Abstract
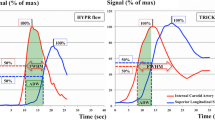
The objective of the study was to use 320-detector row 4D CT angiography (CTA) for measuring cerebral circulation times (CCT) and to assess early venous drainage (EVD) and shortening of CCT in arteriovenous malformations (AVM) and to compare with DSA. CCT of 12 physiological patients and five AVM patients were acquired using a 4D CTA protocol by recording cerebrovascular bolus passage time. In the AVM patients EVD time (EVDT) was measured. Identical measurements were performed on DSA for the AVM patients. It was found that the physiological CCTs were 5.8 ± 1.4 s (M ± SD). EVD was seen in all AVMs and resulted in a shortened CCT of 3.4 ± 1.1 s (p = 0.01). There was no significant difference for CCT and EVDT values derived from DSA and 4D CTA. Thus, the CCTs can be measured non-invasively using clinical 4D CTA. Early venous drainage with shortened CCTs was observed by 4D CTA in all five patients with AVMs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingebiel R, Siebert E, Diekmann S, Wiener E, Masuhr F, Wagner M et al (2009) 4-D Imaging in cerebrovascular disorders by using 320-slice CT: feasibility and preliminary clinical experience. Acad Radiol 16:123–129
Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, Masuhr F, Hoffmann KT, Mews J et al (2009) 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 82:561–570
Doepp F, Valdueza JM, Schreiber SJ (2006) Transcranial and extracranial ultrasound assessment of cerebral hemodynamics in vascular and Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurol Res 28:645–649
Gilroy J, Bauer RB, Krabbenhoft KL, Meyer JS (1963) Cerebral circulation time in cerebral vascular disease measured by serial angiography. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 90:490–505
Puls I, Becker G, Maurer M, Mullges W (1999) Cerebral arteriovenous transit time (CTT): a sonographic assessment of cerebral microcirculation using ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol 25:503–507
Schreiber SJ, Franke U, Doepp F, Staccioli E, Uludag K, Valdueza JM (2002) Dopplersonographic measurement of global cerebral circulation time using echo contrast-enhanced ultrasound in normal individuals and patients with arteriovenous malformations. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:453–458
Schreiber SJ, Kauert A, Doepp F, Valdueza JM (2003) Measurement of global cerebral circulation time using power duplex echo-contrast bolus tracking. Cerebrovasc Dis 15:129–132
Schurr PH, Wickbom I (1952) Rapid serial angiography: further experience. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 15:110–118
Hoffmann O, Weih M, Schreiber S, Einhaupl KM, Valdueza JM (2000) Measurement of cerebral circulation time by contrast-enhanced Doppler sonography. Cerebrovasc Dis 10:142–146
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth-Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L (1999) Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet 354:1594–1597
Heiserman JE, Dean BL, Hodak JA, Flom RA, Bird CR, Drayer BP et al (1994) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1401–1407
Mehraein S, Schmidtke K, Villringer A, Valdueza JM, Masuhr F (2003) Heparin treatment in cerebral sinus and venous thrombosis: patients at risk of fatal outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis 15:17–21
Ogilvy CS, Stieg PE, Awad I, Brown RD Jr, Kondziolka D, Rosenwasser R et al (2001) Recommendations for the management of intracranial arteriovenous malformations: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Stroke Association. Circulation 103:2644–2657
Salomon EJ, Barfett J, Willems PW, Geibprasert S, Bacigaluppi S, Krings T (2009) Dynamic CT angiography and CT perfusion employing a 320-detector row CT: protocol and current clinical applications. Klin Neuroradiol 19:187–196
Cohnen M, Wittsack HJ, Assadi S, Muskalla K, Ringelstein A, Poll LW et al (2006) Radiation exposure of patients comprehensive computed tomography of the head in stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1741–1745
Marshall NW, Noble J, Faulkner K (1995) Patient and staff dosimetry in neuroradiological procedures. Br J Radiol 68:495–501
McParland BJ (1998) A study of patient radiation doses in interventional radiological procedures. Br J Radiol 71:175–185
Hadizadeh DR, von Falkenhausen M, Gieseke J, Urbach H, Hoogeveen R, Schild HH et al (2008) Cerebral arteriovenous malformation: Spetzler-Martin classification at subsecond-temporal-resolution four-dimensional MR angiography compared with that at DSA. Radiology 246:205–213
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A, Kitajima M, Morioka M, Kai Y et al (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:80–85
Kukuk GM, Hadizadeh, Boström A, Gieseke J, Bergener J, Nelles M et al (2010) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations at 3.0 T: intraindividual comparative study of 4D-MRA in combination with selective arterial spin labeling and digital subtraction angiography. Invest Radiol 45:126–132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siebert, E., Diekmann, S., Masuhr, F. et al. Measurement of cerebral circulation times using dynamic whole-brain CT-angiography: feasibility and initial experience. Neurol Sci 33, 741–747 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0785-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0785-z