Abstract
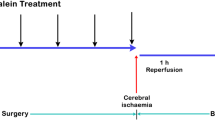
To determine the impact of ω3 fatty acids on post-ischemic expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins in hippocampus, male rats were received 10 or 100 mg/kg [Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) + Ecosapentaenoic acid (EPA); gavage; 21 days before ischemia to 2–10 days after ischemia]. Global cerebral ischemia reperfusion (IR) was performed using the four-vessel occlusion model; ischemia 8 min and reperfusion 6, 48 h and 10 days. IR increased Bcl-2 and Bax expression after 48 h (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 vs. sham) and 10 days (only Bax; p < 0.05), without significant difference with DHA + EPA groups after 6 h. But after 48 h expression of Bcl-2 increased (p < 0.05 vs. IR) and Bax decreased (p < 0.05). At day 10 after ischemia expression of Bax in DHA + EPA acid groups was less than IR (p < 0.05) and in 100 mg/kg DHA + EPA group Bcl-2 expression was more than IR (p < 0.05). These data suggested that long-term gavage with DHA + EPA increase hippocampal neurons survival for days after ischemia, revealed by increased Bcl-2 and decreased Bax expressions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeFilippis AP, Sperling LS (2006) Understanding omega-3’s. Am Heart J 151:564–570
Das UN (2006) Essential fatty acids: a review. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 7:467–482
Petursdottir AL, Farr SA, Morley JE, Banks WA, Skuladottir GV (2008) Effect of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on brain lipid fatty acid composition, learning ability, and memory of senescence-accelerated mouse. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 63(11):1153–1160
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2008) Docosahexaenoic acid and the aging brain. J Nutr 138(12):2510–2514
Calviello G, Serini S, Piccioni E (2008) Alzheimers disease and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: beneficial effects and possible molecular pathways involved. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 3:152–157
Peet M, Stokes C (2005) Omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Drugs 65(8):1051–1059
Yuen AWC, Sander JW, Fluegel D, Patsalos PN, Bell GS, Johnson T, Koepp MJ (2005) Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in patients with chronic epilepsy: a randomized trial. Epilepsy Behav 7(2):253–258
Ozen OA, Cosar M, Sahin O, Fidan H, Eser O, Mollaoglu H, Alkoc O, Yaman M, Songur A (2008) The protective effect of fish n-3 fatty acids on cerebral ischemia in rat prefrontal cortex. Neurol Sci 29(3):147–152
Bas O, Songur A, Sahin O, Mollaoglu H, Ozen OA, Yaman M, Eser O, Fidan H, Yagmurca M (2007) The protective effect of fish n-3 fatty acids on cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int 50(3):548–554
Bazan NG (2007) Omega-3 fatty acids, pro-inflammatory signaling and neuroprotection. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 10(2):136–141
Okada M, Amamoto T, Tomonaga M, Kawachi A, Yazawa K, Mine K et al (1996) The chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid reduces the spatial congnitive deficit following transient forebrain ischemia in rats. Neuroscience 71:17–25
Cao D, Xu JF, Xue RH, Zheng WF, Liu ZL (2004) Protective effect of chronic ethyl docosahexaenoate administration on brain injury in ischemic gerbils. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:651–659
Cao D, Li M, Xue R, Zheng W, Liu Z, Wang X (2005) Chronic administration of ethyl docosahexaenoate decreases mortality and cerebral edema in ischemic gerbils. Life Sci 78:74–81
Plamondon H, Roberge MC (2008) Dietary PUFA supplements reduce memory deficits but not CA1 ischemic injury in rats. Physiol Behav 95(3):492–500
Fernandes JS, Mori MA, Ekuni R, Oliveira RM, Milani H (2008) Long-term treatment with fish oil prevents memory impairments but not hippocampal damage in rats subjected to transient, global cerebral ischemia. Nutr Res 28(11):798–808
Moreira JD, Knorr L, Thomazi AP, Simao F, Battu C, Oses JP, Gottfried C, Wofchuk S, Salbego C, Souza DO, Perry ML, Vinade L (2010) Dietary omega-3 fatty acids attenuate cellular damage after a hippocampal ischemic insult in adult rats. J Nutr Biochem 21(4):351–356
Kuan CY, Roth KA, Flavell RA, Rakic P (2000) Mechanisms of programmed cell death in the developing brain. Trends Neurosci 23:291–297
Northington FJ, Ferriero DM, Flock DL, Martin LJ (2001) Delayed neurodegeneration in neonatal rat thalamus after hypoxia-ischemia is apoptosis. J Neurosci 21:1931–1938
