Abstract
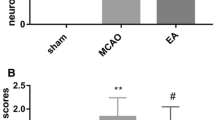
This study aims to investigate the mechanism of electroacupuncture (EA) in promoting behavioral recovery after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. The SD rats received filament occlusion of the right middle cerebral artery for 2 h followed by reperfusion for 1, 3, 7, 14, and 21 days, respectively. Rats were randomly divided into sham group, model group and EA group. After 2 h of the reperfusion, EA was given at bilateral “Hegu” point (LI 4) in the EA group. Neurobehavioral evaluation, the expression of stem cell factor (SCF), its receptor c-kit and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) protein and mRNA in the cortical ischemic region were measured. EA treatment can improve behavioral recovery after ischemia/reperfusion. Compared with the sham group, the positive cells and mRNA expression of SCF, c-kit, MMP-9, the protein expression of SCF were increased significantly in the model and EA groups (P < 0.001). Compared with the model group, the positive cells, protein and mRNA expression of SCF were increased significantly in EA groups (P < 0.01). The positive cells and mRNA expression of c-kit were increased in EA groups beginning at 3 day and remained significantly high thereafter. The expression of MMP-9 positive cells and mRNA were deceased significantly in the 1 day subgroup in EA (P < 0.01), but increased significantly in the 3, 7 days subgroups (P < 0.01). We conclude that EA treatment up-regulates the positive cells and mRNA expression of SCF, c-kit and MMP-9 after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. EA may promote neurobehavioral recovery by increasing the protein and mRNA expression of SCF, c-kit and MMP-9 after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EPCs:
-
Endothelial progenitor cells
- SCF:
-
Stem cell factor
- MMP-9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
- EA:
-
Electroacupuncture
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer saline
- NSCs:
-
Neuronal stem cells
- HSCs:
-
Hematopoietic stem cells
- SKitL:
-
Soluble kit ligand
- MKitL:
-
Membrane bound kit ligand
- PB:
-
Peripheral blood
- BM:
-
Bone marrow
References
Wang CX, Li ZR, Chen BY (2006) Protective effect of electroacupuncture on cerebral function via ameliorating oxidative stress in MCAO rats. Neurosci Bull 21:153–157
Murayama T, Tepper OM, Silver M et al (2002) Determination of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell significance in angiogenic growth factor-induced neovascularization in vivo. Exp Hematol 30:967–972
Ohta T, Kikuta K, Imamura H et al (2006) Administration of ex vivo-expanded bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells attenuates focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Neurosurgery 59:679–686
Fan Y, Shen F, Frenzel T et al (2010) Endothelial progenitor cell transplantation improves long-term outcome in mice. Ann Neurol 67:488–497
Ma JX, Luo Y (2007) Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of angiogenic growth factors and anti-angiogenic growth factors in the brain tissue of the rat after focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion 27:129–133
Wu L, Luo Y, Zhang SS (2010) Effects of electroacupuncture on mRNA and protein expression of placental growth factor and Flt-1 and promotes revascularization in the brain after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in SD rats. Chin J Arterioscler 18:589–593
Cai SX, Yu WJ, Zhang L et al (2009) Effect of electroacupuncture on plasma endogenous endothelial progenitor cell counts in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Acupunct Res 34:114–119
Zhang T, Lin T, Wang XZ et al (2009) The influence of electroacupuncture pretreatment to endothelial progenitor cells and vessel endothelial growth factor in marrow and peripheral blood of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Chin J Rehabil Med 24:428–432
Jin KL, Mao XO, Sun XJ et al (2002) Stem cell factor stimulates neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 110:311–319
Sun LX, Lee J, Fine HA (2004) Neuronally expressed stem cell factor induces neural stem cell migration to areas of brain injury. J Clin Invest 113:1364–1374
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S et al (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Luo Y, Dong WW (2002) An experimentaI study on focaI cerebraI ischemia/reperfusion model in Wistar rats with suture method. J Chongqing Med Univ 27:1–4
