Abstract
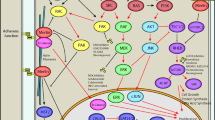
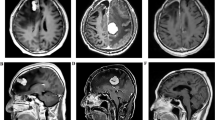
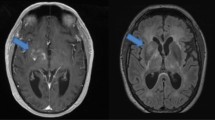
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder, which confers an increased risk of a wide range of cancers, and malignant tumors are the most common cause of death in individuals with NF1. Although in children with NF1, the most common neoplasms are optic nerve gliomas and brain tumors, an elevated risk of myeloid leukemia and an increased relative risk of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma were reported. In adults with NF1, the relative risk of brain tumor is 100 times higher than in the general population. Cases of malignant lymphoma occurring in NF1 adult patients have been reported. However, the association between NF1 and lymphoproliferative diseases is still debated. We report a case of CNS primitive lymphoma in an adult patient who resulted positive for NF1 at genetic testing. At present, only one case of CNS lymphoma in an adult patient displaying clinical criteria for NF1 diagnosis has been reported.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman JM (1999) Epidemiology of neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Med Genet 89(1):1–6
Zöller ME, Rembeck B, Odén A, Samuelsson M, Angervall L (1997) Malignant and benign tumors in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 in a defined Swedish population. Cancer 79(11):2125–2131
Sørensen SA, Mulvihill JJ, Nielsen A (1986) Long-term follow-up of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. Survival and malignant neoplasms. N Engl J Med 314(16):1010–1015
Rasmussen SA, Friedman JM (2000) NF1 gene and neurofibromatosis 1. Am J Epidemiol 151:33–40
Niemayer CM, Arico M, Basso G et al (1997) Chronic myelomonocitic leukaemia in childhood: a retrspecitive analysis of 10 cases. European Working Group on Myelodysplastic Sindromes in choldhood (EWONG-MDS). Blood 89:3534–3543
Stiller CA, Chessells JM, Fitchett M (1994) Neurofibromatosis and childhood leukaemia/lymphoma: a population-based UKCCSG study. Br J Cancer 70(5):969–972
Gutmann DH, Rasmussen SA, Wolkstein P, MacCollin MM, Guha A, Inskip PD, North KN, Poyhonen M, Birch PH, Friedman JM (2002) Gliomas presenting after 10 in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). Neurology 59:759–761
Dohi O, Hatori M, Ichinohasama R, Hosaka M, Hashimoto S, Kokubun S (2006) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising in a patient with neurofibromatosis type I and in a patient with neurofibromatosis type II. Tohoku J Exp Med 208(2):169–176
Herbert CR, McBurney EI (2003) Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Cutis. 72(1):27–30
Zein G, Yu E, Tawansy K, Berta A, Foster CS (2004) Neurofibromatosis type 1 associated with central nervous system lymphoma. Ophthalmic Genet 25(1):49–51
Upadhyaya M, Kluwe L, Spurlock G, Monem B, Majounie E, Mantripragada K, Ruggieri M, Chuzhanova N, Evans DG, Ferner R, Thomas N, Guha A, Mautner V (2008) Germline and somatic NF1 gene mutation spectum in NF1 associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Human mutat 29(1):74–82
Side L, Taylor B, Cayouette M, Conner E, Thompson P, Luce M, Shannon K (1997) Homozygous inactivation of the NF1 gene in bone marrow cells from children with neurofibromatosis type 1 and malignant myeloid disorders. N Engl J Med 336:1713–1720
Steinemann D, Arning L, Praulich I, Stuhrmann M, Hasle H, Stary J, Schlegelberger B, Niemeyer CM, Flotho C (2010) Mitotic recombination and compound heterozygous mutations are predominat Nf1 inactivation mechanisms in children with Juvenile myelomonocitic leukemia and neurofibromatosis type 1. Haematologica 95:320–323
De Raedt T, Maertens O, Chmara M, Brems H, Heyns I, Sciot R, Majounie E, Upadhyaya M, De Schepper S, Speleman F, Messiaen L, Vermeesch JR, Legius E (2006) Somatic loss. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45(10):893–904
Rücker FG, Bullinger L, Schwaenen C, Lipka DB, Wessendorf S, Fröhling S, Bentz M, Miller S, Scholl C, Schlenk RF, Radlwimmer B, Kestler HA, Pollack JR, Lichter P, Döhner K, Döhner H (2006) Disclosure of candidate genes in acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotypes using microarray-based molecular characterization. J Clin Oncol 24(24):3887–3894
Stephens K, Weaver M, Leppig KA, Maruyama K, Emanuel PD, Le Beau MM, Shannon KM (2006) Interstitial uniparental isodisomy at clustered breakpoint intervals is a frequent mechanism of NF1 inactivation in myeloid malignancies. Blood 108(5):1684–1689
Balgobind BV, Raimondi SC, Harbott J, Zimmermann M, Alonzo TA, Auvrignon A, Beverloo HB, Chang M, Creutzig U, Dworzak MN, Forestier E, Gibson B, Hasle H, Harrison CJ, Heerema NA, Kaspers GJ, Leszl A, Litvinko N, Nigro LL, Morimoto A, Perot C, Pieters R, Reinhardt D, Rubnitz JE, Smith FO, Stary J, Stasevich I, Strehl S, Taga T, Tomizawa D, Webb D, Zemanova Z, Zwaan CM, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM (2006) Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: results of an international retrospective study. Blood 114(12):2489–2496
Staser K, Yang FC, Clapp DW (2010) Mast cells and the neurofibroma microenvironment. Blood 116(2):157–164
Kim SJ, Seo JH, Lee SW, Han E, Lee ES, Cha SH, Seo BK (2003) A case of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Korean J Intern Med 18(3):202–205
Itoh T, Tamegane T, Ohmae Y, Nakayama S (1998) Malignant lymphoma occurring in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease). Rinsho Ketsueki 39(9):698–702
Trattner A, David M, Ingber A, Sandbank MJ (1990) Coexistence of late-onset neurofibromatosis and cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Am Acad Dermatol 23(5 Pt 1):932–934
Matsuzaki M, Shimamoto Y, Yokoyama Y, Suga K, Tokioka T, Sueoka E, Ono K, Sano M, Yamaguchi M (1989) von Recklinghausen’s disease associated with malignant lymphoma. Rinsho Ketsueki 30(3):382–386
Acknowledgments
This report was supported by grant RS18 of the Istituto Superiore di Sanità to GF. We thank Dr. B. Pollo for sharing information on patient histology and Maria Cristina Ibba for helping in genetic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eoli, M., Bianchessi, D., Di Stefano, A.L. et al. Central nervous system lymphoma occurring in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease). Neurol Sci 33, 1429–1433 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0886-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0886-8