Waldmeier PC (2003) Prospects for antiapoptotic drug therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:303–321
Bendel O, Alkass K, Bueters T, von Euler M, von Euler G (2005) Reproducible loss of CA1 neurons following carotid artery occlusion combined with halothane-induced hypotension. Brain Res 1033:135–142
Colbourne F, Li H, Buchan AM (1999) Continuing postischemic neuronal death in CA1. Influence of ischemia duration and cytoprotective doses of NBQX and SNX-111 in rats. Stroke 30:662–668
Stewart ZA, Pietenpol JA (2001) p53 Signaling and cell cycle checkpoints. Chem Res Toxicol 14:243–263
Linnik MD, Zahos P, Geschwind MD, Federoff HJ (1995) Expression of bcl-2 from a defective herpes simplex virus-1 vector limits neuronal death in focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 26:1670–1674
Lawrence MS, Ho DY, Sun GH, Steinberg GK, Sapolsky RM (1996) Overexpression of Bcl-2 with herpes simplex virus vectors protects CNS neurons against neurological insults in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci 16:486–496
Lawrence MS, McLaughlin JR, Sun GH et al (1997) Herpes simplex viral vectors expressing Bcl-2 are neuroprotective when delivered after a stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:740–744
Zhang R, Xue YY, Lu SD, Wang Y, Zhang LM, Huang YL, Signore AP, Chen J, Sun FY (2006) Bcl-2 enhances neurogenesis and inhibits apoptosis of newborn neurons in adult rat brain following a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurobiol Dis 24(2):345–356
Pan HC, Kao TK, Ou YC, Yang DY, Yen YJ, Wang CC, Chuang YH, Liao SL, Raung SL, Wu CW, Chiang AN, Chen CJ (2009) Protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid against brain injury in ischemic rats. J Nutr Biochem 20(9):715–725
Sinha RA, Khare P, Rai A, Maurya SK, Pathak A, Mohan V, Nagar GK, Mudiam MK, Godbole MM, Bandyopadhyay S (2009) Anti-apoptotic role of omega-3-fatty acids in developing brain: perinatal hypothyroid rat cerebellum as apoptotic model. Int J Dev Neurosci 27(4):377–383
Yu JH, Kang SG, Jung UY, Jun CH, Kim H (2009) Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on apoptosis of human gastric epithelial cells exposed to silica-immobilized glucose oxidase. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:359–364
Park KS, Lim JW, Kim H (2009) Inhibitory mechanism of omega-3 fatty acids in pancreatic inflammation and apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:421–427
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB (1979) A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke 10(3):267–272
Choi-Kwon S, Park KA, Lee HJ, Park MS, Lee JH, Jeon SE et al (2004) Temporal changes in cerebral antioxidant enzyme activities after ischemia and reperfusion in a rat focal brain ischemia model: effect of dietary fish oil. Dev Brain Res 152:11–18
Greco R, Amantea D, Blandini F, Nappi G, Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT, Tassorelli C (2007) Neuroprotective effect of nitroglycerin in a rodent model of ischemic stroke: evaluation of Bcl-2 expression. Int Rev Neurobiol 82:423–435
Zhang CY, Shen WH, Zhang GY (2004) Ischemia-induced release of cytochrome c from mitochondria and up-regulation of Bcl-2 expression in rat hippocampus. Sheng Li Xue Bao 56(2):147–152
Letai A (2005) Pharmacological manipulation of Bcl-2 family members to control cell death. J Clin Invest 115(10):2648–2655
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2003) Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J Neurochem 85(4):1026–1036
Phillips RG, Lawrence MS, Ho DY, Sapolsky RM (2000) Limitations in the neuroprotective potential of gene therapy with Bcl-2. Brain Res 859:202–206
Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Yagita Y, Sugiura S, Omura-Matsuoka E, Tanaka S, Matsushita K, Okano H, Tsujimoto Y, Hori M (2006) Bcl2 enhances survival of newborn neurons in the normal and ischemic hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 84(6):1187–1196
Blondeau N, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2002) Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce ischemic and epileptic tolerance. Neuroscience 109(2):231–241
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for supporting equipments and measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajami, M., Eghtesadi, S., Razaz, J.M. et al. Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax after hippocampal ischemia in DHA + EPA treated rats. Neurol Sci 32, 811–818 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0621-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0621-5