Hua XB, Li CR, Zhou HL et al (1991) Development of the atlas of acupoints for rat. Exp Anim and Anim 1:1–5
Zhang HL, Gu ZL, Savitz SI et al (2008) Neuroprotective effects of prostaglandin A1 in rat models of permanent focal cerebral ischemia are associated with nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition and peroxisome proliferators- activated receptor gamma up-regulation. J Neurosci Res 86:1132–1141
Han ZB, Ren H, Zhao H et al (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha directly enhances the transcriptional activity of stem cell factor (SCF) in response to hypoxia and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Carcinogenesis 29:1853–1861
Fazel S, Cimini M, Chen L et al (2006) Cardioprotective ckit + cells are from the bone marrow and regulate the myocardial balance of angiogenic cytokines. J Clin Invest 116:1865–1877
Dhandapani KM, Wade FM, Wakade C et al (2005) Neuroprotection by stem cell factor in rat cortical neurons involves AKT and NFkappaB. J Neurochem 95:9–19
Abu El-Asrar AM, Struyf S, Opdenakker G et al (2010) Expression of stem cell factor/c-kit signaling pathway components in diabetic fibrovascular epiretinal membranes. Mol Vis 16:1098–1107
Kuang D, Zhao X, Xiao GX et al (2008) Stem cell factor/c-kit signaling mediated cardiac stem cell migration via activation of p38 MAPK. Basic Res Cardiol 103:265–273
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A et al (1997) Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 5320:964–967
Takahashi T, Kalka C, Masuda H et al (1999) Ischemia-and cytokine induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat Med 5:434–438
Zhang SS, Luo Y, Wu L (2010) Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway in promoting angiogenesis in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion using electrical acupuncture. Acta Academiae Medicinae Militaris Tertiae 32:2488–2491
Wang YN, Xu JM (2007) Progress on marker of hematopoietic stem cell-ACl33. Chin J New Drugs Clin Rem 26:708–714
Romanic AM, White RF, Arleth AJ et al (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase expression increases after cerebral focal ischemia in rats: inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 reduces infarct size. Stroke 29:1020–1030
Heissig B, Hattori K, Dias S et al (2002) Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of kit-ligand. Cell 109:625–637
Huang EJ, Nocka KH, Buck J et al (1992) Differential expression and processing of two cell associated forms of the kit ligand KL-1 and KL-2. Mol Biol Cell 3:349–362
Dong H, Fan YH, Zhang W et al (2009) Repeated electroacupuncture preconditioning attenuates matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and activity after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurol Res 31:853–858
Zhao Y, Chen SJ, Yu WJ et al (2010) The effect of electroacupuncture on endogenous EPCs and serum cytokines in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rat. J Biomed Eng 27:1322–1326
Smith MA, Court EL, Smith JG (2001) Stem cell factor: laboratory and clinical aspects. Blood Rev 15:191–197
Matsumoto T, Ii M, Nishimura H et al (2010) Lnk-dependent axis of SCF-cKit signal for osteogenesis in bone fracture healing. J Exp Med 207:2207–2223
Dentelli P, Rosso A, Balsamo A et al (2007) C-kit, by interacting with the membrane-bound ligand, recruits endothelial progenitor cells to inflamed endothelium. Blood 109:4264–4271
Kim KL, Meng Y, Kim JY et al (2011) Direct and differential effects of stem cell factor on the neovascularization activity of endothelial progenitor cells. Cardiovascular Res 92:132–140
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Special Fund for Scientific Research of Doctorial Subjects in College and Universities of Ministry of Education (NO:20095503110001) and the Program of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Research of Chongqing Municipal Health Bureau (2005-B-24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Luo, Y., Sun, H. et al. Electroacupuncture improves behavioral recovery and increases SCF/c-kit expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neurol Sci 34, 487–495 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1081-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1081-2