Abstract
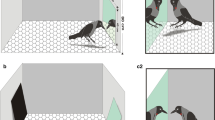
Four jungle crows (Corvus macrorhynchos) were exposed to a mirror placed either vertically or horizontally. The most frequently observed behaviors were pecking at the mirror and wing flapping when looking toward the mirror. These behavior patterns, which were only rarely observed when the mirror was reversed, can be interpreted as aggressive behaviors against a conspecific. The vertical mirror evoked the behaviors more often than the horizontal mirror. The present results suggest that crows perceive their mirror image as an image of a conspecific, not as their own.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 December 1999 / Accepted after revision 29 January 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusayama, T., Bischof, HJ. & Watanabe, S. Responses to mirror-image stimulation in jungle crows (Corvus macrorhynchos). Anim Cogn 3, 61–64 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100710050051
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100710050051