Abstract
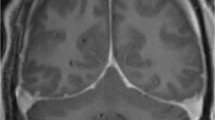
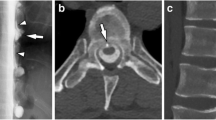
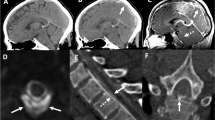
We examined 59 consecutive patients presenting between 1993 and 2006 at our centre diagnosed with headache associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome (SIH). Thirty-six (61%) patients were women; the mean age was 47 years (range 20–68). Cerebral MRI with contrast confirmed SIH in all patients. Headache characteristics were obtained by direct semistructured interview; in a minority of cases information was completed retrospectively through a phone call. All SIH patients suffered from headache. Early recognition of SIH may avoid dangerous worsening due to delayed diagnosis. Orthostatic headache, the main symptom, suggests the diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mea, E., Savoiardo, M., Chiapparini, L. et al. Headache and spontaneous low cerebrospinal fluid pressure syndrome. Neurol Sci 28 (Suppl 2), S232–S234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-007-0785-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-007-0785-1