Abstract
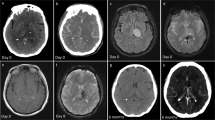
Although the association between PFO and cryptogenic stroke is well shown in young adults, the causality is still unclear. The pathogenetic mechanism of ischemic stroke related to PFO is not entirely understood. Indeed, besides the well-known paradoxical embolism, formations of thrombi in situ, especially in the presence of ASA, a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation have been often observed. Cerebral sinus venous thrombosis may be due to local inflammation or to acquired or genetic thrombophilia including hyperhomocysteinemia. We report a case of a young man presenting with a cerebellar infarction probably secondary to a paradoxical brain-to-brain embolism, in which the only detectable embolic source was a cerebral vein thrombosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wechsler LR (2008) PFO and stroke: what are the data? Cardiol Rev 16:53–57
Alsheikh-Ali AA, Thaler DE, Kent DM (2009) Patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke: incidental or pathogenic? Stroke 40:2349–2355
Cramer SC, Rordorf G, Maki JH, Kramer LA, Grotta JC, Burgin WS, Hinchey JA, Benesch C, Furie KL, Lutsep HL, Kelly E, Longstreth WT Jr (2004) Increased pelvic vein thrombi in cryptogenic stroke: results of the paradoxical emboli from large veins in ischemic stroke (PELVIS) study. Stroke 35:46–50
Cabanes L, Mas JL, Cohen A, Amarenco P, Cabanes PA, Oubary P, Chedru F, Guérin F, Bousser MG, de Recondo J (1993) Atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale as risk factors for cryptogenic stroke in patients less than 55 years of age: a study using transesophageal echocardiography. Stroke 24:1865–1873
Thaler DE, Saver JL (2008) Cryptogenic stroke and patent foramen ovale. Curr Opin Cardiol 23:537–544
Stollberger C, Finsterer J (2003) Search for coagulopathy does not obviate search for venous thrombosis in suspected paradoxical embolism. Stroke 34:e146–e147
Del Sette M, Dinia L, Gandolfo C (2007) Brain-to-brain paradoxical embolism through patent foramen ovale after cerebral vein thrombosis. Eur Neurol 57:176–177
Valdueza JM, Harms L, Doepp F, Koscielny J, Einhäupl KM (1997) Venous microembolic signals detected in patients with cerebral sinus thrombosis. Stroke 28:1607–1609
Di Tullio MR, Homma S (2009) Patent foramen ovale and stroke: what should be done? Curr Opin Hematol 16:391–396
Giardini A, Donti A, Formigari R, Bronzetti G, Prandstraller D, Bonvicini M, Palareti G, Guidetti D, Gaddi O, Picchio FM (2004) Comparison of results of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale for paradoxical embolism in patients with versus without thrombophilia. Am J Cardiol 94:1012–1016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La Spina, P., Calabrò, R.S., Casella, C. et al. Cerebellar infarction in a patient with cerebral vein thrombosis and patent foramen ovale: brain-to-brain embolism?. Neurol Sci 33, 1415–1417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0908-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0908-6