbital injection), while BoNT injection in the pretarsal part of OOc muscle is helpful especially for the atypical BS (opening eyelid apraxia). The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of two injection techniques, the orbital versus the combined (injection in both orbital and pretarsal part of OOc) in BS patients with unsatisfactory response to BoNT. Nineteen patients with typical BS not having a satisfactory response from BoNT treatment with the orbital injection (primary and secondary resistant patients) were studied. After 3 months from the last orbital injection patients received the combined injection; they were assessed with the JRS and BSDI scales after 4 weeks from the last orbital and the first combined injection. Statistical analysis showed a significant reduction (p < 0.05) of the mean score of JRS and BSDI scales comparing the combined with orbital injection. This study shows that the treatment of typical BS can have better results when BoNT is injected with the combined technique in primary and secondary resistant patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Defazio G, Livrea P (2004) Primary blepharospasm: diagnosis and management. Drugs. 64:237–244
Hallett M, Evinger C, Jankovic J, Stacy M (2008) Update on blepharospasm: report from the BEBRF International Workshop. BEBRF International Workshop. Neurology 71:1275–1282
Bentivoglio AR, Ialongo T, Bove F, De Nigris F, Fasano A (2012) Retrospective evaluation of the dose equivalence of Botox (®) and Dysport (®) in the management of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm: a novel paradigm for a never ending story. Neurol Sci. 33:261–267
Gill HS, Kraft SP (2010) Long-term efficacy of botulinum a toxin for blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Can J Neurol Sci 37:631–636
Aramideh M, Ongerboer de Visser BW, Brans JW, Koelman JH, Speelman JD (1995) Pretarsal application of botulinum toxin for treatment of blepharospasm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:309–311
Jankovic J, Kenney C, Grafe S, Goertelmeyer R, Comes G (2009) Relationship between various clinical outcome assessments in patients with blepharospasm. Mov Disord 15(24):407–413
Kenney C, Jankovic J (2008) Botulinum toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neural Transm. 115:585–591
Gordon PH, Gooch CL, Greene PE (2002) Extensor digitorum brevis test and resistance to botulinum toxin type A. Muscle Nerve 26:828–831
Albanese A, Bentivoglio AR, Colosimo C, Galardi G, Maderna L, Tonali P (1996) Pretarsal injections of botulinum toxin improve blepharospasm in previously unresponsive patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60:693–694
Cakmur R, Ozturk V, Uzunel F, Donmez B, Idiman F (2002) Comparison of preseptal and pretarsal injections of botulinum toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neurol 249(1):64–68
Acknowledgments
The authors do not have financial disclosures or conflict of interest concerning the research related to the manuscript. There are no funding sources for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esposito, M., Fasano, A., Crisci, C. et al. The combined treatment with orbital and pretarsal botulinum toxin injections in the management of poorly responsive blepharospasm. Neurol Sci 35, 397–400 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1526-2